The zinc cluster protein Sut1 contributes to filamentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 23223039
- PMCID: PMC3571311
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.00214-12
The zinc cluster protein Sut1 contributes to filamentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
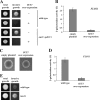
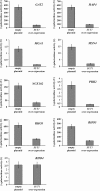
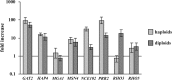
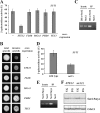
Sut1 is a transcriptional regulator of the Zn(II)(2)Cys(6) family in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The only function that has been attributed to Sut1 is sterol uptake under anaerobic conditions. Here, we show that Sut1 is also expressed in the presence of oxygen, and we identify a novel function for Sut1. SUT1 overexpression blocks filamentous growth, a response to nutrient limitation, in both haploid and diploid cells. This inhibition by Sut1 is independent of its function in sterol uptake. Sut1 downregulates the expression of GAT2, HAP4, MGA1, MSN4, NCE102, PRR2, RHO3, and RHO5. Several of these Sut1 targets (GAT2, HAP4, MGA1, RHO3, and RHO5) are essential for filamentation in haploids and/or diploids. Furthermore, the expression of the Sut1 target genes, with the exception of MGA1, is induced during filamentous growth. We also show that SUT1 expression is autoregulated and inhibited by Ste12, a key transcriptional regulator of filamentation. We propose that Sut1 partially represses the expression of GAT2, HAP4, MGA1, MSN4, NCE102, PRR2, RHO3, and RHO5 when nutrients are plentiful. Filamentation-inducing conditions relieve this repression by Sut1, and the increased expression of Sut1 targets triggers filamentous growth.
Figures




References
-
- Ness F, Bourot S, Régnacq M, Spagnoli R, Bergès T, Karst F. 2001. SUT1 is a putative Zn[II]2Cys6-transcription factor whose upregulation enhances both sterol uptake and synthesis in aerobically growing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 268:1585–1595 - PubMed
-
- Bourot S, Karst F. 1995. Isolation and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SUT1 gene involved in sterol uptake. Gene 165:97–102 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

