Comparison of pain and swelling after removal of oral leukoplakia with CO₂ laser and cold knife: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 23229239
- PMCID: PMC3548643
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.17960
Comparison of pain and swelling after removal of oral leukoplakia with CO₂ laser and cold knife: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
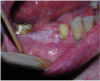
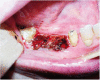
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare conventional surgery with carbon dioxide (CO₂) laser in patients with oral leukoplakia, and to evaluate the postoperative pain and swelling.
Study design: A total of 48 patients (27 males and 21 females) with a mean age of 53.7 ± 11.7 years and diagnosed with oral leukoplakia were randomly assigned to receive treatment either with conventional surgery using a cold knife or with a CO₂ laser technique. A visual analog scale (VAS) was used to score pain and swelling at different postoperative time points.
Results: Pain and swelling reported by the patients was greater with the conventional cold knife than with the CO₂ laser, statistically significant differences for pain and swelling were observed between the two techniques during the first three days after surgery. Followed by a gradual decrease over one week. In neither group was granuloma formation observed, and none of the patients showed malignant transformation during the period of follow-up.
Conclusions: The CO₂ laser causes only minimal pain and swelling, thus suggesting that it may be an alternative method to conventional surgery in treating patients with oral leukoplakia.
Figures
References
-
- Van der Waal I, Axell T. Oral leukoplakia: a proposal for uniform reporting. Oral Oncol. 2002;38:521–26. - PubMed
-
- Van der Waal I. Potentially malignant disorders of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa; present concepts of management. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:423–5. - PubMed
-
- Kramer IRH, Lucas RB, Pindborg JJ, Sobin LH. WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Precancerous Lesions. Definition of leukoplakia and related lesions: an aid to studies on oral precancer. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1978;46:518–39. - PubMed
-
- Proia NK, Paszkiewicz GM, Nasca MA, Franke GE, Pauly JL. Smoking and smokeless tobacco-associated human buccal cell mutations and their association with oral cancer—a review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:1061–77. - PubMed
-
- Axell T, Pindborg JJ, Smith CJ, Van der Waal I. Oral white lesions with special reference to precancerous and tobacco related lesions: conclusions of an international symposium held in Uppsala, Sweden, May 18-21 1994. International Collaborative Group on Oral White Lesions. J Oral Pathol Med. 1996;25:49–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical