A novel dnaJ family gene, sflA, encodes an inhibitor of flagellation in marine Vibrio species
- PMID: 23222726
- PMCID: PMC3562094
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01850-12
A novel dnaJ family gene, sflA, encodes an inhibitor of flagellation in marine Vibrio species
Abstract
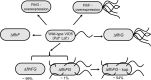
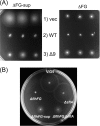
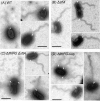
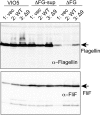
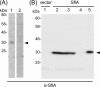
The marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus has a single polar flagellum. Formation of that flagellum is regulated positively and negatively by FlhF and by FlhG, respectively. The ΔflhF mutant makes no flagellum, whereas the ΔflhFG double-deletion mutant usually lacks a flagellum. However, the ΔflhFG mutant occasionally reverts to become motile by forming peritrichous flagella. We have isolated a suppressor pseudorevertant from the ΔflhFG strain (ΔflhFG-sup). The suppressor strain forms peritrichous flagella in the majority of cells. We identified candidate suppressor mutations by comparing the genome sequence of the parental strain, VIO5, with the genome sequences of the suppressor strains. Two mutations were mapped to a gene, named sflA (suppressor of ΔflhFG), at the VEA003730 locus of the Vibrio sp. strain EX25 genome. This gene is specific for Vibrio species and is predicted to encode a transmembrane protein with a DnaJ domain. When the wild-type gene was introduced into the suppressor strain, motility was impaired. Introducing a mutant version of the sflA gene into the ΔflhFG strain conferred the suppressor phenotype. Thus, we conclude that loss of the sflA gene is responsible for the suppressor phenotype and that the wild-type SflA protein plays a role in preventing polar-type flagella from forming on the lateral cell wall.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Localization and domain characterization of the SflA regulator of flagellar formation in Vibrio alginolyticus.Genes Cells. 2017 Jul;22(7):619-627. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12501. Epub 2017 May 22. Genes Cells. 2017. PMID: 28544270
-
Conversion of mono-polar to peritrichous flagellation in Vibrio alginolyticus.Microbiol Immunol. 2011 Feb;55(2):76-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2010.00290.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21204943
-
Collaboration of FlhF and FlhG to regulate polar-flagella number and localization in Vibrio alginolyticus.Microbiology (Reading). 2008 May;154(Pt 5):1390-1399. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/012641-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2008. PMID: 18451048
-
Regulation of the Single Polar Flagellar Biogenesis.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 1;10(4):533. doi: 10.3390/biom10040533. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32244780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-driven motor of the polar flagellum in marine bacteria Vibrio.Genes Cells. 2011 Oct;16(10):985-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2011.01545.x. Epub 2011 Sep 5. Genes Cells. 2011. PMID: 21895888 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat Shock Protein DnaJ in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Affects Biofilm Formation via Pyocyanin Production.Microorganisms. 2020 Mar 12;8(3):395. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8030395. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32178243 Free PMC article.
-
HubP, a Polar Landmark Protein, Regulates Flagellar Number by Assisting in the Proper Polar Localization of FlhG in Vibrio alginolyticus.J Bacteriol. 2016 Oct 21;198(22):3091-3098. doi: 10.1128/JB.00462-16. Print 2016 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27573015 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into flagellar function and mechanism from the squid-vibrio symbiosis.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019 Oct 25;5(1):32. doi: 10.1038/s41522-019-0106-5. eCollection 2019. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2019. PMID: 31666982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Vibrio Polar Flagellum: Structure and Regulation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1404:77-97. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-22997-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36792872
-
FliL association with flagellar stator in the sodium-driven Vibrio motor characterized by the fluorescent microscopy.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 24;8(1):11172. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29447-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30042401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hlady WG, Klontz KC. 1996. The epidemiology of Vibrio infections in Florida, 1981-1993. J. Infect. Dis. 173: 1176–1183 - PubMed
-
- Reilly GD, Reilly CA, Smith EG, Baker-Austin C. 2011. Vibrio alginolyticus-associated wound infection acquired in British waters, Guernsey, July 2011. Euro Surveill. 16(42): pii=19994 http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19994 - PubMed
-
- Pezzlo M, Valter PJ, Burns MJ. 1979. Wound infection associated with Vibrio alginolyticus. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 71: 476–478 - PubMed
-
- Caccamese SM, Rastegar DA. 1999. Chronic diarrhea associated with Vibrio alginolyticus in an immunocompromised patient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 29: 946–947 - PubMed
-
- Bardy SL, Ng SY, Jarrell KF. 2003. Prokaryotic motility structures. Microbiology 149: 295–304 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

