Toll-like receptor-mediated, enhanced production of profibrotic TIMP-1 in monocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis: role of serum factors
- PMID: 23223421
- PMCID: PMC3711494
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201958
Toll-like receptor-mediated, enhanced production of profibrotic TIMP-1 in monocytes from patients with systemic sclerosis: role of serum factors
Abstract
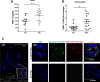
Objectives: To investigate whether monocytes contribute to matrix deposition in systemic sclerosis (SSc) by production of tissue-inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1).
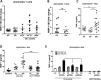
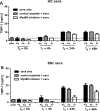
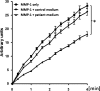
Methods: Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and TIMP-1 expression and secretion were measured by qRT-PCR and ELISA in circulating monocytes from patients with SSc, patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and healthy controls (HC) and in healthy monocytes cultured in the presence of SSc or HC serum samples. Production of TIMP-1 was determined in response to a panel of Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists and MyD88 inhibitory peptide. The functional effect of conditioned media from SSc and HC serum samples or TLR8-stimulated monocytes was studied in an MMP-1 activity assay.
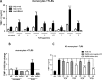
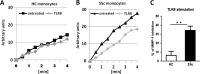
Results: TIMP-1 production by monocytes was upregulated in patients with SSc compared with patients with RA and HC. Incubation of HC monocytes with SSc serum samples resulted in functionally active TIMP-1 production. However, pretreatment with MyD88 inhibitor, but not control peptide, decreased TIMP-1 secretion. TIMP-1 production was significantly stronger when SSc and HC monocytes were stimulated with TLR8 (ssRNA) agonist, but the response was more pronounced in SSc monocytes. TIMP-1 production after TLR stimulation was also strongly reduced in the presence of MyD88 inhibitory peptide or in the monocytes isolated from a patient with a genetic TLR signalling defect. MMP-1 activity was significantly inhibited in media from serum samples or TLR8-stimulated monocytes indicative of functional TIMP activity.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates profibrotic properties of circulating monocytes from patients with SSc and a key role for TLR signalling, particularly TLR8, in TIMP-1 secretion and matrix remodelling.
Figures
References
-
- Chizzolini C, Brembilla NC, Montanari E, et al. Fibrosis and immune dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 2011;10:276–81 - PubMed
-
- Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Miyamoto Y, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 promotes liver fibrosis development in a transgenic mouse model. Hepatology 2000;32:1248–54 - PubMed
-
- Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Circ Res 2003;92:827–39 - PubMed
-
- Woessner JF. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991;5:2145–54 - PubMed
-
- Iredale JP, Benyon RC, Arthur MJ, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 messenger RNA expression is enhanced relative to interstitial collagenase messenger RNA in experimental liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 1996;24:176–84 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

