Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging with [Lys40(Ahx-HYNIC- 99mTc/EDDA)NH2]-exendin-4 for the detection of insulinoma
- PMID: 23224740
- PMCID: PMC3590421
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-012-2299-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor imaging with [Lys40(Ahx-HYNIC- 99mTc/EDDA)NH2]-exendin-4 for the detection of insulinoma
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this article is to present a new method for the diagnosis of insulinoma with the use of [Lys(40)(Ahx-HYNIC-(99m)Tc/EDDA)NH2]-exendin-4.
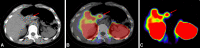
Methods: Studies were performed in 11 patients with negative results of all available non-isotopic diagnostic methods (8 with symptoms of insulinoma, 2 with malignant insulinoma and 1 with nesidioblastosis). In all patients glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor imaging (whole-body and single photon emission computed tomography/CT examinations) after the injection of 740 MBq of the tracer was performed.
Results: Both sensitivity and specificity of GLP-1 receptor imaging were assessed to be 100 % in patients with benign insulinoma. In all eight cases with suspicion of insulinoma a focal uptake in the pancreas was found. In six patients surgical excision of the tumour was performed (type G1 tumours were confirmed histopathologically). In one patient surgical treatment is planned. One patient was disqualified from surgery. In one case with malignant insulinoma pathological accumulation of the tracer was found only in the region of local recurrence. The GLP-1 study was negative in the other malignant insulinoma patient. In one case with suspicion of nesidioblastosis, a focal accumulation of the tracer was observed and histopathology revealed coexistence of insulinoma and nesidioblastosis.
Conclusion: [Lys(40)(Ahx-HYNIC-(99m)Tc/EDDA)NH2]-exendin-4 seems to be a promising diagnostic tool in the localization of small insulinoma tumours, but requires verification in a larger series of patients.
Figures


References
-
- Vaidakis D, Karoubalis J, Pappa T, Piaditis G, Zografos GN. Pancreatic insulinoma: current issues and trends. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2010;9:234–241. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

