Meta-analysis of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 23226773
- PMCID: PMC3494118
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.718
Meta-analysis of broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
Patients with Crohn's disease (CD) or ulcerative colitis (UC) undergo various therapies, including antibiotic therapy. This meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials was conducted to evaluate whether the use of antibacterial therapy improves the clinical symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The Medline and Scopus databases were searched and a systematic review was performed. Randomized, controlled trials in which antibiotic therapy was compared with placebo were investigated. A total of 10 randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials for CD were included in the meta-analysis. The pooling of the data from these trials yielded an odds ratio (OR) of 1.35 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.16-1.58] for antibiotic therapy compared with placebo in patients with CD. Furthermore, nine randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials for UC matched our criteria and were included in the analysis. The pooling of the data from these trials yielded an OR of 2.17 (95% CI, 1.54-3.05) in favor of antibiotic therapy. These results suggest that antibiotics improve clinical outcomes in patients with IBD.
Figures
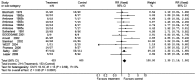


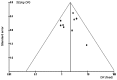
References
-
- Sartor RB. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1620–1633. - PubMed
-
- Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Prantera C, Scribano ML. Antibiotics and probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: why, when, and how. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2009;25:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG. Review article: mild to moderate Crohn’s disease – defining the basis for a new treatment algorithm. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18:263–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
