Coil embolization of an intracranial aneurysm in an infant with tuberous sclerosis complex: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 23227434
- PMCID: PMC3513845
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.102944
Coil embolization of an intracranial aneurysm in an infant with tuberous sclerosis complex: A case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Tuberous sclerosis (TS) is a multiorgan neurocutaneous syndrome. Vascular manifestations are often extracranial. There is a paucity of cases involving TS combined with intracranial aneurysms reported in the literature. As a result, treatment has not been well described.
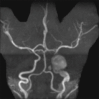
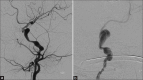
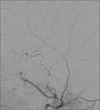
Case description: We report the case of a 13-month-old female infant with a prior diagnosis of TS that was found to have new onset of left eye ptosis, anisocoria, and papillary mydriasis indicative of left third cranial nerve palsy. A magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) of the brain revealed a left internal carotid artery (ICA) aneurysm. Endovascular embolization was determined to be the best option for treatment. After a successful balloon test occlusion with neuromonitoring, the left internal carotid artery was sacrificed via coil embolization.
Conclusions: This is only the third case report of endovascular coil embolization of an intracranial aneurysm in an infant with TS. We report no complications during the procedure, and the patient was discharged with resolving left third cranial nerve palsy. Neither surgical nor endovascular outcomes have been well described in the literature. Follow-up on this patient will be useful for establishing protocols of treatment.
Keywords: Hamartin; intracranial aneurysm; tuberin; tuberous sclerosis.
Figures

References
-
- Beall S, Delaney P. Tuberous sclerosis with intracranial aneurysm. Arch Neurol. 1983;40:826–7. - PubMed
-
- Beltramello A, Puppini G, Bricolo A, Andreis IA, el-Dalati G, Longa L, et al. Does the tuberous sclerosis complex include intracranial aneurysms? A case report with a review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol. 1999;29:206–11. - PubMed
-
- Blumenkopf B, Huggins MJ. Tuberous sclerosis and multiple intracranial aneurysms: Case report. Neurosurgery. 1985;17:797–800. - PubMed
-
- Bourneville D. Sclerose tubereuse des circonvolutions cerebrales: Idiotie et epilepsie hemipleguique. Arch Neurol. 1880;1:81–91.
-
- Brill CB, Peyster RG, Hoover ED, Keller MS. Giant intracranial aneurysm in a child with tuberous sclerosis: CT demonstration. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985;9:377–80. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

