Epigenetic control of neurotransmitter expression in olfactory bulb interneurons
- PMID: 23220178
- PMCID: PMC3622794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.11.009
Epigenetic control of neurotransmitter expression in olfactory bulb interneurons
Abstract
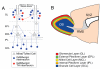
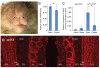
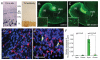
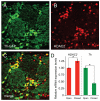
Defining the molecular mechanisms that underlie development and maintenance of neuronal phenotypic diversity in the CNS is a fundamental challenge in developmental neurobiology. The vast majority of olfactory bulb (OB) interneurons are GABAergic and this neurotransmitter phenotype is specified in migrating neuroblasts by transcription of either or both glutamic acid decarboxylase 1 (Gad1) and Gad2. A subset of OB interneurons also co-express dopamine, but transcriptional repression of tyrosine hydroxylase (Th) suppresses the dopaminergic phenotype until these neurons terminally differentiate. In mature OB interneurons, GABA and dopamine levels are modulated by odorant-induced synaptic activity-dependent regulation of Gad1 and Th transcription. The molecular mechanisms that specify and maintain the GABAergic and dopaminergic phenotypes in the OB are not clearly delineated. In this report, we review previous studies and present novel findings that provide insight into the contribution of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms for controlling expression of these neurotransmitter phenotypes in the OB. We show that HDAC enzymes suppress the dopaminergic phenotype in migrating neuroblasts by repressing Th transcription. In the mature interneurons, both Th and Gad1 transcription levels are modulated by synaptic activity-dependent recruitment of acetylated Histone H3 on both the Th and Gad1 proximal promoters. We also show that HDAC2 has the opposite transcriptional response to odorant-induced synaptic activity when compared to Th and Gad1. These findings suggest that HDAC2 mediates, in part, the activity-dependent chromatin remodeling of the Th and Gad1 proximal promoters in mature OB interneurons.
Keywords: Adult neurogenesis; ChIP; Dopamine; GABA; GAD; Glutamic acid decarboxylase; HDAC; NRSE; OB; Olfactory bulb; RMS; SVZ; TH; TSA; Tyrosine hydroxylase; acH3; acetylated Histone H3; chromatin immunoprecipitation; gamma aminobutyric acid; glutamic acid decarboxylase; histone deacetylase; neural restrictive silencer elements; olfactory bulb; qPCR; quantitative polymerase chain reaction; rostral migratory stream; subventricular zone; trichostatin A; tyrosine hydroxylase.
Copyright © 2012 ISDN. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Allen ZJ, 2nd, Waclaw RR, Colbert MC, Campbell K. Molecular identity of olfactory bulb interneurons: transcriptional codes of periglomerular neuron subtypes. Journal of molecular histology. 2007;38:517–525. - PubMed
-
- Aranyi T, Faucheux BA, Khalfallah O, Vodjdani G, Biguet NF, Mallet J, Meloni R. The tissue-specific methylation of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene reveals new regulatory elements in the first exon. Journal of neurochemistry. 2005;94:129–139. - PubMed
-
- Baker H, Morel K, Stone DM, Maruniak JA. Adult naris closure profoundly reduces tyrosine hydroxylase expression in mouse olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 1993;614:109–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

