Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 and matrix metalloproteinases in Lewis lung carcinoma cells
- PMID: 23226772
- PMCID: PMC3494119
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.702
Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 and matrix metalloproteinases in Lewis lung carcinoma cells
Abstract
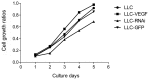
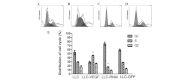
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays a critical role in tumor progression, angiogenesis and metastasis. Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)2, MMP9 and wild-type (WT) p53 has been found to regulate the production of VEGF. Whether VEGF regulates the production of COX-2, MMP2, MMP9 and WTp53, however, has yet to be determined. This study examined the influence of the overexpression or knockdown of VEGF on the protein levels of COX-2, MMP2, MMP9 and WTp53 as well as cell growth and cell cycle progression in Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells. LLC cells were transfected with pIRES2-VEGF-GFP in the VEGF-overexpressing group (LLC-VEGF), pIRES2-GFP in the mock group (LLC-GFP) or pSUPER-VEGF-GFP in the VEGF knockdown group (LLC-RNAi). Protein levels were detected by western blot analysis. LLC cell growth exhibited no marked change in the LLC-VEGF group, but was significantly retarded in the LLC-RNAi group. Further examination revealed that more cells entered the S stage in the LLC-VEGF group than in the control (or mock) group (45.3 vs. 29.1%, P<0.05), and that cell growth was retarded in the LLC-RNAi group. Moreover, COX-2 and MMP2 and MMP9 proteins were significantly increased in the LLC-VEGF group (approximately 1.84-, 1.89- and 1.83-fold, respectively, vs. control, P<0.05), but significantly decreased in the LLC-RNAi group, whereas the expression of WTp53 exhibited the opposite pattern of change. VEGF expression was positively correlated with COX-2, MMP2 and MMP9 expression (r=0.984, r=0.978, r=0.969, respectively, P<0.01) and negatively correlated with WTp53 (r=-0.833, p<0.01). The activities of MMP2 and MMP9 were increased in the LLC-VEGF group. In conclusion, VEGF overexpression may promote the expression of COX-2 and MMPs, but inhibits WTp53 production in LLC cells; VEGF underexpression may have an inverse effect. These changes are closely correlated with the infiltration and metastasis of lung cancer.
Figures
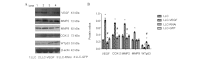

References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Brundage MD, Davies D, Mackillop WJ. Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: a decade of progress. Chest. 2002;122:1037–1057. - PubMed
-
- Folkman J. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1757–1763. - PubMed
-
- Saphir A. Angiogenesis the unifying concept in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;89:1658–1659. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
