Phlorotannin extracts from fucales characterized by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn: approaches to hyaluronidase inhibitory capacity and antioxidant properties
- PMID: 23222802
- PMCID: PMC3528125
- DOI: 10.3390/md10122766
Phlorotannin extracts from fucales characterized by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn: approaches to hyaluronidase inhibitory capacity and antioxidant properties
Abstract
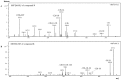
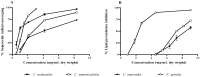
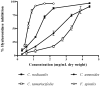
Purified phlorotannin extracts from four brown seaweeds (Cystoseira nodicaulis (Withering) M. Roberts, Cystoseira tamariscifolia (Hudson) Papenfuss, Cystoseira usneoides (Linnaeus) M. Roberts and Fucus spiralis Linnaeus), were characterized by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. Fucophloroethol, fucodiphloroethol, fucotriphloroethol, 7-phloroeckol, phlorofucofuroeckol and bieckol/dieckol were identified. The antioxidant activity and the hyaluronidase (HAase) inhibitory capacity exhibited by the extracts were also assessed. A correlation between the extracts activity and their chemical composition was established. F. spiralis, the species presenting higher molecular weight phlorotannins, generally displayed the strongest lipid peroxidation inhibitory activity (IC₅₀ = 2.32 mg/mL dry weight) and the strongest HAase inhibitory capacity (IC₅₀ = 0.73 mg/mL dry weight). As for superoxide radical scavenging, C. nodicaulis was the most efficient species (IC₅₀ = 0.93 mg/mL dry weight), followed by F. spiralis (IC₅₀ = 1.30 mg/mL dry weight). These results show that purified phlorotannin extracts have potent capabilities for preventing and slowing down the skin aging process, which is mainly associated with free radical damage and with the reduction of hyaluronic acid concentration, characteristic of the process.
Figures



References
-
- Fallarero A., Peltoketo A., Loikkanen J., Tammela P., Vidal A., Vuorela P. Effects of the aqueous extract of Bryothamnion triquetrum on chemical hypoxia and aglycemia-induced damage in GT1–7 mouse hypothalamic immortalized cells. Phytomedicine. 2006;13:240–245. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2003.10.009. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopes G., Sousa C., Silva L.R., Pinto E., Andrade P.B., Bernardo J., Mouga T., Valentão P. Can phlorotannins purified extracts constitute a novel pharmacological alternative for microbial infections with associated inflammatory conditions? PLoS One. 2012;7:e31145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031145. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang T., Jónsdóttir R., Liu H., Gu L., Kristinsson H.G., Raghavan S., Ólafsdóttir G. Antioxidant capacities of phlorotannins extracted from the brown algae Fucus vesiculosus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012;60:5874–5883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

