Dissociable brain signatures of choice conflict and immediate reward preferences in alcohol use disorders
- PMID: 23231650
- PMCID: PMC3871988
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12017
Dissociable brain signatures of choice conflict and immediate reward preferences in alcohol use disorders
Abstract
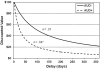
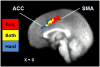
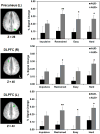
Impulsive delayed reward discounting (DRD) is an important behavioral process in alcohol use disorders (AUDs), reflecting incapacity to delay gratification. Recent work in neuroeconomics has begun to unravel the neural mechanisms supporting DRD, but applications of neuroeconomics in relation to AUDs have been limited. This study examined the neural mechanisms of DRD preferences in AUDs, with emphasis on dissociating activation patterns based on DRD choice type and level of cognitive conflict. Heavy drinking adult men with (n = 13) and without (n = 12) a diagnosis of an AUD completed a monetary DRD task during a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan. Participant responses were coded based on choice type (impulsive versus restrained) and level of cognitive conflict (easy versus hard). AUD+ participants exhibited significantly more impulsive DRD decision-making. Significant activation during DRD was found in several decision-making regions, including dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), insula, posterior parietal cortex (PPC), and posterior cingulate. An axis of cognitive conflict was also observed, with hard choices associated with anterior cingulate cortex and easy choices associated with activation in supplementary motor area. AUD+ individuals exhibited significant hyperactivity in regions associated with cognitive control (DLPFC) and prospective thought (PPC) and exhibited less task-related deactivation of areas associated with the brain's default network during DRD decisions. This study provides further clarification of the brain systems supporting DRD in general and in relation to AUDs.
Keywords: Alcohol use disorders; delay discounting; neuroeconomics.
© 2012 The Authors, Addiction Biology © 2012 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural correlates of reward magnitude and delay during a probabilistic delay discounting task in alcohol use disorder.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Jan;237(1):263-278. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05364-3. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 31673722 Free PMC article.
-
Neural and behavioral mechanisms of impulsive choice in alcohol use disorder.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011 Jul;35(7):1209-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01455.x. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011. PMID: 21676001 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dissociable neural representations of future reward magnitude and delay during temporal discounting.Neuroimage. 2009 Mar 1;45(1):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.004. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19071223 Free PMC article.
-
The alcoholic brain: neural bases of impaired reward-based decision-making in alcohol use disorders.Neurol Sci. 2018 Mar;39(3):423-435. doi: 10.1007/s10072-017-3205-1. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29188399 Review.
-
The differential neural substrates for reward choice under gain-loss contexts and risk in alcohol use disorder: Evidence from a voxel-based meta-analysis.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023 Jul 1;248:109912. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.109912. Epub 2023 May 4. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023. PMID: 37182355 Review.
Cited by
-
Steep delay discounting and addictive behavior: a meta-analysis of continuous associations.Addiction. 2017 Jan;112(1):51-62. doi: 10.1111/add.13535. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Addiction. 2017. PMID: 27450931 Free PMC article.
-
An Event-Related Potential Study of Decision-Making and Feedback Utilization in Female College Students Who Binge Drink.Front Psychol. 2019 Nov 22;10:2606. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02606. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31824383 Free PMC article.
-
The Behavioral Economics and Neuroeconomics of Alcohol Use Disorders.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Apr;40(4):672-85. doi: 10.1111/acer.13004. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 26993151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot Study of Endurance Runners and Brain Responses Associated with Delay Discounting.Int J Exerc Sci. 2017 Sep 1;10(5):690-701. doi: 10.70252/MSGF8616. eCollection 2017. Int J Exerc Sci. 2017. PMID: 28966709 Free PMC article.
-
Choice impulsivity: Definitions, measurement issues, and clinical implications.Personal Disord. 2015 Apr;6(2):182-98. doi: 10.1037/per0000099. Personal Disord. 2015. PMID: 25867841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker F, Johnson MW, Bickel WK. Delay discounting in current and never-before cigarette smokers: similarities and differences across commodity, sign, and magnitude. J Abnorm Psychol. 2003;112:382–392. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (Methodological) 1995;57:289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

