Elevated Salivary Levels of Oxytocin Persist More than 7 h after Intranasal Administration
- PMID: 23233832
- PMCID: PMC3516702
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00174
Elevated Salivary Levels of Oxytocin Persist More than 7 h after Intranasal Administration
Abstract
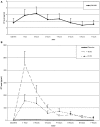
We addressed the question how long salivary oxytocin levels remain elevated after intranasal administration, and whether it makes a difference when 16 or 24 IU of oxytocin administration is used. Oxytocin levels were measured in saliva samples collected from 46 female participants right before intranasal administration (at 9:30 a.m.) of 16 IU (n = 18) or 24 IU (n = 10) of oxytocin, or a placebo (n = 18), and each hour after administration, for 7 h in total. Oxytocin levels did not differ among conditions before use of the nasal spray. Salivary oxytocin levels in the placebo group showed high stability across the day. After oxytocin administration oxytocin levels markedly increased, they peaked around 1 h after administration, and were still significantly elevated 7 h after administration. The amount of oxytocin (16 or 24 IU) did not make a difference for oxytocin levels. The increase of oxytocin levels for at least 7 h shows how effective intranasal administration of oxytocin is. Our findings may raise ethical questions about potentially persisting behavioral effects after participants have left the lab setting. More research into the long-term neurological and behavioral effects of sniffs of oxytocin is urgently needed.
Keywords: 16 IU; behavioral effects; daily oxytocin curve; ethics; healthy female volunteers; intranasal administration; oxytocin; saliva.
Figures
References
-
- Bartz J. A., Zaki J., Bolger N., Ochsner K. N. (2011). Social effects of oxytocin in humans: context and person matter. Trends Cogn. Sci. (Regul. Ed.) 15, 301–309 - PubMed
-
- Cardoso C., Ellenbogen M. A., Orlando M. A., Bacon S. L., Joober R. (2012). Intranasal oxytocin attenuates the cortisol response to physical stress: a dose–response study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. Advance online publication: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.07.013 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous