A recombinase paralog from the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus enhances SsoRadA ssDNA binding and strand displacement
- PMID: 23220019
- PMCID: PMC4057309
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.11.010
A recombinase paralog from the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus enhances SsoRadA ssDNA binding and strand displacement
Abstract
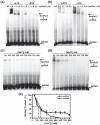
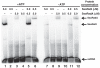
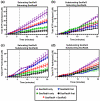
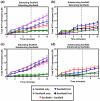
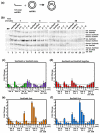
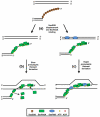
Homologous recombination (HR) is a major pathway for the repair of double-strand DNA breaks, a highly deleterious form of DNA damage. The main catalytic protein in HR is the essential RecA-family recombinase, which is conserved across all three domains of life. Eukaryotes and archaea encode varying numbers of proteins paralogous to their main recombinase. Although there is increasing evidence for the functions of some of these paralog proteins, overall their mechanism of action remains largely unclear. Here we present the first biochemical characterization of one of the paralog proteins, SsoRal3, from the crenarchaeaon Sulfolobus solfataricus. The SsoRal3 protein is a ssDNA-dependent ATPase that can catalyze strand invasion at both saturating and subsaturating concentrations. It can bind both ssDNA and dsDNA, but its binding preference is altered by the presence or absence of ATP. Addition of SsoRal3 to SsoRadA nucleoprotein filaments reduces total ATPase activity. Subsaturating concentrations of SsoRal3 increase the ssDNA binding activity of SsoRadA approximately 9-fold and also increase the persistence of SsoRadA catalyzed strand invasion products. Overall, these results suggest that SsoRal3 functions to stabilize the SsoRadA presynaptic filament.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of an archaeal recombinase paralog that exhibits novel anti-recombinase activity.Mutat Res. 2020 May-Dec;821:111703. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111703. Epub 2020 May 7. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32416400
-
An archaeal RadA paralog influences presynaptic filament formation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Jun 1;12(6):403-13. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Apr 24. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23622866 Free PMC article.
-
The single-stranded DNA binding protein of Sulfolobus solfataricus acts in the presynaptic step of homologous recombination.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 19;397(1):31-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.004. Epub 2010 Jan 18. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20080104
-
RecA and DNA recombination: a review of molecular mechanisms.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Oct 31;47(5):1511-1531. doi: 10.1042/BST20190558. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 31654073 Review.
-
Structure/function relationships in RecA protein-mediated homology recognition and strand exchange.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;50(6):453-76. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1092943. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26459995 Review.
Cited by
-
Divalent metal cofactors differentially modulate RadA-mediated strand invasion and exchange in Saccharolobus solfataricus.Biosci Rep. 2023 Feb 27;43(2):BSR20221807. doi: 10.1042/BSR20221807. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36601994 Free PMC article.
-
Mediators of homologous DNA pairing.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 9;6(12):a016451. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016451. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25301930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commentary on: Divalent metal cofactors differentially modulate RadA-mediated strand invasion and exchange in Saccharolobus solfataricus.Biosci Rep. 2023 Jun 28;43(6):BSR20230058. doi: 10.1042/BSR20230058. Biosci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37334574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arenson TA, Tsodikov OV, Cox MM. Quantitative analysis of the kinetics of end-dependent disassembly of RecA filaments from ssDNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;288:391–401. - PubMed
-
- Braybrooke JP, Spink KG, Thacker J, Hickson ID. The RAD51 family member, RAD51L3, is a DNA-stimulated ATPase that forms a complex with XRCC2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:29100–29106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

