Global analysis of yeast mRNPs
- PMID: 23222640
- PMCID: PMC3537908
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2468
Global analysis of yeast mRNPs
Abstract
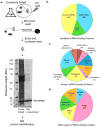
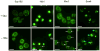
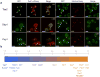
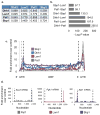
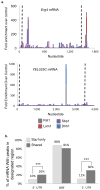
Proteins regulate gene expression by controlling mRNA biogenesis, localization, translation and decay. Identifying the composition, diversity and function of mRNA-protein complexes (mRNPs) is essential to understanding these processes. In a global survey of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNA-binding proteins, we identified 120 proteins that cross-link to mRNA, including 66 new mRNA-binding proteins. These include kinases, RNA-modification enzymes, metabolic enzymes and tRNA- and rRNA-metabolism factors. These proteins show dynamic subcellular localization during stress, including assembly into stress granules and processing bodies (P bodies). Cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) analyses of the P-body components Pat1, Lsm1, Dhh1 and Sbp1 identified sites of interaction on specific mRNAs, revealing positional binding preferences and co-assembly preferences. When taken together, this work defines the major yeast mRNP proteins, reveals widespread changes in their subcellular location during stress and begins to define assembly rules for P-body mRNPs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schwanhäusser B, et al. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature. 2011;473:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Castello A, et al. Insights into RNA Biology from an Atlas of Mammalian mRNA-Binding Proteins. Cell. 2012;149:1393–1406. - PubMed
-
- Baltz AG, et al. The mRNA-Bound Proteome and Its Global Occupancy Profile on Protein-Coding Transcripts. Molecular Cell. 2012;46:674–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

