A matter of life and death: self-renewal in stem cells
- PMID: 23229591
- PMCID: PMC3537149
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.197
A matter of life and death: self-renewal in stem cells
Abstract
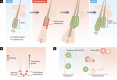
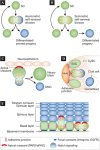
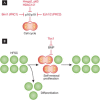
If Narcissus could have self-renewed even once on seeing his own reflection, he would have died a happy man. Stem cells, on the other hand, have an enormous capacity for self-renewal; in other words, the ability to replicate and generate more of the same. In adult organisms, stem cells reside in specialized niches within each tissue. They replenish tissue cells that are lost during normal homeostasis, and on injury they repair damaged tissue. The ability of a stem cell to self-renew is governed by the dynamic interaction between the intrinsic proteins it expresses and the extrinsic signals that it receives from the niche microenvironment. Understanding the mechanisms governing when to proliferate and when to differentiate is vital, not only to normal stem cell biology, but also to ageing and cancer. This review focuses on elucidating conceptually, experimentally and mechanistically, our understanding of adult stem cell self-renewal. We use skin as a paradigm for discussing many of the salient points about this process, but also draw on the knowledge gained from these and other adult stem cell systems to delineate shared underlying principles, as well as highlight mechanistic distinctions among adult tissue stem cells. By doing so, we pinpoint important questions that still await answers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Copley MR, Beer PA, Eaves CJ (2012) Hematopoietic stem cell heterogeneity takes center stage. Cell Stem Cell 10: 690–697 - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Oudenaarden A, Clevers H (2012) Identifying the stem cell of the intestinal crypt: strategies and pitfalls. Cell Stem Cell 11: 452–460 - PubMed
-
- He S, Nakada D, Morrison SJ (2009) Mechanisms of stem cell self-renewal. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25: 377–406 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

