Significance of localization of mandibular foramen in an inferior alveolar nerve block
- PMID: 23225978
- PMCID: PMC3510910
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-9668.101896
Significance of localization of mandibular foramen in an inferior alveolar nerve block
Abstract
Background: The mandibular foramen (MF) is an opening on the internal surface of the ramus for divisions of the mandibular vessels and nerve to pass. The aim of this study is to determine the position of the MF from various anatomical landmarks in several dry adult mandibles.
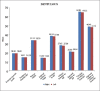
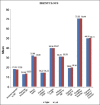
Materials and methods: A total of 102 human dry mandibles were examined, of which 93 were of dentulous and 9 were of edentulous. The measurements were taken from the anterior border of the ramus (coronoid notch) to the midportion of the MF and then from the midportion of the MF to the other landmarks such as internal oblique ridge, inferior border, sigmoid notch, and condyle were measured and recorded.
Results: The data were compared using Student's t-test. The MF is positioned at a mean distance of 19 mm (with SD 2.34) from coronoid notch of the anterior border of the ramus. Superio-inferiorly from the condyle to the inferior border MF is situated 5 mm inferior to the midpoint of condyle to the inferior border distance (ramus height).
Conclusion: We conclude that failures in the anesthesia of the inferior alveolar nerve are due to the operator error and not due to the anatomical variation.
Keywords: Failure of anesthesia; inferior alveolar nerve; mandible foramen.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Narayana K, Soubhagya RN, Prashanthi N, Latha VP. The location of the mandibular foramen maintains absolute bilateral symmetry in mandibles of different age groups. Hong Kong Dent J. 2005;2:35–7.
-
- Ono E, Medici FE, Moraes LC, Castilho JC, Moraes ME. Anteroposterior location of the mandibular foramen of 7 to 12 yearold children in panoramic radiographs. Braz Dent J. 2005;8:6–12.
-
- Ennes JP, Medeiros RM, Grant JC. Localization of Mandibular Foramen and Clinical Implications. Int J Morphol. 2009;27:1305–11.
-
- Nicholson ML. A study of the position of the mandibular foramen in adult human mandible. Anat Rec. 1985;212:110–2. - PubMed
-
- Simon B, Komives O. Dimensional and positional variations of the ramus of the mandible. J Dent Res. 1938;17:125–49.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources