Serenoa repens for benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 23235581
- PMCID: PMC7084061
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001423.pub3
Serenoa repens for benign prostatic hyperplasia
Update in
-
Serenoa repens for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic enlargement.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 22;6(6):CD001423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001423.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37345871 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a nonmalignant enlargement of the prostate, which can lead to obstructive and irritative lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). The pharmacologic use of plants and herbs (phytotherapy) for the treatment of LUTS associated with BPH is common. The extract of the berry of the American saw palmetto, or dwarf palm plant, Serenoa repens (SR), which is also known by its botanical name of Sabal serrulatum, is one of several phytotherapeutic agents available for the treatment of BPH.
Objectives: This systematic review aimed to assess the effects and harms of Serenoa repens in the treatment of men with LUTS consistent with BPH.
Search methods: We searched for trials in general and in specialized databases, including the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE®, EMBASE, CINAHL®, Web of Science, SCOPUS, BIOSIS Previews®, LILACS, ClinicalTrials.gov, Controlled-Trials.com, World Health Organization (WHO), and Google Scholar. We also handsearched systematic reviews, references, and clinical practice guidelines. There were no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: Trials were eligible if they randomized men with symptomatic BPH to receive preparations of SR (alone or in combination) for at least four weeks in comparison with placebo or other interventions, and included clinical outcomes, such as urologic symptom scales, symptoms, and urodynamic measurements. Eligibility was assessed by at least two independent observers (JT, RM).
Data collection and analysis: One review author (JT) extracted Information on patients, interventions, and outcomes which was then checked by another review author (RM). The main outcome measure for comparing the effectiveness of SR with active or inert controls was change in urologic symptom-scale scores, with validated scores taking precedence over non validated ones. Secondary outcomes included changes in nocturia and urodynamic measures. The main outcome measure for harms was the number of men reporting side effects.
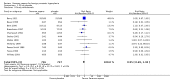
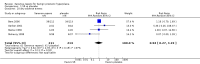
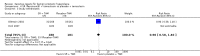
Main results: In a meta-analysis of two high quality long-term trials (n = 582), Serenoa repens therapy was not superior to placebo in reducing LUTS based on the AUA (mean difference (MD) 0.25 points, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.58 to 1.07). A 72 week trial with high quality evidence, using the American Urological Association Symptom Score Index, reported that SR was not superior to placebo at double and triple doses. In the same trial the proportions of clinical responders (≥ three-point improvement) were nearly identical (42.6% and 44.2% for SR and placebo, respectively), and not significant (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.22).This update, which did not change our previous conclusions, included two new trials with 444 additional men, an 8.5% (5666/5222) increase from our 2009 updated review, and a 28.8% (1988/1544) increase for our main comparison, SR monotherapy versus placebo control (17 trials). Overall, 5666 men were assessed from 32 randomized, controlled trials, with trial lengths from four to 72 weeks. Twenty-seven trials were double blinded and treatment allocation concealment was adequate in 14.In a trial of high quality evidence (N = 369), versus placebo, SR did not significantly decrease nightly urination on the AUA Nocturia scale (range zero to five) at 72 weeks follow-up (one-sided P = 0.19).The three high quality, moderate-to-long term trials found peak urine flow was not improved with Serenoa repens compared with placebo (MD 0.40 mL/s, 95% CI -0.30 to 1.09).Comparing prostate size (mean change from baseline), one high quality 12-month trial (N = 225) reported no significant difference between SR and placebo (MD -1.22 cc, 95% CI -3.91 to 1.47).
Authors' conclusions: Serenoa repens, at double and triple doses, did not improve urinary flow measures or prostate size in men with lower urinary tract symptoms consistent with BPH.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
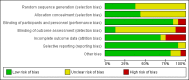
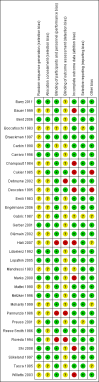


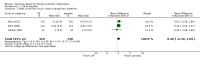


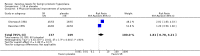









Update of
-
Serenoa repens for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;(2):CD001423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001423.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD001423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001423.pub3. PMID: 19370565 Free PMC article. Updated.
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club: review: Serenoa repens does not improve symptom scale scores in benign prostatic hyperplasia.Ann Intern Med. 2013 Apr 16;158(8):JC10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-158-8-201304160-02010. Ann Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23588763 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Barry 2011 {published data only}
-
- Barry MJ, Meleth S, Lee JY, Kreder KJ, Avins AL, Nickel JC, et al. Effect of increasing doses of Saw palmetto extract on lower urinary tract symptoms. JAMA 2011;306(12):1344‐51. [clinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT00603304] - PMC - PubMed
Bauer 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bauer HW. Casarosa C. Cosci M. Fratta M. Bleβmann G. Saw palmetto fruit extract for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Results of a placebo‐controlled double‐blind study [Behandlung der benignen Prostatahyperplasie mit Sabalfrucht‐Extrakt: Wirksamkeit und Verträglichkeit ‐ Ergebnisse einer plazebokontrollierten Doppelblindstudie]. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 1999;141(25):127‐32. - PubMed
Bent 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bent S, Kane C, Shinohara K, Neuhaus J, Hudes E, Goldberg H, et al. Saw palmetto for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(6):557‐66. - PubMed
Boccafoschi 1983 {published data only}
-
- Boccafoschi C, Annoscia S. Serenoa repens extract and placebo in prostatic benign hyperplasia: clinical results [Confronto fra estratto di serenoa repens e placebo mediate prova clinica controllata in pazienti con adenomatosi prostatica]. Urologia 1983;50:1257‐68.
Braeckman 1997 {published data only}
-
- Braeckman J. The extract of Serenoa repens in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a multicenter open study. Current Therapeutic Research 1994;55(7):776‐85.
-
- Braeckman J, Bruhwyler J, Vanderkerckhove K, Géczy J. Efficacy and safety of the extract of Serenoa repens in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: therapeutic equivalence between twice and once daily dosage forms. Phytotherapy Research 1997;1:558‐63.
-
- Braeckman J, Denis L, Leval J, Keuppens F, Cornet A, De Bruyne, et al. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the plant extract Serenoa repens in the treatment of benign hyperplasia of the prostate. European Journal of Clinical Research 1997;9:247‐59.
Carbin 1990 {published data only}
-
- Carbin BE, Larsson B, Lindahl O. Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with phytosterols. British Journal of Urology 1990;66(6):639‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Carraro 1996 {published data only}
-
- Carraro JC, Raynaud JP, Koch G, Chisholm GD, Silverio F, Teillac P, et al. Comparison of phytotherapy (Permixon) with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia: a randomized international study of 1,098 patients. The Prostate 1996;29(4):231‐40. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Champault 1984 {published data only}
Cukier 1985 {published data only}
-
- Cukier J, Ducassou J, Guillou M, Leriche A, Lobel B, Toubol J. [Permixon versus placebo; resultats d'une étude multicentrique]. Comptes Rendus de Therapeutique et de Pharmacologie Clinique 1985;4:15‐21.
Debruyne 2002 {published data only}
-
- Debruyne F, Boyle P, Calais Da Silva F, Gillenwater JG, Hamdy FC, Perrin P, et al. Evaluation of the clinical benefit of Permixon and tamsulosin in severe BPH patients‐‐PERMAL study subset analysis [Evaluation du benefice clinique de Permixon® et de la tamsulosine dans le traitement de l'hypertrophie bénigne de la prostate (HBP) sévére: Analyse d'une sous‐groupe de l'étude Permal]. European Urology 2004;45:773‐80. - PubMed
-
- Debruyne F, Koch G, Silva FC, Gillenwater JG, Hamdy FC, Perrin P, et al. Comparison of a phytotherapeutic agent (Permixon®) with an a‐blocker (tamsulosin) in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a 1‐year randomized international study [Comparaison d'un produit de phytothérapie (Permixon®) et d'un alpha‐bloquant (tamsulosine) dans le traitement de l'hypertrophie bénigne de la prostate: étude internationale randomisée d'une durée de 12 mois]. Progrès en Urologie 2002;41:497‐507. - PubMed
Descotes 1995 {published data only}
-
- Descotes JL, Rambeaud JJ, Deschaseaux P, Faure G. Placebo‐controlled evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of Permixon® in benign prostatic hyperplasia after the exclusion of placebo responders. Clinical Drug Investigation 1995;5:291‐7.
Emili 1983 {published data only}
-
- Emili E, Lo Cigno M, Petrone U. [Risultati clinici su un nuovo farmaco nella terapia dell'ipertofia della prostata (Permixon)]. Urologia 1983;50:1042‐8.
Engelmann 2006 {published data only}
-
- Engelmann U, Walther C, Bondarenko B, Funk P, Schläfke S. Efficacy and safety of a combination of sabal and urtica extract in lower urinary tract symptoms. A randomized, double‐blind study versus tamsulosin. Arzneimittel‐Forschung 2006;56(3):222‐9. - PubMed
Gabric 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gabric V, Miskic H. [Behandlung des benignen prostata‐adenoms und der chronischen prostatatitis]. Therapiewoche 1987;37:1775‐88.
Gerber 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gerber GS, Kuznetsov D, Johnson BC, Burstein JD. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of saw palmetto in men with lower urinary tract symptoms. Urology 2001;58(6):960‐4. - PubMed
Glémain 2002 {published data only}
-
- Glémain P, Coulange C, Billebaud T, Gattegno B, Muszynski R, Loeb G, et al. Tamsulosin with or without Serenoa repens in benign prostatic hyperplasia: the OCOS trial [Tamsulosine avec ou sans Serenoa repens dans l'hypertrophie bénigne de la prostate: l'essai OCOS]. Progrès en Urologie 2002;12:395‐403. - PubMed
Hizli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hizli F, Uygur MC. A prospective study of the efficacy of Serenoa repens, tamsulosin, and Serenoa repens plus tamsulosin treatment for patients with benign prostate hyperplasia. International Urology and Nephrology 2007;39:879‐86. - PubMed
Löbelenz 1992 {published data only}
-
- Löbelenz J. [Extractum Sabal fructus bei benigner prostatahyperplasie (BPH). klinische prufung im stadium I und II]. Therapeutikon 1992;6(1‐2):34‐7.
Lopatkin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lopatkin N, Sivkov A, Walther C, Schläfke S, Medvedev A, Avdeichuk J, et al. Combined extract of sabal palm and nettle in the treatment of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms in the double blind, placebo‐controlled trial. World Journal of Urology 2005;23(2):139‐46. - PubMed
Mandressi 1983 {published data only}
-
- Mandressi S, Tarallo U, Maggioni A, Tombolini P, Rocco F, Quadraccia. Medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: efficacy of the extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon®) compared to that of the extract of Pygeum africanum and a placebo [Terapia medica dell'adenoma prostatico: confronto della efficacia dell'estratto di serenoa repens (Permixon®) versus l'estratto di pigeum africanum e placebo]. Urologia 1983;50(4):752‐8.
Marks 2000 {published data only}
-
- Marks LS, Partin AW, Epstein JI, Tyler VE, Simon I, Macairan ML, et al. Effects of a saw palmetto herbal blend in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Journal of Urology 2000;163(5):1451‐6. - PubMed
Mattei 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mattei FM, Capone M, Acconcia A. [Medikamentose therapie der benignen prostatahyperplasie mit einem extrakt der sagepalme]. TW Urologie Nephrologie 1990;2:346‐50.
Metzker 1996 {published data only}
-
- Metzker H, Kieser M, Holscher U. [Wirksamkeit eines Sabal‐Urtica‐kombinationspraparates bei der behandlung der benignen prostatahyperplasie (BPH)]. Der Urologe B 1996;36(4):292‐300.
Mohanty 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mohanty NK, Jha RJ, Dutt C. Randomized double‐blind controlled clinical trial of Serenoa repens versus placebo in the management of patients with symptomatic Grade I to Grade II benign prostatic hyperplasia (PBH). Indian Journal of Urology 1999;16(1):26‐31.
Pannunzio 1986 {published data only}
-
- Pannunzio E, D’Ascenzo R, Giardinetti F, Civili P, Persichelli E. [Serenoa repens vs. gestonorone caproato nel trattamento dell’ipertofia prostatica benigna: Studio randomizzato]. Urologia 1986;53(5):696‐705.
Preuss 2001 {published data only}
-
- Preuss HG, Marcusen C, Regan J, Klimberg IW, Welebir TA, Jones WA. Randomized trial of a combination of natural products (Cernitin, saw palmetto, ß‐sitosterol, vitamin E) on symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). International Urology and Nephrology 2001;33:217‐25. - PubMed
Reece Smith 1986 {published data only}
-
- Reece Smith H, Memon A, Smart CJ, Dewbury K. The value of Permixon in benign prostatic hypertrophy. British Journal of Urology 1986;58:36‐40. - PubMed
Roveda 1994 {published data only}
-
- Roveda S, Colombo P. Clinical controlled trial on therapeutical bioequivalence and tolerability of Serenoa repens oral capsules 160 mg or rectal capsules 640 mg [Sperimentazione clinica controllata sulla bioequivalenza terapeutica e sulla tollerabilita dei prodotti a base di Serenoa repens in capsule da 160 mg o capsule rettali da 640 mg]. Archivio di Medicina Interna 1994;46(2):61‐75.
Shi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Shi R, Xie Q, Gang X, Lun J, Life C, Pantuck A, et al. Effect of saw palmetto soft gel capsule on lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a randomized trial in Shanghai, China. The Journal of Urology 2008;179:610‐5. - PubMed
Sökeland 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sökeland J. Combined sabal and urtica extract compared with finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of prostate volume and therapeutic outcome. British Journal of Urology International 2000;86:439‐42. - PubMed
-
- Sökeland J, Albrecht J. Combined sabal and urtica extract compared with finasteride in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of prostate volume and therapeutic outcome [Kombination aus Sabal‐ und Urticaestrakt vs. finasterid bei BPH (Stad. I bis II nach Alken); Vergleich der therapeutischen wirksamkeit in einer einjahrigen doppelblindstudie]. Urologe A 1997;36(4):327‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tasca 1985 {published data only}
-
- Tasca A, Barulli M, Cavazzana A, Zattoni F, Artibani W, Pagano F. Treatment of obstructive symptomatology caused by prostatic adenoma with an extract of Serenoa repens. Double‐blind clinical study vs placebo [Trattamento della sintomatologia ostruttiva da adenoma prostatico con estratto di Serenoa repens. Studio clinico in doppio cieco vs. placebo]. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica 1985;37:87‐91. [PUBMED: 2413558] - PubMed
Willetts 2003 {published data only}
-
- Willetts KE, Clements MS, Champion S, Ehsman S, Eden JA. Serenoa repens extract for benign prostate hyperplasia: a randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Urology International 2003;92:267‐70. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adriazola Semino 1992 {published data only}
-
- Adriazola Semino M, Lozano Ortega JL, Garcia Cobo E, Tejeda Banez E, Romero Rodriguez F. Symptomatic treatment of benign hypertrophy of the prostate. Comparative study of prazosin and Serenoa repens [Tratamiento sintomatico de la hipertrofia benigna de prostata. Estudio comparativo entre prazosin y Serenoa repens]. Archivos Espanoles de Urologia 1992;45(3):211‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Aliaev 2009 {published data only}
-
- Aliaev IG, Apolikhin OI, Mazo EB, Vinarov AZ, Lokshin KL, Medvedev AA, et al. Efficacy and safety of prostamol‐Uno in patients with chronic abacterial prostatitis [article in Russian] [ЭФФЕКТИВНОСТЬ И БЕЗОПАСНОСТЬ ПРОСТАМОЛА‐УНО У БОЛЬНЫХ ХРОНИЧЕСКИМ АБАКТЕРИАЛЬНЫМ ПРОСТАТИТОМ]. Urologiia 2006;1:47‐50. - PubMed
Al‐Shukri 2000 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Shukri SH, Deschaseaux P, Kuzmin IV. Early urodynamic effects of the lipido‐sterolic extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon®) in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases 2000;3:195‐9. - PubMed
Authié 1987 {published data only}
-
- Authié D, Cauquil J. [Appréciation de l'efficacité de Permixon en pratique quotidienne: étude multicentrique]. Comptes Rendus de Thérapeutique et de Pharmacologie Clinique 1987;5(56):4‐13.
Comar 1986 {published data only}
-
- Comar OB, Rienzo A. Mepartricin versus Serenoa repens: double‐blind study in 20 cases of benign prostate hypertrophy. Rivista Italiana di Biologia e Medicina 1986;6(2):122‐5.
Di Silverio 1992 {published data only}
-
- Siverio F, D'Eramo G, Lubrano C, Flammia GP, Sciarra A, Palma E, et al. Evidence that Serenoa repens extract displays an antiestrogenic activity in prostatic tissue of benign prostatic hypertrophy patients. European Urology 1992;21(4):309‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gerber 1998 {published data only}
-
- Gerber GS, Zagaja GP, Bales GT, Chodak GW, Contreras BA. Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens) in men with lower urinary tract symptoms: effects on urodynamic parameters and voiding symptoms. Urology 1998;51(6):1003‐7. - PubMed
Giannakopoulos 2002 {published data only}
-
- Giannakopoulos X, Baltogiannis D, Giannakis D, Tasos A, Sofikitis N, Charalabopoulos K, et al. The lipidosterolic extract of Serenoa repens in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a comparison of two dosage regimens. Advances in Natural Therapy 2002;19(2):285‐96. - PubMed
Grasso 1995 {published data only}
-
- Grasso M, Montesano A, Buonaguidi A, Castelli M, Lania C, Rigatti P, et al. Comparative effects of alfuzosin versus Serenoa repens in the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Archivos Españoles de Urología 1995;48(1):97‐103. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pavone 2010 {published data only}
-
- Pavone C, Abbadessa D, Taraintino ML, Oxenius I, Laganà A, Lupo A, et al. [Associazione di Serenoa repens, Urtica dioica e Pinus pinaster. Sicurezza ed efficacia nel trattamento dei sintomi del basso tratto ruinario. Studio prospettico su 320 pazienti]. Urologia 2010;77(1):43‐51. - PubMed
Pecoraro 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pecoraro S, Annecchiarico A, Gambardella M‐C, Sepe G. Efficacy of pretreatment with Serenoa repens on bleeding associated with transurethral resection of prostate [Effetto del pretrattamento con serenoa repens sul sanguinamento associato a resezione transuretrale della prostata]. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica 2004;56:73‐8. - PubMed
Popa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Popa G, Hägele‐Kaddour H, Walther C. [Symptomatische wirksamkeit eines sabal‐urtica‐kombinationspräparats in der therapie des benignen prostatasyndroms: ergebnisse einer plazebokontrollierten doppelblindstudie]. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 2005;147(Supp 3):103‐8. - PubMed
Sinescu 2011 {published data only}
Sivkov 2001 {published data only}
-
- Sivkov A, Köhler S, Engelmann U, Medvedev A, Lopatkin N. Long‐term efficacy and safety of a combination of sabal and urtica extracts in LUTS ‐ a placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, multicenter trial. Urologe A 2001;40(Suppl 1):S19.
Stepanov 1999 {published data only}
-
- Stepanov VN, Siniakova LA, Sarrazin B, Raynaud JP. Efficacy and tolerability of the lipidosterolic extract of Serenoa repens (Permixon®) in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a double‐blind comparison of two dosage regimens. Advances in Therapy 1999;16(5):231‐41. - PubMed
Strauch 1994 {published data only}
-
- Strauch G, Perles P, Vergult G, Gabriel M, Gibelin B, Cummings S, et al. Comparison of finasteride (Proscar®) and Serenoa repens (Permixon®) in the inhibition of 5‐alpha reductase in healthy male volunteers. European Urology 1994;26(3):247‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vela‐Navarrete 2003 {published data only}
-
- Vela‐Navarrete R, Garcia Cardoso JV, Barat A, Manzarbeitia F, Lopez Farre A. BPH and inflammation: pharmacological effects of Permixon on histological and molecular inflammatory markers. Results of a double blind pilot clinical assay. European Urology 2003;44:549‐55. - PubMed
Vela‐Navarrete 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vela‐Navarrete R, Escribano‐Burgos M, Lopez Farre A, Garcia‐Cardoso J, Manzarbeitia F, Carrasco C. Serenoa repens treatment modifies BAX/BCL‐2 index expression and CASPASE‐3 activity in prostatic tissue from patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Journal of Urology 2005;173:507‐10. - PubMed
Veltri 2002 {published data only}
-
- Veltri RW, Marks LS, Miller CM, Bales WD, Fan J, MacAiran ML, et al. Saw palmetto alters nuclear measurements reflecting DNA content in men with symptomatic BPH: evidence for a possible molecular mechanism. Urology 2002;60:617‐22. [PUBMED: 12385921] - PubMed
Vinarov 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vinarov AZ, Aliaev IuG, Apolikhin OI, Mazo EB, Darenkov SP, Demidko IuL, et al. Results of three‐year clinical study of prostamol Uno efficacy and safety in patients with initial symptoms of prostatic adenoma and risk of its progression [Russian]. Urologiia 2010;6:3‐10. [21433319] - PubMed
Weisser 1997 {published data only}
-
- Weissser H, Behnke, Helpap B, Bach D, Krieg M. Enzyme activities in tissue of human benign prostatic hyperplasia after three months' treatment with the Sabal serrulata extract IDS 89 (Strogen) or placebo. European Urology 1997;31(1):97‐101. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Abrams 1979
-
- Abrams PH, Griffiths DJ. The assessment of prostatic obstruction from urodynamic measurements and from residual urine. British Journal of Urology 1979;51(2):129‐34. - PubMed
Bales 1999
-
- Bales G, Christiano AP, Kirsh E, Gerber GS. Phytotherapeutic agents in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms: a demographic analysis of awareness and use at the University of Chicago. Urology 1999;54:86‐9. - PubMed
Barnes 2002
-
- Barnes PM, Powell‐Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults: United States, 2002. Advance data from vital and health statistics of the National Center for Health Statistics 2004;27(343):1‐19. - PubMed
Berry 1984
-
- Berry SL, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, Ewing LL. The development of human benign prostatic hyperplasia with age. The Journal of Urology 1984;132:474‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boyle 2004
-
- Boyle P, Robertson C, Lowe F, Roehrborn C. Updated meta‐analysis of clinical trials of Serenoa repens extract in the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. British Journal of Urology International 2004;93(6):751‐6. - PubMed
Buck 1996
-
- Buck AC. Phytotherapy for the prostate. British Journal of Urology 1996;78(3):325‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Buck 2004
-
- Buck AC. Is there a scientific basis for the therapeutic effects of Serenoa repens in benign prostatic hyperplasia? Mechanisms of action. The Journal of Urology 2004;172:1792. - PubMed
Campbell‐Walsh Urology 2010
-
- Roehrborn CG. Chapter 92 ‐ Benign prostatic hyperplasia: etiology, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and natural history. In: Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA editor(s). Campbell‐Walsh Urology. 10th Edition. Vol. 3, Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2010.
Christensen 1990
-
- Christensen MM, Bruskewitz RC. Clinical manifestations of benign prostatic hyperplasia and the indications for therapeutic intervention. Urology Clinics of North America 1990;17:509‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cochrane Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Stern JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In:Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration (Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org (accessed 4 March 2011) 2011.
Dedhia 2008
-
- Dedhia RC, McVary KT. Phytotherapy for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Journal of Urology 2008;179:2119‐25. - PubMed
Di Silverio 1993
-
- Silverio F, Flammia GP, Sciarra A, Caponera M, Mauro M, Buscarini M, et al. Plant extracts in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Minerva Urologica e Nefrologica 1993;45:143‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dickersin 1994
Dreikorn 1990
-
- Dreikorn K, Richter R, Schönhöfer PS. Conservative nonhormonal treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urologe A 1990;29(1):8‐16. [PUBMED: 1690486] - PubMed
GRADEPro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows., 2008.
Habib 2004
-
- Habib FK, Wyllie MG. Not all brands are created equal: a comparison of selected components of different brands of Serenoa repens extract. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases 2004;7:195‐200. - PubMed
Lavori 1992
-
- Lavori PW. Clinical trials in psychiatry: should protocol deviation censor patient data?. Neuropsychopharmacology 1992;6:39‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lepor 1996
-
- Lepor H, Williford WO, Barry MJ, Brawer MK, Dixon CM, Gormley G, et al. The efficacy of terazosin and finasteride, or both in benign prostatic hyperplasia. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;335:533‐9. - PubMed
Lowe 1996
-
- Lowe FC Ku JC. Phytotherapy in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a critical review. Urology 1996;48:12‐20. - PubMed
Maccagnano 2006
-
- Maccagnano C, Salonia A, Briganti A, Teillac P, Schulman C, Montorsi F, et al. A critical analysis of Permixon™ in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic enlargement. European Urology 2006;5 suppl:430‐40.
Marwick 1995
-
- Marwick C. Growing use of medicinal botanicals forces assessment by drug regulators. JAMA 1995;273:607‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
McConnell 1994
-
- McConnell JD, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: diagnosis and treatment. Agency for Health Care Policy and Research. Clinical practice guideline. Quick reference guide for clinicians 1994;8:1‐17. [PUBMED: 7507389] - PubMed
McConnell 2003
-
- McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole GL Jr, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. The long‐term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;349:2387‐98. - PubMed
McGuire 1987
-
- McGuire E. Detrusor response to obstruction. NIH Publication No. 87‐2881 1987; Vol. 221.
Meigs 2001
-
- Meigs JB, Mohr B, Barry MJ, Collins MM, McKinlay JB. Risk factors for clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia in a community‐based population of healthy aging men. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2001;54:935‐44. - PubMed
Platz 2002
-
- Platz EA, Smit E, Curhan GC, Nyberg Jr LM, Giovannucci E. Prevalence of and racial/ethnic variation in lower urinary tract symptoms and noncancer prostate surgery in US men. Urology 2002;59:877‐83. - PubMed
Roehrborn 2001
-
- Roehrborn CG, Malice M‐P, Cook TJ, Girman CJ. Clinical predictors of spontaneous acute urinary retention in men with LUTS and clinical BPHL a comprehensive analysis of the pooled placebo groups of several large studies. Urology 2001;58:210‐6. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Urologic Diseases in American 2007
-
- Wei JT, Calhoun EA, Jacobsen SJ. Chapter 2, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. In: Litwin MS, Saigal CS editor(s). Urologic Diseases in America. Washington, DC: US Government Publishing Office, 2007:45‐69. [NIH Publication No. 07‐5512]
Vacherot 2000
-
- Vacherot F, Azzouz M, Gil‐Diez‐de‐Medina S, Colombel M, Taille A, Lefrere Belda MA, et al. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by the lipido‐sterolic extract of Serenoa repens (LSESr, Permixon®) in benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Prostate 2000;45:507. - PubMed
Weisser 1996
-
- Weisser H, Tunn S, Behnke B, Krieg M. Effects of the sabal serrulata extract IDS 89 and its subfractions on 5 alpha‐reductase activity in human benign prostatic hyperplasia. The Prostate 1996;28:300. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Tacklind 2009
Wilt 2000
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

