Myeloid Antigen Expression in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Relevance for Clinical Outcome in Indonesian ALL-2006 Protocol
- PMID: 23227046
- PMCID: PMC3513752
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/135186
Myeloid Antigen Expression in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Its Relevance for Clinical Outcome in Indonesian ALL-2006 Protocol
Abstract
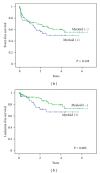
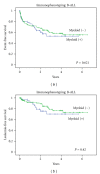
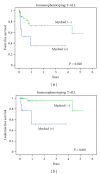
The frequency of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients expressing myeloid antigens on their ALL cells varies between 5 and 36% in several different studies. The clinical relevance of myeloid antigen expression in childhood ALL is controversial. In Indonesian patients, no data were present. Therefore, in Yogyakarta, Indonesia, we analyzed 239 ALL patients who were immunophenotyped including myeloid markers (CD13, CD33, CD117, and/or cMPO). Myeloid antigen expression was found in 25% of patients. Expression of myeloid antigen in B-lineage leukemia was 27%, and in T-lineage leukemia, it was 18% (P = 0.15). No association was found between myeloid antigen expression and clinical or biological features. In the whole cohort of patients we did not find a significant association between myeloid antigen expression and survival, although leukemia-free survival at 3 years was higher in the myeloid-negative patients (73% ± 6%) compared to myeloid-positive patients (67% ± 8%). Interestingly, in T-ALL patients, expression of myeloid antigens was an independent adverse prognostic factor (hazard ratio: 3.26, 95% CI: 1.06-9.98, P = 0.04). Kaplan-Meier analysis for event-free survival was also significant (log rank P = 0.03) in this subgroup. In conclusion, in the Indonesian ALL population, in particular, myeloid antigen-expressing T-ALL patients had a higher chance of having induction failure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical importance of myeloid-antigen expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood.N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 21;324(12):800-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103213241204. N Engl J Med. 1991. PMID: 1997852
-
[Immunologic characteristics and prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia M1].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Aug;15(4):687-91. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17708783 Chinese.
-
Clinical features and treatment outcome of children with myeloid antigen positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children's Cancer Group.Blood. 1997 Jul 1;90(1):28-35. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9207434
-
Review of the incidence and clinical relevance of myeloid antigen-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leukemia. 1991 Aug;5(8):637-45. Leukemia. 1991. PMID: 1886419 Review.
-
[Biological properties and sensitivity to induction therapy of differentiated cells expressing atypical immunophenotype in acute leukemia of children].Folia Med Cracov. 2001;42(3):5-80. Folia Med Cracov. 2001. PMID: 12353422 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with co-expression of CD56, CD34, CD117 and CD33: A case with poor prognosis.Mol Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug;5(2):331-332. doi: 10.3892/mco.2016.927. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Mol Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27446573 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant immunophenotypic expressions in childhood acute leukemias: A tertiary care hospital experience.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Mar;41(3):816-820. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.3.9717. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40103873 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of subtypes and immunophenotypic characterization of 1379 cases of paediatric acute leukaemia.Pak J Med Sci. 2021 May-Jun;37(3):805-811. doi: 10.12669/pjms.37.3.3552. Pak J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34104169 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Immunophenotypic Aberrancies in Adult and Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Lessons from Regional Variation.Iran J Pathol. 2020 Winter;15(1):1-7. doi: 10.30699/IJP.2019.93974.1926. Iran J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32095142 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum and Immunophenotypic Profile of Acute Leukemia: A Tertiary Center Flow Cytometry Experience.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2019 Mar 1;11(1):e2019017. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2019.017. eCollection 2019. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30858955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camós M, Colomer D. Molecular biology in acute leukemia. Clinical and Translational Oncology. 2006;8(8):550–559. - PubMed
-
- Margolin JF, Steuber CP, Poplack DG. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG, editors. Principles and Practice of Pediatric Oncology. 5th edition. Philadelphia, Pa, USA: Williams & Wilkins; 2006. pp. 1605–1616.
-
- Haferlach T, Kern W, Schnittger S, Schoch C. Modern diagnostics in acute leukemias. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 2005;56(2):223–234. - PubMed
-
- Van Dongen JJ. Immunophenotyping of Hematopoietic Malignancies. Rotterdam, The Netherlands: Departement of Immunology, Erasmus University Medical Center; 2003.
-
- Uckun FM, Sather HN, Gaynon PS, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcome of children with myeloid antigen positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Blood. 1997;90(1):28–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

