Activating HER2 mutations in HER2 gene amplification negative breast cancer
- PMID: 23220880
- PMCID: PMC3570596
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0349
Activating HER2 mutations in HER2 gene amplification negative breast cancer
Abstract
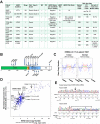
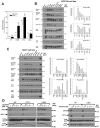
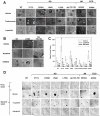
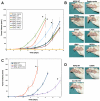
Data from 8 breast cancer genome-sequencing projects identified 25 patients with HER2 somatic mutations in cancers lacking HER2 gene amplification. To determine the phenotype of these mutations, we functionally characterized 13 HER2 mutations using in vitro kinase assays, protein structure analysis, cell culture, and xenograft experiments. Seven of these mutations are activating mutations, including G309A, D769H, D769Y, V777L, P780ins, V842I, and R896C. HER2 in-frame deletion 755-759, which is homologous to EGF receptor (EGFR) exon 19 in-frame deletions, had a neomorphic phenotype with increased phosphorylation of EGFR or HER3. L755S produced lapatinib resistance, but was not an activating mutation in our experimental systems. All of these mutations were sensitive to the irreversible kinase inhibitor, neratinib. These findings show that HER2 somatic mutation is an alternative mechanism to activate HER2 in breast cancer and they validate HER2 somatic mutations as drug targets for breast cancer treatment.
Significance: We show that the majority of HER2 somatic mutations in breast cancer patients are activating mutations that likely drive tumorigenesis. Several patients had mutations that are resistant to the reversible HER2 inhibitor lapatinib, but are sensitive to the irreversible HER2 inhibitor, neratinib. Our results suggest that patients with HER2 mutation–positive breast cancers could benefit from existing HER2-targeted drugs.
Figures

Comment in
-
Activating mutations in HER2: neu opportunities and neu challenges.Cancer Discov. 2013 Feb;3(2):145-7. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0585. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23400474
References
-
- Baselga J. Targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer: the second wave. Science. 2006;312:1175–8. - PubMed
-
- Chin L, Andersen JN, Futreal PA. Cancer genomics: from discovery science to personalized medicine. Nat Med. 2011;17:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Hynes NE, Lane HA. ERBB receptors and cancer: the complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:341–54. - PubMed
-
- Awada A, Bozovic-Spasojevic I, Chow L. New therapies in HER2-positive breast cancer: a major step towards a cure of the disease? Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:494–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

