Discoidin domain receptor 2 regulates neutrophil chemotaxis in 3D collagen matrices
- PMID: 23233663
- PMCID: PMC3587327
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-451575
Discoidin domain receptor 2 regulates neutrophil chemotaxis in 3D collagen matrices
Abstract
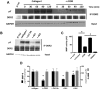
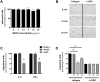
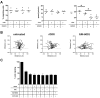
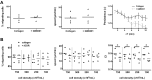
Neutrophils express a variety of collagen receptors at their surface, yet their functional significance remains unclear. Although integrins are essential for neutrophil adhesion and migration on 2-dimensional (2D) surfaces, neutrophils can compensate for the absence of integrins in 3-dimensional (3D) lattices. In contrast, we demonstrate that the inhibition of the tyrosine-kinase collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) has no impact on human primary neutrophil migration on 2D surfaces but is an important regulator of neutrophil chemotaxis in 3D collagen matrices. In this context, we show that DDR2 activation specifically regulates the directional migration of neutrophils in chemoattractant gradients. We further demonstrate that DDR2 regulates directionality through its ability to increase secretion of metalloproteinases and local generation of collagen-derived chemotactic peptide gradients. Our findings highlight the importance of collagen-derived extracellular signaling during neutrophil chemotaxis in 3D matrices.
Figures


Comment in
-
ECM: chemoattraction but not adhesion.Blood. 2013 Feb 28;121(9):1489-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-474221. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23449615
References
-
- Renkawitz J, Schumann K, Weber M, et al. Adaptive force transmission in amoeboid cell migration. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(12):1438–1443. - PubMed
-
- Lammermann T, Bader BL, Monkley SJ, et al. Rapid leukocyte migration by integrin-independent flowing and squeezing. Nature. 2008;453(7191):51–55. - PubMed
-
- Vogel W. Discoidin domain receptors: structural relations and functional implications. FASEB J. 1999;13(Suppl):S77–82. - PubMed
-
- Lemeer S, Bluwstein A, Wu Z, et al. Phosphotyrosine mediated protein interactions of the discoidin domain receptor 1. J Proteomics. 2012;75(12):3465–3477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

