SPION-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of Alzheimer's disease plaques in AβPP/PS-1 transgenic mouse brain
- PMID: 23229079
- PMCID: PMC4801216
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-121171
SPION-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of Alzheimer's disease plaques in AβPP/PS-1 transgenic mouse brain
Abstract
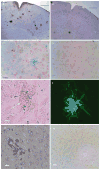
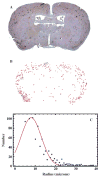
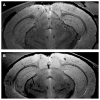
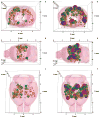
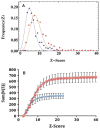
In our program to develop non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD), we have synthesized antibody-conjugated, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for use as an in vivo agent for MRI detection of amyloid-β plaques in AD. Here we report studies in AβPP/PS1 transgenic mice, which demonstrate the ability of novel anti-AβPP conjugated SPIONs to penetrate the blood-brain barrier to act as a contrast agent for MR imaging of plaques. The conspicuity of the plaques increased from an average Z-score of 5.1 ± 0.5 to 8.3 ± 0.2 when the plaque contrast to noise ratio was compared in control AD mice with AD mice treated with SPIONs. The number of MRI-visible plaques per brain increased from 347 ± 45 in the control AD mice, to 668 ± 86 in the SPION treated mice. These results indicated that our SPION enhanced amyloid-β detection method delivers an efficacious, non-invasive MRI detection method in transgenic mice.
Figures
References
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Alzheimer’s disease in the U.S. population: Prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:1119–1122. - PubMed
-
- Fodero-Tavoletti AT, Villemagne VL, Rowe CC, Masters CL, Barnham KJ, Cappai R. Amyloid-β: The seeds of darkness. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:1247–1251. - PubMed
-
- Masters CL, Cappai R, Barnham KJ, Villemagne VL. Molecular mechanisms for Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for neuroimaging and therapeutics. J Neurochem. 2006;106:1700–1725. - PubMed
-
- Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: An appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Med. 2011;10:698–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

