Uric acid-induced endothelial dysfunction is associated with mitochondrial alterations and decreased intracellular ATP concentrations
- PMID: 23235493
- PMCID: PMC3656428
- DOI: 10.1159/000345509
Uric acid-induced endothelial dysfunction is associated with mitochondrial alterations and decreased intracellular ATP concentrations
Abstract
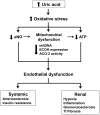
Background/aims: Endothelial dysfunction is associated with mitochondrial alterations. We hypothesized that uric acid (UA), which can induce endothelial dysfunction in vitro and in vivo, might also alter mitochondrial function.
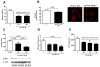
Methods: Human aortic endothelial cells were exposed to soluble UA and measurements of oxidative stress, nitric oxide, mitochondrial density, ATP production, aconitase-2 and enoyl Co-A hydratase-1 expressions, and aconitase-2 activity in isolated mitochondria were determined. The effect of hyperuricemia induced by uricase inhibition in rats on renal mitochondrial integrity was also assessed.
Results: UA-induced endothelial dysfunction was associated with reduced mitochondrial mass and ATP production. UA also decreased aconitase-2 activity and lowered enoyl CoA hydratase-1 expression. Hyperuricemic rats showed increased mitDNA damage in association with higher levels of intrarenal UA and oxidative stress.
Conclusions: UA-induced endothelial dysfunction is associated with mitochondrial alterations and decreased intracellular ATP. These studies provide additional evidence for a deleterious effect of UA on vascular function that could be important in the pathogenesis of hypertension and vascular disease.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Johnson has a patent with the University of Washington for allopurinol in the treatment of hypertension (7,799,794) and has patent applications with the University of Florida and with the University of Colorado for UA-lowering therapy and or treatments to block fructose metabolism in the treatment of metabolic syndrome or diabetic nephropathy.
Figures


References
-
- Khosla UM, Zharikov S, Finch JL, Nakagawa T, Roncal C, Mu W, Krotova K, Block ER, Prabhakar S, Johnson RJ. Hyperuricemia induces endothelial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1739–1742. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T, Hu H, Zharikov S, Tuttle KR, Short RA, Glushakova O, Ouyang X, Feig DI, Block ER, Herrera-Acosta J, et al. A causal role for uric acid in fructose-induced metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:F625–631. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

