Management strategies after nondiagnostic results with frameless stereotactic needle biopsy: Retrospective review of 28 patients
- PMID: 23230536
- PMCID: PMC3514914
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.103026
Management strategies after nondiagnostic results with frameless stereotactic needle biopsy: Retrospective review of 28 patients
Abstract
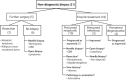
Background: Although frameless stereotactic needle biopsy is an accepted procedure for the diagnosis of intracranial lesions, findings are nondiagnostic in 2-15% of patients and no recommendations yet exist to guide subsequent care. After reviewing the postoperative course after nondiagnostic biopsy of 28 patients, we developed a paradigm to guide management in the future.
Methods: In reviewing the medical records of 284 frameless stereotactic needle biopsies (January 2000 to December 2006), we identified a subset of 28 patients who underwent 29 (10.2%) biopsies that did not yield a definitive diagnosis based on permanent pathologic samples. Postoperative treatment plans and clinical courses were further examined in 21 patients; 7 without follow-up were excluded.
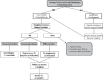
Results: Of the 21 patients, lesion location and characteristics guided the surgeon's decision to recommend further surgery or initiate empiric treatment. Soon after initial biopsy, five patients underwent a second procedure (biopsy or resection) that yielded diagnostic pathologic tissue. Of 16 patients who had empiric treatment, 7 (43.7%) subsequently had their treatment plan changed because of a lack of improvement and 5 underwent a second biopsy (4 diagnostic). Evolving clinical information precipitated treatment change in two patients. Of 10 patients who had a second surgery for better diagnostic information, the diagnostic yield was 90%.
Conclusions: Considering the 90% diagnostic yield, we now recommend repeat surgery for most patients with nondiagnostic biopsies, especially for lesions considered potentially neoplastic or infectious. Empiric management, for lesions likely to be neurodegenerative, is an option but requires close follow-up examination.
Keywords: Brain tumor; diagnosis; frameless stereotactic biopsy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy procedure: diagnostic yield, surgical morbidity, and comparison with the frame-based technique.J Neurosurg. 2006 Feb;104(2):233-7. doi: 10.3171/jns.2006.104.2.233. J Neurosurg. 2006. PMID: 16509497 Clinical Trial.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy and Field for Improvement of Frameless Stereotactic Brain Biopsy: A Focus on Nondiagnostic Cases.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2024 Jan;85(1):48-61. doi: 10.1055/a-1994-8033. Epub 2022 Dec 8. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 36481998 Review.
-
A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors.Brain Sci. 2023 Feb 20;13(2):362. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020362. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 36831906 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of frameless and frame-based image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy in the diagnosis of glioma: comparison of biopsy and open resection specimen.Neurol Res. 2005 Jun;27(4):358-62. doi: 10.1179/016164105X40057. Neurol Res. 2005. PMID: 15949232
-
Comparison of Frame-Based Versus Frameless Intracranial Stereotactic Biopsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.World Neurosurg. 2019 Jul;127:607-616.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.016. Epub 2019 Apr 8. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30974279
Cited by
-
Next-generation sequencing of tissue: A logical extension.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2016 Jul 14;3(4):e261. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000261. eCollection 2016 Aug. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2016. PMID: 27458600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The ratio of HLA-DR and VNN2+ expression on CD14+ myeloid derived suppressor cells can distinguish glioblastoma from radiation necrosis patients.J Neurooncol. 2017 Aug;134(1):189-196. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2508-7. Epub 2017 May 27. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28551851
-
Diffusion histology imaging differentiates distinct pediatric brain tumor histology.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 26;11(1):4749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84252-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33637807 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosurgical techniques for the treatment of brain neoplasms: A short review.World J Methodol. 2018 Dec 14;8(4):51-58. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v8.i4.51. eCollection 2018 Dec 14. World J Methodol. 2018. PMID: 30596035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Minimally invasive approach to a deep-seated motor eloquent brain tumour: a technical note.J Surg Case Rep. 2022 Jan 21;2022(1):rjab611. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjab611. eCollection 2022 Jan. J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35079339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Air EL, Leach JL, Warnick RE, McPherson CM. Comparing the risks of frameless stereotactic biopsy in eloquent and non-eloquent regions of the brain: A retrospective review of 284 Cases. J Neurosurg. 2009;111:820–4. - PubMed
-
- Apuzzo ML, Chandrasoma PT, Cohen D, Zee CS, Zelman V. Computed imaging stereotaxy: Experience and perspective related to 500 procedures applied to brain masses. Neurosurgery. 1987;20:930–7. - PubMed
-
- Barnett GH, Miller DW, Weisenberger J. Frameless stereotaxy with scalp-applied fiducial markers for brain biopsy procedures: Experience in 218 cases. J Neurosurg. 1999;91:569–76. - PubMed
-
- Bernays RL, Kollias SS, Khan N, Brandner S, Meier S, Yonekawa Y. Histological yield, complications, and technological considerations in 114 consecutive frameless stereotactic biopsy procedures aided by open intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:354–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

