JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation
- PMID: 23223452
- PMCID: PMC3835653
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1227568
JNK expression by macrophages promotes obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation
Abstract
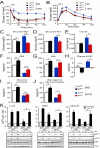
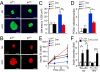
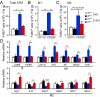
The cJun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway contributes to inflammation and plays a key role in the metabolic response to obesity, including insulin resistance. Macrophages are implicated in this process. To test the role of JNK, we established mice with selective JNK deficiency in macrophages. We report that feeding a high-fat diet to control and JNK-deficient mice caused similar obesity, but only mice with JNK-deficient macrophages remained insulin-sensitive. The protection of mice with macrophage-specific JNK deficiency against insulin resistance was associated with reduced tissue infiltration by macrophages. Immunophenotyping demonstrated that JNK was required for pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization. These studies demonstrate that JNK in macrophages is required for the establishment of obesity-induced insulin resistance and inflammation.
Figures
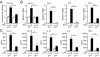
Comment in
-
Biomedicine. Improving metabolism by throwing out all the JNK.Science. 2013 Jan 11;339(6116):147-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1233223. Science. 2013. PMID: 23307726 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

