Predictors of refractory ascites development in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis hospitalized to control ascitic decompensation
- PMID: 23225811
- PMCID: PMC3521257
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.1.145
Predictors of refractory ascites development in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis hospitalized to control ascitic decompensation
Abstract
Purpose: Refractory ascites (RA) is closely related to a high morbidity and mortality. In this study, we investigated predictors of RA development in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related cirrhosis who were hospitalized to control ascitic decompensation, and determined predictors for survival in patients who experienced RA.
Materials and methods: We analyzed 199 consecutive patients with HBV-related cirrhosis who were hospitalized to control ascitic decompensation between January 1996 and December 2008.
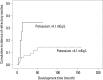
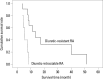
Results: Multivariate analyses showed that only serum potassium at admission predicted RA development independently [p=0.013; hazard ratio (HR), 2.800; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.166-6.722]. During the follow-up period, 16 (8.0%) patients experienced RA within 4.2 (range, 1.0-39.2) months after admission for controlling ascitic decompensation, and they survived a median of 8.7 (range, 3.9-51.3) months. Child-Pugh class and RA type were identified as independent prognostic factors affecting the survival in patients with RA (p=0.045; HR, 8.079; 95% CI, 1.231-67.984 and p=0.013; HR, 14.510; 95% CI, 1.771-118.874, respectively).
Conclusion: Serum potassium was an independent predictor of RA development in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis who were hospitalized to control ascitic decompensation. After RA development, Child-Pugh class and RA type were independent predictors for survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Natural history of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhotic patients hospitalized to control ascites.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Nov;23(11):1722-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05510.x. Epub 2008 Aug 20. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18717757
-
Poor Outcomes of Cirrhosis due to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Compared With Hepatitis B After Decompensation With Ascites.Am J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 1;116(7):1437-1446. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001176. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33834737
-
Prognosis of refractory ascites in cirrhosis.Tunis Med. 2016 Jan;94(1):12-5. Tunis Med. 2016. PMID: 27525599
-
Ascitic fluid infection in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis: culture-negative neutrocytic ascites versus spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jan;25(1):122-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05970.x. Epub 2009 Oct 19. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19845823
-
[Ascitic decompensation].Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006 Jun-Jul;30(6-7):870-4. doi: 10.1016/s0399-8320(06)73334-6. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2006. PMID: 16885871 Review. French. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
KASL clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis: Ascites and related complications.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018 Sep;24(3):230-277. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2018.1005. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29991196 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Child-Pugh score is an independent risk factor for immediate bleeding after colonoscopic polypectomy in liver cirrhosis.Yonsei Med J. 2014 Sep;55(5):1281-8. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.5.1281. Yonsei Med J. 2014. PMID: 25048486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SU, Han KH, Nam CM, Park JY, Kim do Y, Chon CY, et al. Natural history of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhotic patients hospitalized to control ascites. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;23:1722–1727. - PubMed
-
- Lee JM, Han KH, Ahn SH. Ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an Asian perspective. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:1494–1503. - PubMed
-
- Kim SU, Kim do Y, Lee CK, Park JY, Kim SH, Kim HM, et al. Ascitic fluid infection in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis: culture-negative neutrocytic ascites versus spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:122–128. - PubMed
-
- Ginés P, Quintero E, Arroyo V, Terés J, Bruguera M, Rimola A, et al. Compensated cirrhosis: natural history and prognostic factors. Hepatology. 1987;7:122–128. - PubMed
-
- Arroyo V, Ginès P, Gerbes AL, Dudley FJ, Gentilini P, Laffi G, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology. 1996;23:164–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

