Deguelin, a natural rotenoid, inhibits mouse myeloma cell growth in vitro via induction of apoptosis
- PMID: 23226790
- PMCID: PMC3506627
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2012.790
Deguelin, a natural rotenoid, inhibits mouse myeloma cell growth in vitro via induction of apoptosis
Abstract
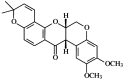
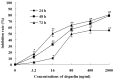
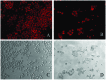
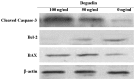
Deguelin is a naturally occurring rotenoid with strong cancer chemopreventive and antitumor activities. In the present study, we investigated the antitumor activity of deguelin against MPC-11 murine myeloma cells and the possible mechanism of action in vitro. Our results revealed that deguelin inhibited the proliferation of MPC-11 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner and caused the apoptotic death of MPC-11 cells. Following exposure to deguelin, the phosphorylation of Akt was decreased. The inhibition of cell growth may be associated with decreased levels of phosphorylated Akt. Deguelin-induced apoptosis was characterized by the upregulation of Bax, downregulation of Bcl-2 and activation of caspase-3. In conclusion, deguelin inhibits murine myeloma cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis via regulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and by inhibition of the activation of Akt. Its potential as an anticancer agent against multiple myeloma warrants further investigation.
Figures


References
-
- Becker N. Epidemiology of multiple myeloma. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;183:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1046–1060. - PubMed
-
- Gerhäuser C, Mar W, Lee SK, et al. Rotenoids mediate potent cancer chemopreventive activity through transcriptional regulation of ornithine decarboxylase. Nat Med. 1995;1:260–266. - PubMed
-
- Chun KH, Kosmeder JW, II, Sun S, et al. Effects of deguelin on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and apoptosis in premalignant human bronchial epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:291–302. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
