Mannose-binding lectin deficiency and acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 23226013
- PMCID: PMC3514010
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S33714
Mannose-binding lectin deficiency and acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Background: Mannose-binding lectin is a collectin involved in host defense against infection. Whether mannose-binding lectin deficiency is associated with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is debated.
Methods: Participants in a study designed to determine if azithromycin taken daily for one year decreased acute exacerbations had serum mannose-binding lectin concentrations measured at the time of enrollment.
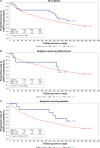
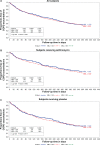
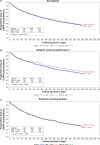
Results: Samples were obtained from 1037 subjects (91%) in the trial. The prevalence of mannose-binding lectin deficiency ranged from 0.5% to 52.2%, depending on how deficiency was defined. No differences in the prevalence of deficiency were observed with respect to any demographic variable assessed, and no differences were observed in time to first exacerbation, rate of exacerbations, or percentage of subjects requiring hospitalization for exacerbations in those with deficiency versus those without, regardless of how deficiency was defined.
Conclusion: In a large sample of subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease selected for having an increased risk of experiencing an acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, only 1.9% had mannose-binding lectin concentrations below the normal range and we found no association between mannose-binding lectin concentrations and time to first acute exacerbation or frequency of acute exacerbations during one year of prospective follow-up.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00325897.
Keywords: COPD; acute exacerbations; mannose-binding lectin.
Figures
References
-
- Ikeda K, Sannoh T, Kawasaki N, Kawasaki T, Yamashina I. Serum lectin with known structure activates complement through the classical pathway. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:7451–7454. - PubMed
-
- Thiel S, Vorup-Jensen T, Stover CM, et al. A second serine protease associated with manna-binding lectin that activates complement. Nature. 1997;386:506–510. - PubMed
-
- Soell M, Lett E, Holveck F, Scholler M, Wachsmann D, Klein JP. Activation of human monocytes by streptococcal rhamnose glues polymers is mediated by CD14 antigen and mannan binding protein inhibits TNF-alpha release. J Immunol. 1995;154:851–860. - PubMed
-
- Chaka W, Verheul AF, Vaishnav VV, et al. Induction of TNF-alpha in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by the mannoprotein of Cryptococcus neoformans involves human mannose binding protein. J Immunol. 1997;159:2979–2985. - PubMed
-
- Jack DL, Read RC, Tenner AJ, Frosch M, Turner MW, Klein NH. Mannose-binding lectin regulates the inflammatory response of human professional phagocytes to Neisseria meningitides serogroup B. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:1152–1162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

