Analysis of copy number variation in Alzheimer's disease in a cohort of clinically characterized and neuropathologically verified individuals
- PMID: 23227193
- PMCID: PMC3515604
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050640
Analysis of copy number variation in Alzheimer's disease in a cohort of clinically characterized and neuropathologically verified individuals
Abstract
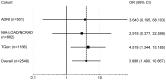
Copy number variations (CNVs) are genomic regions that have added (duplications) or deleted (deletions) genetic material. They may overlap genes affecting their function and have been shown to be associated with disease. We previously investigated the role of CNVs in late-onset Alzheimer's disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment using Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) and National Institute of Aging-Late Onset AD/National Cell Repository for AD (NIA-LOAD/NCRAD) Family Study participants, and identified a number of genes overlapped by CNV calls. To confirm the findings and identify other potential candidate regions, we analyzed array data from a unique cohort of 1617 Caucasian participants (1022 AD cases and 595 controls) who were clinically characterized and whose diagnosis was neuropathologically verified. All DNA samples were extracted from brain tissue. CNV calls were generated and subjected to quality control (QC). 728 cases and 438 controls who passed all QC measures were included in case/control association analyses including candidate gene and genome-wide approaches. Rates of deletions and duplications did not significantly differ between cases and controls. Case-control association identified a number of previously reported regions (CHRFAM7A, RELN and DOPEY2) as well as a new gene (HLA-DRA). Meta-analysis of CHRFAM7A indicated a significant association of the gene with AD and/or MCI risk (P = 0.006, odds ratio = 3.986 (95% confidence interval 1.490-10.667)). A novel APP gene duplication was observed in one case sample. Further investigation of the identified genes in independent and larger samples is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association, Thies W, Bleiler L (2011) 2011 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 7: 208–244. - PubMed
-
- Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, et al. (2006) Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63: 168–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIA AG05128/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P50-AG08671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01AG000950-06/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P30-AG13846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH060451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG030514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH60451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NIA P50AG16570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005128/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031581/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH U01AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2AG036535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG19610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG031581/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS039764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P50AG05681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIA R01AG19771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000950/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K01AG030514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG034504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH AG05144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIA P30AG19610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005144/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG10161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NIH AG10161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS059873/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIA AG05146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059873/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NINDS NS39764/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NIH P50AG05136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

