Overexpression of human selenoprotein H in neuronal cells enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and function through activation of protein kinase A, protein kinase B, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein pathway
- PMID: 23220172
- PMCID: PMC3568772
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.11.022
Overexpression of human selenoprotein H in neuronal cells enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and function through activation of protein kinase A, protein kinase B, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein pathway
Abstract
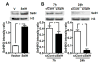
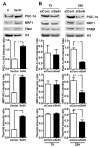
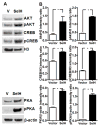
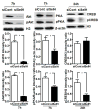
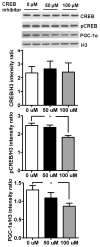
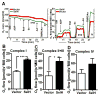
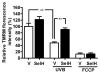
Mitochondrial biogenesis is activated by nuclear encoded transcription co-activator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), which is regulated by several upstream factors including protein kinase A and Akt/protein kinase B. We have previously shown that selenoprotein H enhances the levels of nuclear regulators for mitochondrial biogenesis, increases mitochondrial mass and improves mitochondrial respiratory rate, under physiological condition. Furthermore, overexpression of selenoprotein H protects neuronal HT22 cells from ultraviolet B irradiation-induced cell damage by lowering reactive oxygen species production, and inhibiting activation of caspase-3 and -9, as well as p53. The objective of this study is to identify the cell signaling pathways by which selenoprotein H initiates mitochondrial biogenesis. We first confirmed our previous observation that selenoprotein H transfected HT22 cells increased the protein levels of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial biogenesis factors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α, nuclear respiratory factor 1 and mitochondrial transcription factor A. We then observed that total and phosphorylation of protein kinase A, Akt/protein kinase B and cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (CREB) were significantly increased in selenoprotein H transfected cells compared to vector transfected HT22 cells. To verify whether the observed stimulating effects on mitochondrial biogenesis pathways are caused by selenoprotein H and mediated through CREB, we knocked down selenoprotein H mRNA level using siRNA and inhibited CREB with napthol AS-E phosphate in selenoprotein H transfected cells and repeated the measurements of the aforementioned biomarkers. Our results revealed that silencing of selenoprotein H not only decreased the protein levels of PGC-1α, nuclear respiratory factor 1 and mitochondrial transcription factor A, but also decreased the total and phosphorylation levels of protein kinase A, protein kinase B, and CREB. Similarly, CREB inhibition reduced CREB activation and PGC-1α protein levels in selenoprotein H transfected cells. Moreover, selenoprotein H transfection increased the activity of mitochondrial complexes and prevented the ultraviolet B induced fall of mitochondrial membrane potential. We conclude that the effects of selenoprotein H on mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial function are probably mediated through protein kinase A-CREB-PGC-1α and Akt/protein kinase B-CREB-PGC-1α pathways.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
No conflict of interest are declared by the authors
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Guardia D, Palomer X, Coll T, Davidson MM, Chan TO, Feldman AM, Laguna JC, Vazquez-Carrera M. The p65 subunit of NF-kB binds to PGC-1a, linking inflammation and metabolic disturbances in cardiac cells. Cardiovascular Research. 2010;87:449–58. - PubMed
-
- Arteel GE, Mostert V, Oubrahim H, Briviba K, Abel J, Sies H. Protection by selenoprotein P in human plasma against peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation and nitration. Biological Chemistry. 1998;379:1201–5. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Hattori Y, Nakajima K, Eizawa T, Ehara T, Koyama M, Hirai T, Fukuda Y, Kinoshita M, Sugiyama A, Hayashi J, Onaya T, Kobayashi T, Tawata M. Mitochondrial complex I activity is significantly decreased in a patient with maternally inherited type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy associated with mitochondrial DNA C3310T mutation: a cybrid study. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2006;74:148–53. - PubMed
-
- Chowanadisai W, Bauerly KA, Tchaparian E, Wong A, Cortopassi GA, Rucker RB. Pyrroloquinoline quinone stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis through cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation and increased PGC-1alpha expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285:142–52. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

