Observation of super-resolution in digital breast tomosynthesis
- PMID: 23231301
- PMCID: PMC3523583
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4757583
Observation of super-resolution in digital breast tomosynthesis
Abstract
Purpose: Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is a 3D x-ray imaging modality in which tomographic sections of the breast are generated from a limited range of tube angles. Because oblique x-ray incidence shifts the image of an object in subpixel detector element increments with each increasing projection angle, it is demonstrated that DBT is capable of super-resolution (i.e., subpixel resolution).
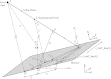
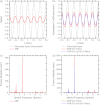
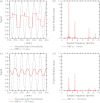
Methods: By convention, DBT reconstructions are performed on planes parallel to the breast support at various depths of the breast volume. In order for resolution in each reconstructed slice to be comparable to the detector, the pixel size should match that of the detector elements; hence, the highest frequency that can be resolved in the plane of reconstruction is the alias frequency of the detector. This study considers reconstruction grids with much smaller pixelation to visualize higher frequencies. For analytical proof of super-resolution, a theoretical framework is developed in which the reconstruction of a high frequency sinusoidal input is calculated using both simple backprojection (SBP) and filtered backprojection. To study the frequency spectrum of the reconstruction, its Fourier transform is also determined. The experimental feasibility of super-resolution was investigated by acquiring images of a bar pattern phantom with frequencies higher than the detector alias frequency.
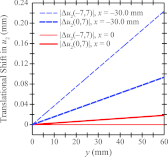
Results: Using analytical modeling, it is shown that the central projection cannot resolve frequencies exceeding the detector alias frequency. The Fourier transform of the central projection is maximized at a lower frequency than the input as evidence of aliasing. By contrast, SBP reconstruction can resolve the input, and its Fourier transform is correctly maximized at the input frequency. Incorporating filters into the reconstruction smoothens pixelation artifacts in the spatial domain and reduces spectral leakage in the Fourier domain. It is also demonstrated that the existence of super-resolution is dependent on position in the reconstruction and on the directionality of the input frequency. Consistent with the analytical results, experimental reconstructions of bar patterns showed visibility of frequencies greater than the detector alias frequency. Super-resolution was present at positions predicted from analytical modeling.
Conclusions: This work demonstrates the existence of super-resolution in DBT. Super-resolution has the potential to impact the visualization of fine structural details in the breast, such as microcalcifications and other subtle signs of cancer.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Oblique reconstructions in tomosynthesis. II. Super-resolution.Med Phys. 2013 Nov;40(11):111912. doi: 10.1118/1.4819942. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24320445 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the Potential for Super-Resolution in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2011 Feb;7961:79615K. doi: 10.1117/12.878845. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2011. PMID: 38846530 Free PMC article.
-
Oblique reconstructions in tomosynthesis. I. Linear systems theory.Med Phys. 2013 Nov;40(11):111911. doi: 10.1118/1.4819941. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24320444 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of back projection methods for breast tomosynthesis image reconstruction.J Digit Imaging. 2015 Jun;28(3):338-45. doi: 10.1007/s10278-014-9736-6. J Digit Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25384538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital tomosynthesis: technique.Radiol Clin North Am. 2014 May;52(3):489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2014.01.003. Radiol Clin North Am. 2014. PMID: 24792651 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of Resolution in Multiplanar Reconstructions for Digital Breast Tomosynthesis.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2016 Feb-Mar;9783:978303. doi: 10.1117/12.2216260. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2016. PMID: 40777163 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical evaluation and optimization of image quality for a Next Generation Tomosynthesis prototype.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022 Feb-Mar;12031:1203142. doi: 10.1117/12.2608811. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022. PMID: 39351015 Free PMC article.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis: lessons learned from early clinical implementation.Radiographics. 2014 Jul-Aug;34(4):E89-102. doi: 10.1148/rg.344130087. Radiographics. 2014. PMID: 25019451 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving Isotropic Super-Resolution with a Non-Isocentric Acquisition Geometry in a Next-Generation Tomosynthesis System.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022 Feb-Mar;12031:120314B. doi: 10.1117/12.2612451. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2022. PMID: 37692411 Free PMC article.
-
Proposing Rapid Source Pulsing for Improved Super-Resolution in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2020 Feb;11312:113125G. doi: 10.1117/12.2542551. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2020. PMID: 37927528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rafferty E. A., “Tomosynthesis: New weapon in breast cancer fight,” Decisions in Imaging Economics 17(4) (2004).
-
- Park S. C., Park M. K., and Kang M. G., “Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview,” IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 20(3), 21–36 (2003).10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207 - DOI
-
- Bushberg J. T., Seibert J. A., Edwin M., Leidholdt J., and Boone J. M., “Image quality,” in The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging, 2nd ed., edited by John J.-R., Snyder A., and DeGeorge T. (Lippincott, Philadelphia, PA, 2002), Chap. 10, pp. 255–291.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

