Lobular capillary hemangioma in the posterior trachea: a rare cause of hemoptysis
- PMID: 23227409
- PMCID: PMC3514818
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/592524
Lobular capillary hemangioma in the posterior trachea: a rare cause of hemoptysis
Abstract
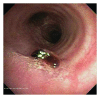
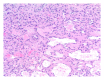
Lobular capillary hemangiomas (LCH) have been cited in the literature as a rare potential cause for recurrent hemoptysis. They are mostly associated with cutaneous and mucosal surfaces. Rarely do they affect the trachea and associated airways in adults. Lobular capillary hemangiomas can be associated with previous trauma to the airway; however, drugs, hormonal shifts, viral oncogenes, production of angiogenic factors, and cytogenetic clonal deletion abnormalities can also influence these lesions. We document a case of a posterior wall tracheal hemangioma with associated recurrent hemoptysis in a 22-year-old male on testosterone therapy. An LCH attached to the posterior tracheal wall can be technically difficult to remove due to risk of perforation and bleeding. There have been no cases documented of posterior wall LCH.
References
-
- Mills SE, Cooper PH, Fechner RE. Lobular capillary hemangioma: the underlying lesion of pyogenic granuloma. A study of 73 cases from the oral and nasal mucous membranes. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 1980;4(5):470–479. - PubMed
-
- Irani S, Brack T, Pfaltz M, Russi EW. Tracheal lobular capillary hemangioma: a rare cause of recurrent hemoptysis. Chest. 2003;123(6):2148–2149. - PubMed
-
- Chawla M, Stone C, Simoff MJ. Lobular capillary hemangioma of the trachea: the second case. Journal of Bronchology and Interventional Pulmonology. 2010;17(3):238–240. - PubMed
-
- Madhumita K, Sreekumar KP, Malini H, Indudharan R. Tracheal haemangioma: case report. Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 2004;118(8):655–658. - PubMed
-
- Porfyridis I, Zisis C, Glinos K, et al. Recurrent cough and hemoptysis associated with tracheal capillary hemangioma in an adolescent boy: a case report. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2007;134(5):1366–1367. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources