Clinical development of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment
- PMID: 23232172
- PMCID: PMC3552942
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-10-161
Clinical development of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer treatment
Abstract
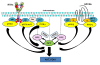
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is commonly deregulated in cancer. In recent years, the results of the first phase I clinical trials with PI3K inhibitors have become available. In comparison to other targeted agents such v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF) inhibitors in melanoma or crizotinib in anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase (ALK) translocated tumors, the number of objective responses to PI3K inhibitors is less dramatic. In this review we propose possible strategies to optimize the clinical development of PI3K inhibitors: by exploring the potential role of PI3K isoform-specific inhibitors in improving the therapeutic index, molecular characterization as a basis for patient selection, and the relevance of performing serial tumor biopsies to understand the associated mechanisms of drug resistance. The main focus of this review will be on PI3K isoform-specific inhibitors by describing the functions of different PI3K isoforms, the preclinical activity of selective PI3K isoform-specific inhibitors and the early clinical data of these compounds.
Figures
References
-
- Falchook GS, Long GV, Kurzrock R, Kim KB, Arkenau TH, Brown MP, Hamid O, Infante JR, Millward M, Pavlick AC, O'Day SJ, Blackman SC, Curtis CM, Lebowitz P, Ma B, Ouellet D, Kefford RF. Dabrafenib in patients with melanoma, untreated brain metastases, and other solid tumours: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 2012;379:1893–1901. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60398-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, Ou SH, Dezube BJ, Janne PA, Costa DB, Varella-Garcia M, Kim WH, Lynch TJ, Fidias P, Stubbs H, Engelman JA, Sequist LV, Tan W, Gandhi L, Mino-Kenudson M, Wei GC, Shreeve SM, Ratain MJ, Settleman J, Christensen JG, Haber DA, Wilner K, Salgia R, Shapiro GI, Clark JW. et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1693–1703. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1006448. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

