Accelerated disease onset with stabilized familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-linked mutant TDP-43 proteins
- PMID: 23235148
- PMCID: PMC3561582
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433615
Accelerated disease onset with stabilized familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-linked mutant TDP-43 proteins
Abstract
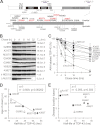
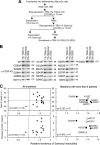
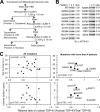
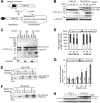
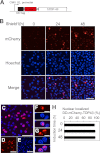
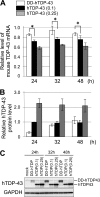
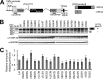
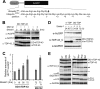
Abnormal protein accumulation is a pathological hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, including accumulation of TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Dominant mutations in the TDP-43 gene are causative for familial ALS; however, the relationship between mutant protein biochemical phenotypes and disease course and their significance to disease pathomechanism are not known. Here, we found that longer half-lives of mutant proteins correlated with accelerated disease onset. Based on our findings, we established a cell model in which chronic stabilization of wild-type TDP-43 protein provoked cytotoxicity and recapitulated pathogenic protein cleavage and insolubility to the detergent Sarkosyl, TDP-43 properties that have been observed in sporadic ALS lesions. Furthermore, these cells showed proteasomal impairment and dysregulation of their own mRNA levels. These results suggest that chronically increased stability of mutant or wild-type TDP-43 proteins results in a gain of toxicity through abnormal proteostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Biochemical abnormality of mutant TDP-43 protein].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014;54(12):1148-50. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.54.1148. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014. PMID: 25519967 Review. Japanese.
-
Pathological Modification of TDP-43 in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with SOD1 Mutations.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Mar;56(3):2007-2021. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1218-2. Epub 2018 Jul 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29982983 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of ALS-associated p.M337V human TDP-43 in mice worsens disease features compared to wild-type human TDP-43 mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;48(1):22-35. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8427-5. Epub 2013 Mar 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23475610 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in TDP-43 link glycine-rich domain functions to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Oct 15;18(R2):R156-62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp303. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19808791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PABPN1 suppresses TDP-43 toxicity in ALS disease models.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Sep 15;24(18):5154-73. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv238. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26130692 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protein quality control system in neurodegeneration: a healing company hard to beat but failure is fatal.Mol Neurobiol. 2013 Aug;48(1):141-56. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8411-0. Epub 2013 Feb 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23378031 Review.
-
TDP-43-The key to understanding amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Rare Dis. 2014 Oct 30;2(1):e944443. doi: 10.4161/21675511.2014.944443. eCollection 2014. Rare Dis. 2014. PMID: 26942097 Free PMC article.
-
TDP-43 stabilises the processing intermediates of mitochondrial transcripts.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 9;7(1):7709. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06953-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28794432 Free PMC article.
-
Frontotemporal dementia-linked P112H mutation of TDP-43 induces protein structural change and impairs its RNA binding function.Protein Sci. 2021 Feb;30(2):350-365. doi: 10.1002/pro.3990. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33151007 Free PMC article.
-
Functional implication of ubiquitinating and deubiquitinating mechanisms in TDP-43 proteinopathies.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 9;10:931968. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.931968. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36158183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neumann M., Sampathu D. M., Kwong L. K., Truax A. C., Micsenyi M. C., Chou T. T., Bruce J., Schuck T., Grossman M., Clark C. M., McCluskey L. F., Miller B. L., Masliah E., Mackenzie I. R., Feldman H., Feiden W., Kretzschmar H. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133 - PubMed
-
- Arai T., Hasegawa M., Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Nonaka T., Mori H., Mann D., Tsuchiya K., Yoshida M., Hashizume Y., Oda T. (2006) TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

