Pain catastrophizing is associated with dental pain in a stressful context
- PMID: 23232145
- PMCID: PMC4813793
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034512467804
Pain catastrophizing is associated with dental pain in a stressful context
Abstract
Pain is associated with anxiety in a dental setting. It has remained unclear how cognitive-affective factors modulate pain and anxiety in a stressful context, such as receiving dental procedures. We hypothesized that both the situational factor (unpredictability about painful stimuli) and the trait factor (pain catastrophizing, i.e., the tendency to interpret pain in negative orientation) account for dental pain. Fifteen healthy participants were recruited to perform an associative learning task. They were asked to learn the pairing between visual cues and the intensity of incoming painful stimuli delivered at the right upper central incisor. Brain activation associated with pain was recorded by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The participants reported increased anxiety and pain in the stressful context, where stimuli intensity was not predicted by the preceding cue. The score of the Pain Catastrophizing Scale was positively correlated with the increased pain modulated by unpredictability. Brain activation at the right posterior hippocampus, a region critically related to associative learning of aversive stimuli and context, was correlated with the individual catastrophizing level. Our findings suggest that both the situational factor (unpredictability) and the trait factor (catastrophizing) influence dental pain, highlighting the role of cognitive-affective factors in pain control of dental patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

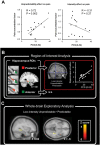
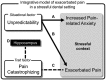
Comment in
-
Interpreting pain as 'catastrophic' makes it worse: the neurological basis.J Dent Res. 2013 Feb;92(2):107-8. doi: 10.1177/0022034512470138. Epub 2012 Dec 11. J Dent Res. 2013. PMID: 23232146 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Armfield JM. (2006). Cognitive vulnerability: a model of the etiology of fear. Clin Psychol Rev 26:746-768. - PubMed
-
- Armfield JM. (2010). Towards a better understanding of dental anxiety and fear: cognitions vs. experiences. Eur J Oral Sci 118:259-264. - PubMed
-
- Asmundson GJ, Norton PJ, Vlaeyen JWS. (2007). Fear-avoidance models of chronic pain: an overview. In: Understanding and treating fear of pain. Asmundson GJ, Vlaeyen JW, Crombez G, editors. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. (1961). An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561-571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

