Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease
- PMID: 23230096
- PMCID: PMC3631843
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0719
Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: The two major classes of antidiabetic drugs, sulfonylureas and metformin, may differentially affect macrovascular complications and mortality in diabetic patients. We compared the long-term effects of glipizide and metformin on the major cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients who had a history of coronary artery disease (CAD).
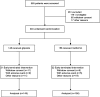
Research design and methods: This study is a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. A total of 304 type 2 diabetic patients with CAD, mean age = 63.3 years (range, 36-80 years), were enrolled. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either glipizide (30 mg daily) or metformin (1.5 g daily) for 3 years. The primary end points were times to the composite of recurrent cardiovascular events, including death from a cardiovascular cause, death from any cause, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or arterial revascularization.
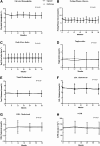
Results: At the end of study drug administration, both groups achieved a significant decrease in the level of glycated hemoglobin (7.1% in the glipizide group and 7.0% in the metformin group). At a median follow-up of 5.0 years, 91 participants had developed 103 primary end points. Intention-to-treat analysis showed an adjusted hazard ratio (HR) of 0.54 (95% CI 0.30-0.90; P = 0.026) for the composites of cardiovascular events among the patients that received metformin, compared with glipizide. The secondary end points and adverse events were not significantly different between the two groups.
Conclusions: Treatment with metformin for 3 years substantially reduced major cardiovascular events in a median follow-up of 5.0 years compared with glipizide. Our results indicated a potential benefit of metformin therapy on cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00513630.
Figures
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club: metformin reduced CV events compared with glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes and CAD.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Apr 16;158(8):JC4. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-8-201304160-02004. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23588769 No abstract available.
-
Comment on Hong et al. Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Diabetes care 2013;36:1304-1311.Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):e19-20. doi: 10.2337/dc13-1806. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24356605 No abstract available.
-
Response to comment on Hong et al. Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Diabetes care 2013;36:1304-1311.Diabetes Care. 2014;37(1):e21. doi: 10.2337/dc13-2003. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24356606 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1090–1101 - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–853 - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1577–1589 - PubMed
-
- Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, et al. ADVANCE Collaborative Group Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2560–2572 - PubMed
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2003;348:383–393 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

