Ginkgo biloba prevents transient global ischemia-induced delayed hippocampal neuronal death through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanism
- PMID: 23228346
- PMCID: PMC3568207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.11.017
Ginkgo biloba prevents transient global ischemia-induced delayed hippocampal neuronal death through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanism
Abstract
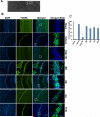
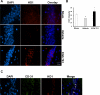
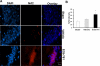
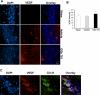
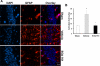
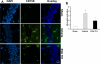
We have previously reported neuroprotective properties of Ginkgo biloba/EGb 761® (EGb 761) in transient and permanent mouse models of brain ischemia. In a quest to extend our studies on EGb 761 and its constituents further, we used a model of transient global ischemia induced delayed hippocampal neuronal death and inflammation. Mice pretreated with different test drugs for 7 days were subjected to 8-min bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (tBCCAO) at day 8. After 7 days of reperfusion, mice brains were dissected out for TUNEL assay and immunohistochemistry. In situ detection of fragmented DNA (TUNEL staining) showed that out of all test drugs, only EGb 761 (13.6% ± 3.2) pretreatment protected neurons in the hippocampus against global ischemia (vs. vehicle, 85.1% ± 9.9; p<0.05). Immunofluorescence-based studies demonstrated that pretreatment with EGb 761 upregulated the expression levels of heme oxygenase 1 (HO1), nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as compared to the vehicle group. In addition, increased number of activated astrocytes and microglia in the vehicle group was observed to be significantly lower in the EGb 761 pretreated group. Together, these results suggest that EGb 761 is a multifunctional neuroprotective agent, and the protection is in part associated with activation of the HO1/Nrf2 pathway, upregulation of VEGF and downregulation of inflammatory mediators such as astrocytes and microglia.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preconditioning with Ginkgo biloba (EGb 761®) provides neuroprotection through HO1 and CRMP2.Neurobiol Dis. 2012 Apr;46(1):180-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Jan 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2012. PMID: 22297164 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of rat hippocampal neurons with NeuN after ischemia/reperfusion and Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) pretreatment.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Oct-Nov;26(7-8):1193-204. doi: 10.1007/s10571-006-9080-6. Epub 2006 Jun 7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16758319 Free PMC article.
-
Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection.Neuroscience. 2011 Apr 28;180:248-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.02.031. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21334424 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S8-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40454. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 13130383 Review.
-
EGb 761: ginkgo biloba extract, Ginkor.Drugs R D. 2003;4(3):188-93. doi: 10.2165/00126839-200304030-00009. Drugs R D. 2003. PMID: 12757407 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Ginkgo biloba Extract EGb761 on Hippocampal Neuronal Injury and Carbonyl Stress of D-Gal-Induced Aging Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 23;2019:5165910. doi: 10.1155/2019/5165910. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31871482 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Role of Nrf2 in Experimental Ischemic Stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 5;10:153. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00153. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30890934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rifampicin Attenuated Global Cerebral Ischemia Injury via Activating the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor Pathway.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Nov 29;10:273. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00273. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27965540 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract Inhibits Astrocytic Lipocalin-2 Expression and Alleviates Neuroinflammatory Injury via the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway After Ischemic Brain Stroke.Front Pharmacol. 2018 May 16;9:518. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00518. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29867513 Free PMC article.
-
Tnfrsf12a-Mediated Atherosclerosis Signaling and Inflammatory Response as a Common Protection Mechanism of Shuxuening Injection Against Both Myocardial and Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injuries.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Apr 6;9:312. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00312. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29681850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastianetto S, Ramassamy C, Dore S, Christen Y, Poirier J, Quirion R. The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects hippocampal neurons against cell death induced by beta-amyloid. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:1882–1890. - PubMed
-
- Chan PC, Xia Q, Fu PP. Ginkgo biloba leave extract: biological, medicinal, and toxicological effects. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2007;25:211–244. - PubMed
-
- Chan SA, Reid KH, Schurr A, Miller JJ, Iyer V, Tseng MT. Fosphenytoin reduces hippocampal neuronal damage in rat following transient global ischemia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1998;140:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekaran K, Mehrabian Z, Spinnewyn B, Chinopoulos C, Drieu K, Fiskum G. Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide, a component of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) in global brain ischemia and in excitotoxicity-induced neuronal death. Pharmacopsychiatry 36 Suppl. 2003;1:S89–94. - PubMed
-
- Chiarugi A. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and stroke. Pharmacol Res. 2005;52:15–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

