Leptin increases HER2 protein levels through a STAT3-mediated up-regulation of Hsp90 in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23228483
- PMCID: PMC5528468
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2012.11.002
Leptin increases HER2 protein levels through a STAT3-mediated up-regulation of Hsp90 in breast cancer cells
Abstract
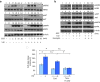
Obesity condition confers risks to breast cancer development and progression, and several reports indicate that the adipokine leptin, whose synthesis and plasma levels increase with obesity, might play an important role in modulating breast cancer cell phenotype. Functional crosstalk occurring between leptin and different signaling molecules contribute to breast carcinogenesis. In this study, we show, in different human breast cancer cell lines, that leptin enhanced the expression of a chaperone protein Hsp90 resulting in increased HER2 protein levels. Silencing of Hsp90 gene expression by RNA interference abrogated leptin-mediated HER2 up-regulation. Leptin effects were dependent on JAK2/STAT3 activation, since inhibition of this signaling cascade by AG490 or ectopic expression of a STAT3 dominant negative abrogated leptin-induced HER2 and Hsp90 expressions. Functional experiments showed that leptin treatment significantly up-regulated human Hsp90 promoter activity. This occurred through an enhanced STAT3 transcription factor binding to its specific responsive element located in the Hsp90 promoter region as revealed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Analysis of HER2, Akt and MAPK phosphorylation levels revealed that leptin treatment amplified the responsiveness of breast cancer cells to growth factor stimulation. Furthermore, we found that long-term leptin exposure reduced sensitivity of breast cancer cells to the antiestrogen tamoxifen. In the same experimental conditions, the combined treatment of tamoxifen with the Hsp90 inhibitor 17-AAG completely abrogated leptin-induced anchorage-independent breast cancer cell growth. In conclusion, our results highlight, for the first time, the ability of the adipocyte-secreted factor leptin to modulate Hsp90/HER2 expressions in breast cancer cells providing novel insights into the molecular mechanism linking obesity to breast cancer growth and progression.
Copyright © 2012 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Farnesoid X receptor inhibits tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth through downregulation of HER2 expression.Oncogene. 2011 Sep 29;30(39):4129-40. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.124. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21499302 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy of leptin/STAT3 with HER2 receptor induces tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells through regulation of apoptosis-related genes.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015 Apr;38(2):155-64. doi: 10.1007/s13402-014-0213-5. Epub 2014 Dec 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2015. PMID: 25539992
-
Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Jun 16;96(12):926-35. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh166. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004. PMID: 15199112
-
Inhibition of erbB receptor (HER) tyrosine kinases as a strategy to abrogate antiestrogen resistance in human breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Dec;7(12 Suppl):4436s-4442s; discussion 4411s-4412s. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11916237 Review.
-
STAT3 Signaling Axis and Tamoxifen in Breast Cancer: A Promising Target for Treatment Resistance.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023;23(16):1819-1828. doi: 10.2174/1871520623666230713101119. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37448364 Review.
Cited by
-
Icaritin reduces prostate cancer progression via inhibiting high-fat diet-induced serum adipokine in TRAMP mice model.J Cancer. 2020 Sep 21;11(22):6556-6564. doi: 10.7150/jca.48413. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33046976 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Mechanism of Leptin Signaling within Tumor Microenvironment in Driving Breast Cancer Growth and Progression.Front Oncol. 2014 Nov 26;4:340. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00340. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25505738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel leptin antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 May;19(5):1122-32. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12517. Epub 2015 Feb 27. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25721149 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer: Analysis of Risk Factors and Current Clinical Evaluation.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:767-819. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287872 Review.
-
Association of physical weight statuses defined by body mass index (BMI) with molecular subtypes of premenopausal breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Feb;203(3):429-447. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07139-z. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 37882920
References
-
- Ahima, R.S. , Osei, S.Y. , 2004. Leptin signaling. Physiol. Behav. 81, (2) 223–241. - PubMed
-
- Allred, D.C. , Clark, G.M. , Molina, R. , Tandon, A.K. , Schnitt, S.J. , Gilchrist, K.W. , Osborne, C.K. , Tormey, D.C. , McGuire, W.L. , 1992. Overexpression of HER-2/neu and its relationship with other prognostic factors change during the progression of in situ to invasive breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 23, (9) 974–979. - PubMed
-
- Andò, S. , Catalano, S. , 2011. The multifactorial role of leptin in driving the breast cancer microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, (5) 263–275. - PubMed
-
- Arpino, G. , Green, S.J. , Allred, D.C. , Lew, D. , Martino, S. , Osborne, C.K. , Elledge, R.M. , 2004. HER-2 amplification, HER-1 expression, and tamoxifen response in estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: a southwest oncology group study. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, (17) 5670–5676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

