Impact of follicular G-CSF quantification on subsequent embryo transfer decisions: a proof of concept study
- PMID: 23223438
- PMCID: PMC3545637
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/des354
Impact of follicular G-CSF quantification on subsequent embryo transfer decisions: a proof of concept study
Abstract
Background: Previous experiments have shown that granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), quantified in the follicular fluid (FF) of individual oocytes, correlates with the potential for an ongoing pregnancy of the corresponding fertilized oocytes among selected transferred embryos. Here we present a proof of concept study aimed at evaluating the impact of including FF G-CSF quantification in the embryo transfer decisions.
Methods: FF G-CSF was quantified with the Luminex XMap technology in 523 individual FF samples corresponding to 116 fresh transferred embryos, 275 frozen embryos and 131 destroyed embryos from 78 patients undergoing ICSI.
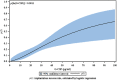
Results: Follicular G-CSF was highly predictive of subsequent implantation. The receiving operator characteristics curve methodology showed its higher discriminatory power to predict ongoing pregnancy in multivariate logistic regression analysis for FF G-CSF compared with embryo morphology [0.77 (0.69-0.83), P < 0.001 versus 0.66 (0.58-0.73), P = 0.01)]. Embryos were classified by their FF G-CSF concentration: Class I over 30 pg/ml (a highest positive predictive value for implantation), Class II from 30 to 18.4 pg/ml and Class III <18.4 pg/ml (a highest negative predictive value). Embryos derived from Class I follicles had a significantly higher implantation rate (IR) than those from Class II and III follicles (36 versus 16.6 and 6%, P < 0.001). Embryos derived from Class I follicles with an optimal morphology reached an IR of 54%. Frozen-thawed embryos transfer derived from Class I follicles had an IR of 37% significantly higher than those from Class II and III follicles, respectively, of 8 and 5% (P < 0.001). Thirty-five per cent of the frozen embryos but also 10% of the destroyed embryos were derived from G-CSF Class I follicles. Non-optimal embryos appear to have been transferred in 28% (22/78) of the women, and their pregnancy rate was significantly lower than that of women who received at least one optimal embryo (18 versus 36%, P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Monitoring FF G-CSF for the selection of embryos with a better potential for pregnancy might improve the effectiveness of IVF by reducing the time and cost required for obtaining a pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Assou S, Haouzi D, Mahmoud K, Aouacheria A, Guillemin Y, Pantesco V, Reme T, Dechaud H, De Vos J, Hamamah S. A non-invasive test for assessing embryo potential by gene expression profiles of human cumulus cells: a proof of concept study. Mol Hum Reprod. 2008;14:711–719. - PubMed
-
- Balaban B, Urman B. Effect of oocyte morphology on embryo development and implantation. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006;12:608–615. - PubMed
-
- Blake DA, Farquhar CM, Johnson N, Proctor M. Cleavage stage versus blastocyst stage embryo transfer in assisted conception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD002118. - PubMed
-
- Broer SL, Mol B, Dolleman M, Fauser BC, Broekmans FJ. The role of anti-Mullerian hormone assessment in assisted reproductive technology outcome. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2010;22:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Gebhardt KM, Feil DK, Dunning KR, Lane M, Russell DL. Human cumulus cell gene expression as a biomarker of pregnancy outcome after single embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 2011;96:47–52. e42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources