Gene survival and death on the human Y chromosome
- PMID: 23223713
- PMCID: PMC3603307
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/mss267
Gene survival and death on the human Y chromosome
Abstract
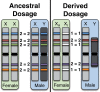
Y chromosomes have long been dismissed as "graveyards of genes," but there is still much to be learned from the genetic relics of genes that were once functional on the human Y. We identified human X-linked genes whose gametologs have been pseudogenized or completely lost from the Y chromosome and inferred which evolutionary forces may be acting to retain genes on the Y. Although gene loss appears to be largely correlated with the suppression of recombination, we observe that X-linked genes with functional Y homologs evolve under stronger purifying selection and are expressed at higher levels than X-linked genes with nonfunctional Y homologs. Additionally, we support and expand upon the hypothesis that X inactivation is primarily driven by gene loss on the Y. Using linear discriminant analysis, we show that X-inactivation status can successfully classify 90% of X-linked genes into those with functional or nonfunctional Y homologs.
Figures

References
-
- Brawand D, Soumillion M, Necsulea A, et al. (18 co-authors) The evolution of gene expression levels in mammalian organs. Nature. 2011;478:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005;434:400–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

