Transformation of human ovarian surface epithelial cells by Krüppel-like factor 8
- PMID: 23222713
- PMCID: PMC3975924
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.545
Transformation of human ovarian surface epithelial cells by Krüppel-like factor 8
Abstract
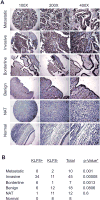
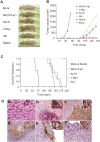
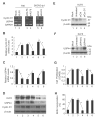
We have previously demonstrated that Krüppel-like factor 8 (KLF8) participates in oncogenic transformation of mouse fibroblasts and is highly overexpressed in human ovarian cancer. In this work, we first correlated KLF8 overexpression with the aggressiveness of ovarian patient tumors and then tested if KLF8 could transform human ovarian epithelial cells. Using the immortalized non-tumorigenic human ovarian surface epithelial cell line T80 and retroviral infection, we generated cell lines that constitutively overexpress KLF8 alone or its combination with the known ovarian oncogenes c-Myc, Stat3c and/or Akt and examined the cell lines for anchorage-independent growth and tumorigenesis. The soft agar clonogenic assay showed that T80/KLF8 cells formed significantly more colonies than the mock cells. Interestingly, the cells expressing both KLF8 and c-Myc formed the largest amounts of colonies, greater than the sum of colonies formed by the cells expressing KLF8 and c-Myc alone. These results suggested that KLF8 might be a weak oncogene that works cooperatively with c-Myc to transform ovarian cells. Surprisingly, overexpression of KLF8 alone was sufficient to induce tumorigenesis in nude mice resulting in short lifespan irrespective of whether the T80/KLF8 cells were injected subcutaneously, intraperitoneally or orthotopically into the ovarian bursa. Histopathological studies confirmed that the T80/KLF8 tumors were characteristic of human serous ovarian carcinomas. Comparative expression profiling and functional studies identified the cell cycle regulators cyclin D1 and USP44 as primary KLF8 targets and effectors for the T80 transformation. Overall, we identified KLF8 overexpression as an important factor in human ovarian carcinoma pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of KLF8 transcription by focal adhesion kinase in human ovarian epithelial and cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 16;283(20):13934-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M709300200. Epub 2008 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18353772
-
KLF8 transcription factor participates in oncogenic transformation.Oncogene. 2007 Jan 18;26(3):456-61. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209796. Epub 2006 Jul 10. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16832343
-
Identification of epithelial stromal interaction 1 as a novel effector downstream of Krüppel-like factor 8 in breast cancer invasion and metastasis.Oncogene. 2014 Sep 25;33(39):4746-55. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.415. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24096480 Free PMC article.
-
The level of Krüppel-like factor 8 expression predicts prognosis and metastasis in various carcinomas.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(18):e15519. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015519. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31045845 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of Kruppel-like factor 6 and Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1 in ovarian cancer progression and treatment.Mt Sinai J Med. 2009 Dec;76(6):557-66. doi: 10.1002/msj.20150. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009. PMID: 20014424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like factors in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Oct;13(10):701-13. doi: 10.1038/nrc3582. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 24060862 Review.
-
Oncogenes in high grade serous adenocarcinoma of the ovary.Genes Cancer. 2020 Nov 11;11(3-4):122-136. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.206. eCollection 2020 Dec 31. Genes Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33488950 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Krüppel-like factor 8 by the NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin ligase.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Mar 15;11(3):1521-1530. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30972179 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factor 8 activates the transcription of C-X-C cytokine receptor type 4 to promote breast cancer cell invasion, transendothelial migration and metastasis.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):23552-68. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8083. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26993780 Free PMC article.
-
KLF8 and FAK cooperatively enrich the active MMP14 on the cell surface required for the metastatic progression of breast cancer.Oncogene. 2014 May 29;33(22):2909-17. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.247. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23812425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005 Jan-Feb;55(1):10–30. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Yang G, Thompson-Lanza JA, Glassman A, Hayes K, Patterson A, et al. A genetically defined model for human ovarian cancer. Cancer research. 2004 Mar 1;64(5):1655–63. - PubMed
-
- Rosen DG, Yang G, Bast RC, Jr, Liu J. Use of Ras-transformed human ovarian surface epithelial cells as a model for studying ovarian cancer. Methods Enzymol. 2006;407:660–76. - PubMed
-
- Yang G, Thompson JA, Fang B, Liu J. Silencing of H-ras gene expression by retrovirus-mediated siRNA decreases transformation efficiency and tumorgrowth in a model of human ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2003 Aug 28;22(36):5694–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

