The efficacy of recombinant human activated protein C (rhAPC) vs antithrombin III (at III) vs heparin, in the healing process of partial-thickness burns: a comparative study
- PMID: 23233823
- PMCID: PMC3506209
The efficacy of recombinant human activated protein C (rhAPC) vs antithrombin III (at III) vs heparin, in the healing process of partial-thickness burns: a comparative study
Abstract
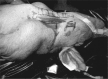
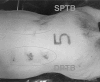
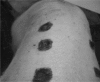
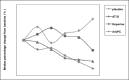
This is an experimental study regarding the positive effect of recombinant human activated protein C (rhAPC) in the healing process of partial-thickness burns, in comparison to antithrombin III and heparin. On a porcine model we induced superficial partial-thickness and deep partial-thickness burns and performed intravenous administration of the elements of study during the first 48 h. The progress of the condition of the injured tissues was evaluated by histopathological examination at specific time intervals. The results showed an improved healing response of the specimens treated with rhAPC compared to those treated with antithrombin III, heparin, and placebo.
Les Auteurs proposent une étude expérimentale sur l’effet positif de la protéine recombinante humaine activée C (PrhAC) dans le processus de la guérison des brûlures d’épaisseur partielle, par rapport à l’antithrombine III et à l’héparine. Sur un modèle porcin ils ont induit des brûlures superficielles d’épaisseur partielle et d’épaisseur profondes. En outre ils ont effectué l’administration intraveineuse des éléments d’étude au cours des 48 premières heures. L’évolution de l’état des tissus lésés a été évaluée par un examen histopathologique à intervalles de temps spécifiques. Les résultats ont montré que les échantillons traités avec PrhAC manifestaient une guérison supérieure par rapport aux échantillons traités avec l’antithrombine III, l’héparine et le placebo.
Keywords: burns; healing; recombinant human activated protein C (rhAPC).
Figures












References
-
- Regas FC, Erlich HP. Elucidating the vascular response to burns with a new rat model. J Trauma. 1992;32:557. - PubMed
-
- Cetinkale O, Demir M, Sayman HB, et al. Effects of allopurinol, ibuprofen and cyclosporine A on local microcirculatory disturbance due to burn injuries. Burns. 1997;23:43. - PubMed
-
- Bucky LP, Vedder NB, Hong HZ, et al. Reduction of burn injury by inhibiting CD 18-mediated leukocyte adherence in rabbits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93:1473. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto I, Nakanishi H, Shono Y, et al. The features of thrombus in a microvessel injury model and the antithrombotic efficacy of heparin, urokinase and prostaglandin E1. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111:2307–14. - PubMed
-
- Danielson P, Nilsson L, Nettelbland H. Is there a need for antithrombin III substitution early after burn injury? Burns. 1997;23:300–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
