Deguelin, a natural rotenoid, inhibits mouse myeloma cell growth in vitro via induction of apoptosis
- PMID: 23226790
- PMCID: PMC3506627
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.790
Deguelin, a natural rotenoid, inhibits mouse myeloma cell growth in vitro via induction of apoptosis
Abstract
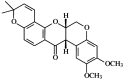
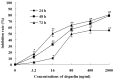
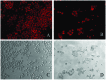
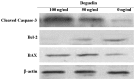
Deguelin is a naturally occurring rotenoid with strong cancer chemopreventive and antitumor activities. In the present study, we investigated the antitumor activity of deguelin against MPC-11 murine myeloma cells and the possible mechanism of action in vitro. Our results revealed that deguelin inhibited the proliferation of MPC-11 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and caused the apoptotic death of MPC-11 cells. Following exposure to deguelin, the phosphorylation of Akt was decreased. The inhibition of cell growth may be associated with decreased levels of phosphorylated Akt. Deguelin-induced apoptosis was characterized by the upregulation of Bax, downregulation of Bcl-2 and activation of caspase-3. In conclusion, deguelin inhibits murine myeloma cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis via regulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and by inhibition of the activation of Akt. Its potential as an anticancer agent against multiple myeloma warrants further investigation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antitumor effects of deguelin on H460 human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo: Roles of apoptotic cell death and H460 tumor xenografts model.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Jan;32(1):84-98. doi: 10.1002/tox.22214. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 26592500
-
Deguelin, an Akt inhibitor, down-regulates NF-κB signaling and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in mice.Dig Dis Sci. 2012 Nov;57(11):2873-82. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2237-x. Epub 2012 May 24. Dig Dis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22623043
-
Anticancer efficacy of deguelin in human prostate cancer cells targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 β/β-catenin pathway.Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 15;129(12):2916-27. doi: 10.1002/ijc.25949. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21472727
-
Deguelin targets multiple oncogenic signaling pathways to combat human malignancies.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105487. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105487. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 33581287 Review.
-
Biopharmacological considerations for accelerating drug development of deguelin, a rotenoid with potent chemotherapeutic and chemopreventive potential.Cancer. 2019 Jun 1;125(11):1789-1798. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32069. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30933320 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory effects of deguelin on proliferation and cell cycle of Raji cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013 Aug;33(4):491-495. doi: 10.1007/s11596-013-1147-2. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23904366
-
Deguelins, Natural Product Modulators of NF1-Defective Astrocytoma Cell Growth Identified by High-Throughput Screening of Partially Purified Natural Product Extracts.J Nat Prod. 2015 Nov 25;78(11):2776-81. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00753. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Nat Prod. 2015. PMID: 26467198 Free PMC article.
-
Cell survival and metastasis regulation by Akt signaling in colorectal cancer.Cell Signal. 2013 Aug;25(8):1711-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23603750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAD, a Proapoptotic Protein, Escapes ERK/RSK Phosphorylation in Deguelin and siRNA-Treated HeLa Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 8;11(1):e0145780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145780. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26745145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker N. Epidemiology of multiple myeloma. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;183:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1046–1060. - PubMed
-
- Gerhäuser C, Mar W, Lee SK, et al. Rotenoids mediate potent cancer chemopreventive activity through transcriptional regulation of ornithine decarboxylase. Nat Med. 1995;1:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Chun KH, Kosmeder JW, II, Sun S, et al. Effects of deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:291–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
