Drugs for nocturnal enuresis in children (other than desmopressin and tricyclics)
- PMID: 23235587
- PMCID: PMC7100585
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002238.pub2
Drugs for nocturnal enuresis in children (other than desmopressin and tricyclics)
Abstract
Background: Enuresis (bedwetting) is a socially stigmatising and stressful condition which affects around 15% to 20% of five-year olds and up to 2% of young adults. Although there is a high rate of spontaneous remission, the social, emotional and psychological costs to the children can be great. Drugs (including desmopressin, tricyclics and other drugs) have often been tried to treat nocturnal enuresis.
Objectives: To assess the effects of drugs other than desmopressin and tricyclics on nocturnal enuresis in children and to compare them with other interventions.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register of trials (searched 15 December 2011), which includes searches of MEDLINE and CENTRAL, to identify published and unpublished randomised and quasi-randomised trials. The reference lists of relevant articles were also searched.
Selection criteria: All randomised trials of drugs (excluding desmopressin or tricyclics) for treating nocturnal enuresis in children up to the age of 16 years were included in the review. Trials were eligible for inclusion if children were randomised to receive drugs compared with placebo, other drugs or behavioral interventions for nocturnal enuresis. Studies which included children with daytime urinary incontinence or children with organic conditions were also included in this review if the focus of the study was on nocturnal enuresis. Trials focused solely on daytime wetting and trials of adults with nocturnal enuresis were excluded.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed the quality of the eligible trials and extracted data. Differences between review authors were settled by discussion with a third review author.
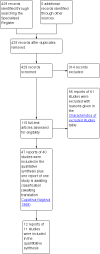
Main results: A total of 40 randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials (10 new in this update) met the inclusion criteria, with a total of 1780 out of 2440 children who enrolled receiving an active drug other than desmopressin or a tricyclic. In all, 31 different drugs or classes of drugs were tested. The trials were generally small or of poor methodological quality. There was an overall paucity of data regarding outcomes after treatment was withdrawn.For drugs versus placebo, when compared to placebo indomethacin (risk ratio [RR] 0.36, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.79), diazepam (RR 0.22, 95% CI 0.11 to 0.46), mestorelone (RR 0.32, 95% CI 0.17 to 0.62) and atomoxetine (RR 0.81, 95% CI 0.70 to 0.94) appeared to reduce the number of children failing to have 14 consecutive dry nights. Although indomethacin and diclofenac were better than placebo during treatment, they were not as effective as desmopressin and there was a higher chance of adverse effects. None of the medications were effective in reducing relapse rates, although this was only reported in five placebo controlled trials.For drugs versus drugs, combination therapy with imipramine and oxybutynin was more effective than imipramine monotherapy (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.94) and also had significantly lower relapse rates than imipramine monotherapy (RR 0.35, 95% CI 0.16 to 0.77). There was an overall paucity of data regarding outcomes after treatment was withdrawn.For drugs versus behavioural therapy, bedwetting alarms were found to be better than amphetamine (RR 2.2, 95% CI 1.12 to 4.29), oxybutynin (RR 3.25, 95% CI 1.77 to 5.98), and oxybutynin plus holding exercises (RR 3.3, 95% CI 1.84 to 6.18) in reducing the number of children failing to achieve 14 consecutive dry nights.Adverse effects of drugs were seen in 19 trials while 17 trials did not adequately report the occurrence of side effects.
Authors' conclusions: There was not enough evidence to judge whether or not the included drugs cured bedwetting when used alone. There was limited evidence to suggest that desmopressin, imipramine and enuresis alarms therapy were better than the included drugs to which they were compared. In other reviews, desmopressin, tricyclics and alarm interventions have been shown to be effective during treatment. There was also evidence to suggest that combination therapy with anticholinergic therapy increased the efficacy of other established therapies such as imipramine, desmopressin and enuresis alarms by reducing the relapse rates, by about 20%, although it was not possible to identify the characteristics of children who would benefit from combination therapy. Future studies should evaluate the role of combination therapy against established treatments in rigorous and adequately powered trials.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures











Update of
-
Drugs for nocturnal enuresis in children (other than desmopressin and tricyclics).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(4):CD002238. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002238. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD002238. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002238.pub2. PMID: 14583948 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Alawwa 2010# {published data only}
-
- Alawwa IA, Matani YS, Saleh AA, Al‐Ghazo MA. A placebo‐controlled trial of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide on nocturnal enuresis. Urologia Internationalis 2010;84(3):319‐24. - PubMed
Al‐Waili 1986# {published data only}
-
- Al‐Waili NS. Diclofenac sodium in the treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis: double‐blind crossover study. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 1986;13(2):139‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Al‐Waili 1989# {published data only}
-
- Al‐Waili NS. Indomethacin suppository to treat primary nocturnal enuresis: double‐blind study. The Journal of Urology 1989;142(5):1290‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Austin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Austin PF, Ferguson G, Yan Y, Campigotto MJ, Royer ME, Coplen DE. Combination therapy with desmopressin and an anticholinergic medication for nonresponders to desmopressin for monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Pediatrics 2008;122(5):1027‐32. - PubMed
Batislam 1995 {published data only}
-
- Batislam E, Nuhoglu B, Peskircioglu L, Emir L, Uygur C, Germiyanoglu C, et al. A prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor, diclofenac sodium in the treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis. Acta Urologica Belgica 1995;63(3):35‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Breger 1961 {published data only}
-
- Breger E. Meprobamate in the management of enuresis. Journal of Pediatrics 1961;59(4):571‐6. - PubMed
Breger 1962 {published data only}
-
- Breger E. Hydroxyzine hydrochloride and methylphenidate hydrochloride in the management of enuresis. Journal of Pediatrics 1962;61(3):443‐7. - PubMed
Dubow 1966 {published data only}
-
- Dubow E. Enuresis: adjunctive therapy. Clinical investigations with an ephedrine‐atropine mixture. Clinical Pediatrics (Phila ) 1966;5(3):177‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
el‐Sadr 1990a {published data only}
-
- el‐Sadr A, Sabry AA, Abdel‐Rahman M, el‐Barnachawy R, Koraitim M. Treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis by oral androgen mesterolone. A clinical and cystometric study. Urology 1990;36(4):331‐5. - PubMed
Esmaeili 2008 {published data only}
-
- Esmaeili M, Esmaeili M. Combined treatment with oxybutynin and imipramine in enuresis. Iranian Journal of Medical Sciences 2008;33(1):12‐6.
Forrester 1964 {published data only}
-
- Forrester RM, Stein Z, Susser MW. A trial of conditioning therapy in nocturnal enuresis. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1964;6:158‐66. [7737] - PubMed
Forsythe 1972 {published data only}
-
- Forsythe WI, Merrett JD, Redmond A. Enuresis and psychoactive drugs. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1972;26(3):116‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gelotte 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gelotte CK, Prior MJ, Gu J. A randomized, placebo‐controlled, exploratory trial of Ibuprofen and pseudoephedrine in the treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis in children. Clinical Pediatrics 2009;48(4):410‐9. - PubMed
Gjessing 1968# {published data only}
-
- Gjessing J. Investigation and therapy of nocturnal enuresis in the Fredericia Medical District. [Danish]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1968;130(48):2053‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
GP Research Gp 1970# {published data only}
-
- General Practitioner Research Group. General Practitioner Clinical Trials: sedative and stimulant compared in enuresis. Practitioner 1970;204(222):584‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Harrington 1960# {published data only}
-
- Harrington M. Phenmetrazine in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis. Practitioner 1960;185:343‐6. - PubMed
Ingle 1968 {published data only}
-
- Ingle VN, Panase V. Enuresis‐‐a comparative study of imipramine and tranquillisers in its management. Indian Pediatrics 1968;5(5):222‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kennedy 1968 {published data only}
-
- Kennedy WA, Sloop EW. Methedrine as an adjunct to conditioning treatment of nocturnal enuresis in normal and institutionalized retarded subjects. Psychological Reports 1968;22:997‐1000. - PubMed
Khosroshahi 1989 {published data only}
-
- Khosroshahi HE, Bozkurt V, Sadikoglu N, Atakan C. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis: a placebo‐controlled trial with piracetam, diphenylhydantoin and psychotherapy. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 1989;31(3):215‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kline 1968 {published data only}
-
- Kline AH. Diazepam and the management of nocturnal enuresis. Clinical Medical 1968;75:20‐2.
Korczyn 1979# {published data only}
-
- Korczyn AD, Kish I. The mechanism of imipramine in enuresis nocturna. Clinical & Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology 1979;6(1):31‐5. - PubMed
Kunin 1970# {published data only}
-
- Kunin SA, Limbert DJ, Platzker AC, McGinley J. The efficacy of imipramine in the management of enuresis. Journal of Urology 1970;104(4):612‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lee 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lee T, Suh HJ, Lee HJ, Lee JE. Comparison of effects of treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis with oxybutynin plus desmopressin, desmopressin alone or imipramine alone: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of Urology 2005;174(3):1084‐7. - PubMed
Leys 1956 {published data only}
Marconi 1985 {published data only}
-
- Marconi AM, Bocciardi A, Roggia A, Fava C. Oxybutynin chloride in enuresis (randomised clinical study). Urologia 1984;51:262‐7.
-
- Marconi AM, Felici E, Roggia A, Torelli F. Anticholinergic treatment in the therapy of primary enuresis. Effectiveness of oxybutynin chloride in a controlled clinical study of 58 patients. [Italian]. Pediatria Medica e Chirurgica 1985;7(4):573‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mayon‐White 1956 {published data only}
Moltke 1979 {published data only}
-
- Moltke H, Verder H. Enuresis nocturna. A double‐blind study with furosemide, imipramine and placebo. [Danish]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1979;141(21):1399‐401. - PubMed
Natochin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Natochin YV, Kuznetsova AA. Nocturnal enuresis: correction of renal function by desmopressin and diclofenac. Pediatric Nephrology 2000;14(1):42‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Neveus 2008# {published data only}
-
- Neveus T, Tullus K. Tolterodine and imipramine in refractory enuresis; a placebo‐controlled crossover study. Pediatric Nephrology 2008;23(2):263‐7. - PubMed
Petersen 1974# {published data only}
-
- Petersen KE, Andersen OO. Treatment of enuresis nocturna with imipramine and related drugs‐ ‐a double blind test with placebos. [Danish]. Nordisk Medicin 1971;85(3):88‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Petersen KE, Andersen OO. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis with imipramine and related preparations. A double blind trial with a placebo. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1971;60(2):244. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Petersen KE, Andersen OO, Hansen T. Mode of action and relative value of imipramine and similar drugs in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1974;7(3):187‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Petersen KE, Andersen OO, Hansen T. The mode of action of imipramine and related drugs and their value in the treatment of different categories of enuresis nocturna. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1973;62 Suppl:63‐4.
Salmon 1973# {published data only}
-
- Salmon MA. Chapter 22. The concept of day‐time treatment for primary nocturnal enuresis. In: Kolvin I, MacKeith RC, Meadow SR editor(s). Bladder control and enuresis. London: William Heinemann Medical Books, 1973.
Sener 1998 {published data only}
-
- Sener F, Hasanoglu E, Soylemezoglu O. Desmopressin versus indomethacin treatment in primary nocturnal enuresis and the role of prostaglandins. Urology 1998;52(5):878‐81. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shaffer 1978# {published data only}
-
- Shaffer D, Hedge B, Stephenson J. Trial of an alpha‐adrenolytic drug (indoramin) for nocturnal enuresis. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1978;20(2):183‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sumner 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson M, Sumner C, Kelsey DK. Atomoxetine versus placebo for treating pediatric nocturnal enuresis (Abstract). 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco CA. 2003:Poster 215.
-
- Sumner CR, Kelsey DK, Sutton V, Gonzales J, Schuh K. Atomoxetine versus placebo for treating pediatric nocturnal enuresis (Abstract). 156th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2003 May 17‐22; San Francisco CA. 2003:NR704.
-
- Sumner CR, Schuh KJ, Sutton VK, Lipetz R, Kelsey DK. Placebo‐controlled study of the effects of atomoxetine on bladder control in children with nocturnal enuresis. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 2006;16(6):699‐711. - PubMed
Tahmaz 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tahmaz L, Kibar Y, Yildirim I, Ceylan S, Dayanc M. Combination therapy of imipramine with oxybutynin in children with enuresis nocturna. Urologia Internationalis 2000;65(3):135‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Hoeck 2008 {published data only}
-
- Hoeck KJ, Bael A, Lax H, Hirche H, Bernaerts K, Vandermaelen V, et al. Improving the cure rate of alarm treatment for monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis by increasing bladder capacity‐‐a randomized controlled trial in children.[see comment]. The Journal of Urology 2008;179(3):1122‐1126; discussion 1126‐7. - PubMed
Varan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Varan B, Saatci U, Ozen S, Bakkaloglu A, Besbas N. Efficacy of oxybutynin, pseudoephedrine and indomethacin in the treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 1996;38(2):155‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wallace 1969 {published data only}
-
- Wallace IR, Forsythe WI. The treatment of enuresis: a controlled clinical trial of propantheline, propantheline‐and‐phenobarbitone and a placebo. British Journal of Clinical Practice 1969;23(5):207‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wright 1974 {published data only}
-
- Wright L, Craig SC. A comparative study of amphetamine, ephedrine‐atropine mixture, placebo and behavioral conditioning in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis. Journal of the Oklahoma State Medical Association 1974;67(10):430‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yuksek 2003 {published data only}
-
- Yuksek MS, Erdem AF, Atalay C, Demirel A. Acupressure versus oxybutynin in the treatment of enuresis. Journal of International Medical Research 2003;31(6):552‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adler 1959 {published data only}
-
- Adler HM. Enuresis in recruits: double blind study with equanil and review of the literature. U.S. Armed Forces Medical Journal 1959;10:767‐86. - PubMed
Al‐Waili 2000 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Waili NSD. Carbamazepine to treat primary nocturnal enuresis: double‐blind study. European Journal of Medical Research 2000;5(1):40‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Arajarvi 1977 {published data only}
-
- Arajarvi T, Kivalo A, Nyberg P. Effect of antidepressants on enuretic school children. Psychiatria Fennica 1977;1977:83‐7.
Ayan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ayan S, Topsakal K, Gokce G, Gultekin EY. Efficacy of combined anticholinergic treatment and behavioral modification as a first line treatment for nonneurogenic and nonanatomical voiding dysfunction in children: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Urology 2007;177(6):2325‐9. - PubMed
Buttarazzi 1977 {published data only}
-
- Buttarazzi PJ. Oxybutynin chloride (Ditropan) in enuresis. Journal of Urology 1977;118(1 Pt 1):46. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Caione 1995 {published data only}
-
- Caione P, Giorgi PL, Passerini‐Glazel G, Chiozza ML, Artibani W, Gado R, et al. Desmopressin (DDAVP) and oxybutynin in nocturnal enuresis: results of a multicentre trial. Proceedings of the International Children's Continence Society, 3rd International Children's Symposium; 1995 Oct 16‐17; Sydney, Australia. 1995:77‐81.
Cheng 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cheng K. Vitamin B12 injection on acupoints versus imipramine monotherapy in treatment of nocturnal enuresis. Guangming Journal of Chinese Medicine 2008;23(10):1552.
Chertin 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chertin B, Koulikov D, Abu‐Arafeh W, Mor Y, Shenfeld OZ, Farkas A. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The Journal of Urology 2007;178(4 Pt 2):1744‐7. - PubMed
Cortina 1994 {published data only}
-
- Cortina J. Enuresis and its homoeopathic treatment: study of twenty cases treated with ilex paraguensis. British Homoeopathy Journal 1994;83(4):220‐2.
Cupalova‐Naglova 1970 {published data only}
-
- Cupalova‐Naglova R. Effectiveness of drug therapy and its relation to mental disorders and to the autonomic nervous system of enuretic children (academic dissertation). [Czech]. Ceskoslovenska Psychiatrie 1970;66(4):237‐8. - PubMed
De Castro 1985 {published data only}
-
- Castro R, Casolari E, Ricci S. Use of oxybutynin chloride (Ditropan) in treatment of enuresis. Rivista Italiana di Pediatrica 1985;11:208‐11.
Elmer 1988# {published data only}
-
- Elmer M, Adolfsson T, Norgaard JP, Djurhuus JC. [Diurnal enuresis in childhood is effectively treated with terodiline]. [Swedish]. Lakartidningen 1991;88(10):850‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Elmer M, Norgaard JP, Djurhuus JC, Adolfsson T. Terodiline in the treatment of diurnal enuresis in children. Scandinavian Journal of Primary Health Care 1988;6(2):119‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Festqe 1989 {published data only}
-
- Festqe OA, Schuldt M, Suchodoletz H, Gross W. Anticholinergic therapy in children with vesicoureteric reflux and detrusor instability ‐ urodynamic and radiographic alterations. Proceedings of the 19th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society; 1989 Sept 7‐9; Ljubljana, Slovenia. 1989:189‐90.
Grassetti 1986 {published data only}
-
- Grassetti F, Noia D, Paone F, Alcini E. Enuresis: aetiopathogenic and therapeutic study with oxybutynin HCL. Ped Oggi 1986;6(1):47‐51.
Hellstrom 1989 {published data only}
-
- Hellstrom A‐L, Bertilsson M, Bjure J, Hjalmas K, Jodal U. Treatment with terodiline improves unstable bladder in children. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 17th Annual Meeting; 1987 Sept 2‐5; Bristol, UK. 1987:67.
-
- Hellstrom AL, Hjalmas K, Jodal U. Terodiline in the treatment of children with unstable bladders. British Journal of Urology 1989;63(4):358‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Holt 1956 {published data only}
-
- Holt KS, Rochester MD. Drug treatment of enuresis controlled trials with propantheline, amphetamine and pituitary snuff. Lancet 1956;2:1334‐7. - PubMed
Ishigooka 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ishigooka M, Hashimoto T, Sasagawa I, Izumiya K, Nakada T. Terodiline in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis in children. International Urology and Nephrology 1992;24(5):509‐13. - PubMed
Jensen 1982# {published data only}
-
- Jensen PO, Jensen PH. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis with emepronium bromide (Ceteprin). A controlled clinical trial. [Danish]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1982;144:2224‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jiang 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jiang SS. Enuresis treated by warm acupuncture. Report of 80 cases. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2000;16(8):43‐4.
Jones 1959 {published data only}
-
- Jones K, Tibbetts RW. Pituitary snuff, propantheline and placebos in the treatment of enuresis. Journal of Mental Science 1959;105:371‐81. - PubMed
Kajiwara 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kajiwara M, Miyamoto K, Masumoto H, Oki M, Teishima J, Matsubara A. Combination treatment with solifenacin plus desmopressin for children with persistent nocturnal incontinence which lasts after obtaining complete cure of urge urinary incontinence (Abstract number 194). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2010;29(6):1083‐4.
Kamel 1969 {published data only}
-
- Kamel M, Mooro H. Treatment of nocturnal enuresis with Preludin. Journal of the Egyptian Medical Association 1969;52(4):329‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kapoor 1969 {published data only}
-
- Kapoor VK, Saksena PN. Methylamphetamine hydrochloride (methedrine) in enuresis. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 1969;36(256):169‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kroll 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kroll P, Jankowski A, Makowiak J. [The comparative study on selective alpha1‐blocker and behavioural therapy in the treatment of discoordinated voiding in children]. [Polish]. Przeglad Lekarski 2006;63 Suppl 3:226‐8. - PubMed
Lake 1979 {published data only}
-
- Lake CR, Mikkelsen EJ, Rapoport JL, Zavadil AP 3d, Kopin IJ. Effect of imipramine on norepinephrine and blood pressure in enuretic boys. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 1979;26(5):647‐53. - PubMed
Lee 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lee T, Lee KH, Seo HJ. Combination therapy of oxybutynin and desmopressin in children with primary nocturnal enuresis (Abstract 12.05 PP). 2002:79.
Li 2002 {published data only}
-
- Li Z‐H. [Clinical research on the treatment of enuresis with electroacupuncture plus TDP irradiation]. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi (Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion) 2002;21(4):28‐9.
Lopez 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lopez Pereira P, Miguelez C, Caffarati J, Estornell F, Anguera A. Trospium chloride for the treatment of detrusor instability in children. Journal of Urology 2003;170(5):1978‐81. - PubMed
Lovering 1988# {published data only}
-
- Lovering JS, Tallett SE, McKendry JB. Oxybutynin efficacy in the treatment of primary enuresis. Pediatrics 1988;82(1):104‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marson 1955 {published data only}
Martins 1994 {published data only}
-
- Martins de Oliveira C. Avaliacao do funcionamento global nas criancas com eburese funcional antes e apos o tratamento farmacologico / Evaluation of children with functional enuresis. Revista Brasileira de Medicina 1994;50(5):515‐24.
McConaghy 1969 {published data only}
-
- McConaghy N. A controlled trial of imipramine, amphetamine, pad‐and‐bell conditioning and random awakening in the treatment of nocturnal enuresis. Medical Journal of Australia 1969;2(5):237‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Metin 1992 {published data only}
-
- Metin A, Aykoi N. Diclofenac sodium suppository in the treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis. International Urology and Nephrology 1992;24(2):113‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mikkelsen 1980 {published data only}
-
- Mikkelsen EJ, Rapoport JL. Enuresis: psychopathology, sleep stage, and drug response. Urologic Clinics of North America 1980;7(2):361‐77. - PubMed
Misselwitz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Misselwitz J, John U, Tamminen‐Mobius T, Lax GH, Hirche H, Gool JD, et al. Oxybutynine‐HCI versus placebo in children with urodynamically proven urge syndrome ‐ a placebo‐controlled study. 2nd International Childrens Continence Society Congress; 1999 Aug 22‐24. Denver, Co, USA, 1999.
Naglo 1979 {published data only}
-
- Naglo AS, Boreus LO, Hellstrom B, Nergardh A. Is beta‐receptor blockade of value in continence training of children?. Scandinavian Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 1979;11(2):63‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nentwich 1986 {published data only}
-
- Nentwich HJ. Therapy of enuresis with a pediatric tablet of propiverine (Mictonettes) [German]. Kinderarzlichte Praxis 1986;54(6):329‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Otto‐Unger 1985 {published data only}
-
- Otto‐Unger G. Treatment of the unstable bladder in children with the anticholinergic agent propiverine hydrochloride (mictonorm/mictonets) [German]. Zeitschrift fur Urologie und Nephrologie 1985;78(3):145‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Persson‐Juneman 1993 {published data only}
-
- Persson‐Junemann C, Seemann O, Kohrmann KU, Junemann KP, Alken P. Comparison of urodynamic findings and response to oxybutynin in nocturnal enuresis. European Urology 1993;24(1):92‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Polak 1981 {published data only}
-
- Polak L, Skoricova M, Dimova N, Havlickova H, Okruhlica L, Molcan J. Treatment of enuresis with sydnocarb. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1981;23(4):263‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rapoport 1978 {published data only}
-
- Rapoport JL, Mikkelsen EJ, Zavadil AP. Plasma imipramine and desmethylimipramine concentration and clinical response in childhood enuresis. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1978;14(4):60‐1. - PubMed
Rapoport 1980 {published data only}
-
- Lake CR, Mikkelsen EJ, Rapoport JL, Zavadil AP3, Kopin IJ. Effect of imipramine on norepinephrine and blood pressure in enuretic boys. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1979;26(5):647‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen EJ, Rapoport JL. Enuresis: psychopathology, sleep stage, and drug response. Urologic Clinics of North America 1980;7(2):361‐77. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rapoport JL, Mikkelsen EJ, Zavadil A, Nee L, Gruenau C, Mendelson W, et al. Childhood enuresis. II. Psychopathology, tricyclic concentration in plasma, and antienuretic effect. Archives of General Psychiatry 1980;37(10):1146‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rapoport JL, Mikkelsen EJ, Zavadil AP. Plasma imipramine and desmethylimipramine concentration and clinical response in childhood enuresis. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1978;14(4):60‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rodriguez 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez do Forno A, Ariceta Iraola G. Results of a therapeutic strategy against monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis background. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 2001;54(1):38‐43. - PubMed
Saeedalzakerin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Saeedalzakerin M, Shafyee F, Heidarnia A, Kazemnejad A. Parents' coping strategy: drug therapy and educational techniques in the treatment of children's enuresis. Andeesheh Va Raftar 2000;5(3):page numbers unknown.
Singh 1980 {published data only}
-
- Singh SB, Nigram A, Liu L, Mehrotra SN, Srivastava JRI. Medical, psychological and combined therapy in the cases of enuresis: A comparative study. Indian Journal of Clinical Psychology 1980;7(2):99‐102.
Site 1974 {published data only}
-
- Site J, Gaillard L, Delphin D, Messy P, Feisthauer J. [966 cases of enuresis ‐ clinical study and trial of imipramine, antispasmodic and sedative therapy]. Lyon Medical 1974;231(7):623‐31.
Soulayrol 1970 {published data only}
-
- Soulayrol R, Julien D. Note on the comparative effect of 2 drugs recommended for enuresis. [French]. Revue de Neuropsychiatrie Infantile et D'Hygiene Mentale de L'Enfance 1970;18(12):933‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Szabo 1999 {published data only}
-
- Szabo L, Martonyi E, Molinar E. Tofisopam therapy in urinary incontinence (Abstract). Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 1999;13(1):62.
Szabo 2002 {published data only}
-
- Szabo L, Martonyi E, Molnar E. Urinary incontinence treated by tofisopam (Abstract number 537). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting, 2002 Aug 28‐30, Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:379.
Thompson 1976 {published data only}
-
- Thompson IM, Lauvetz R. Oxybutynin in bladder spasm, neurogenic bladder, and enuresis. Urology 1976;8(5):452‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thorup 1982 {published data only}
-
- Thorup J, Hansen B. The effect of emepronium bromide on urodynamic findings and clinical symptoms in enuretic children. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 12th Annual Meeting; 1982; Leiden, Germany. 1982:75‐6.
Tiptaft 1984 {published data only}
-
- Tiptaft RC, Woodhouse CR, Badenoch DF. Mazindol for nocturnal enuresis. British Journal of Urology 1984;56(6):641‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ulf 1964 {published data only}
-
- Ulf O. Comparative study of Preparyl, Tofranil and Tryptizol in enuresis nocturna of children with severe developmental disturbances. Svenska Lakartidningen 1964;61:3894. - PubMed
Van Hoeck 2007 {published data only}
-
- Hoeck K, Bael A, Hirche H, Lax H, Gool J, Trouet D. Increasing functional bladder capacity in monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis? A randomized controlled trial in 149 pre‐pubertal children (Abstract number 545 (P)). Pediatric Nephrology 2007;22:1546.
-
- Hoeck KJ, Bael A, Dessel E, Renthergem D, Bernaerts K, Vandermaelen V, et al. Do holding exercises or antimuscarinics increase maximum voided volume in monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis? A randomized controlled trial in children. The Journal of Urology 2007;178(5):2132‐6. - PubMed
Wasz‐Hockert 1971 {published data only}
Werry 1977 {published data only}
-
- Werry JS, Aman MG, Dowrick P, Lampen EL. Imipramine and chlordiazepoxide in enuresis (proceedings). Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1977;13(2):38‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wilken‐Jensen 1959 {published data only}
-
- Wilken‐Jensen K. Nocturnal bedwetting; an attempt to treat school children with banthine and pro‐banthine. Acta Pediatrican (Uppsala) 1959;48:78‐84.
Xiao 1997 {published data only}
-
- Xiao LF. [42 cases of enuresis treated by point injection therapy]. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi 1997;16(1):22.
Yamanishi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Yamanishi T, Igarashi T, Murakami S, Murayama N, Kamura K, Yasuda K, et al. A comparative study of the effects of drug therapy and bladder training therapy (Japanese). Urologic Transactions 1988;34(1):102‐6. - PubMed
Young 1965 {published data only}
-
- Turner RK. CNS stimulant drugs and conditioning treatment of nocturnal enuresis: a long term follow‐up study. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1966;4(3):225‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Young GC, Turner RK. CNS stimulant drugs and conditioning treatment of nocturnal enuresis. Behaviour Research and Therapy 1965;3:93‐101. - PubMed
Yurdakok 1986 {published data only}
-
- Yurdakok M, Kinik E, Beduk Y, Guvenc H, Us O. Treatment of enuresis: a study with imipramine, amitriptyline, chlordiazepoxide‐clidinium and piracetam. Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 1986;28(3):171‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zou 2008 {published data only}
-
- Zou JJ, Ji HJ, Wu DW, Yao J, Hu Q, Xiao DW, et al. Bioequivalence and pharmacokinetic comparison of a single 200‐mg dose of meclofenoxate hydrochloride capsule and tablet formulations in healthy Chinese adult male volunteers: a randomized sequence, open‐label, two‐period crossover study. Clinical Therapeutics 2008;30(9):1651‐7. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Cupalova‐Naglova 1968 {published data only}
-
- Cupalova‐Naglova R. Therapeutic effect of imipramine, chloridzaepoxide and placebo in enuretic children. [Czech]. Activitas Nervosa Superior 1968;10(3):265‐6. - PubMed
Additional references
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Functional enuresis. In: American Psychiatric Association, editor(s). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM). 3rd Edition. Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Publishing Inc, 1980.
Bakwin 1971
-
- Bakwin H. Enuresis in twins. American Journal of Diseases of Childhood 1971;121(3):222‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bakwin 1973
-
- Bakwin H. The genetics of enuresis. In: Kolvin I, MacKeith RC, Meadow SR editor(s). Bladder control and enuresis. London: William Heinemann Medical Books, 1973.
Blackwell 1989
-
- Blackwell C. A guide to enuresis: A guide to treatment of enuresis for professionals. Bristol: ERIC, 1989.
Butler 2004
-
- Butler RJ. Childhood nocturnal enuresis: developing a conceptual framework. Clinical Psychology Review 2004;24(8):909‐31. [PUBMED: 15533278] - PubMed
de Jonge 1973
-
- Jonge GA. Epidemiology of enuresis: A survey of the literature. In: Kolvin I, MacKeith RC, Meadow SR editor(s). Bladder control and enuresis. London: William Heinemann Medical Books, 1973.
Devlin 1991
-
- Devlin JB. Prevalence and risk factors for childhood nocturnal enuresis. Irish Medical Journal 1991;84(4):118‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Djurhuus 1992
-
- Djurhuus JC, Norgaard JP, Rittig S. Monosymptomatic bedwetting. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1992;141 Suppl:7‐19. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eiberg 1995
-
- Eiberg H, Berendt I, Mohr J. Assignment of dominant inherited nocturnal enuresis (ENUR1) to chromosome 13q. Nature Genetetics 1995;10(3):354‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Forsythe 1974
Glazener 2002
Glazener 2003a
Glazener 2004a
Glazener 2004b
Glazener 2005a
Hagglof 1998
-
- Hagglof B, Andren O, Bergstrom E, Marklund L, Wendelius M. Self‐esteem in children with nocturnal enuresis and urinary incontinence: improvement of self‐esteem after treatment. European Urology 1998;33 Suppl 3:16‐9. [PUBMED: 9599731] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration,2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hjalmas 2004
-
- Hjalmas K, Arnold T, Bower W, Caione P, Chiozza LM, Gontard A, et al. Nocturnal enuresis: an international evidence based management strategy. The Journal of Urology 2004;171(6 Pt 2):2545‐61. [PUBMED: 15118418] - PubMed
Huang 2011
Jarvelin 1989
-
- Jarvelin MR. Developmental history and neurological findings in enuretic children. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 1989;31(6):728‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jarvelin 1990
-
- Jarvelin MR, Huttunen NP, Seppanen J, Seppanen U, Moilanen I. Screening of urinary tract abnormalities among day and nightwetting children. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1990;24(3):181‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Koff 1995
-
- Koff SA. Why is desmopressin sometimes ineffective at curing bedwetting?. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1995;173 Suppl:103‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Krantz 1994
-
- Krantz I, Jylkas E, Ahlberg BM, Wedel H. On the epidemiology of nocturnal enuresis‐a critical review of methods used in descriptive epidemiological studies on nocturnal enuresis. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1994;163 Suppl:75‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Maizels 1993
-
- Maizels M, Gandhi K, Keating B, Rosenbaum D. Diagnosis and treatment for children who cannot control urination. Current Problems in Pediatrics 1993;23(10):402‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mallett 2002
-
- Mallett S, Clarke M. The typical Cochrane review ‐ how many trials? how many participants?. Research Notes 2002;18(4):820‐31. - PubMed
Moffatt 1989
-
- Moffatt ME. Nocturnal enuresis: psychologic implications of treatment and nontreatment. Journal of Pediatrics 1989;114(4 Pt 2):697‐704. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morgan 1970
-
- Morgan R. The treatment of enuresis amongst child clients of a social services department. British Journal of Social Work 1970;9(2):217‐31.
Neveus 2006
-
- Neveus T, Gontard A, Hoebeke P, Hjalmas K, Bauer S, Bower W, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: report from the Standardisation Committee of the International Children's Continence Society. The Journal of Urology 2006;176(1):314‐24. [PUBMED: 16753432] - PubMed
Norgaard 1993
-
- Norgaard JP, Djurhuus JC. The pathophysiology of enuresis in children and young adults. Clinical Pediatrics (Philadelphia) 1993;Spec No:5‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rutter 1973
-
- Rutter M, Yule W, Graham P. Enuresis and behavioural deviance. Some epidemiological considerations. In: Kolvin I, MacKeith RC, Meadow SR editor(s). Bladder control and enuresis. London: William Heinemann Medical Books, 1973.
Shaffer 1977
-
- Shaffer D. Enuresis. In: Rutter M editor(s). Child psychiatry: Modern approaches. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1977.
Sureshkumar 2009
-
- Sureshkumar P, Jones M, Cumming R, Craig J. A population based study of 2,856 school‐age children with urinary incontinence. The Journal of urology 2009;181(2):808‐15; discussion 815‐6. [PUBMED: 19110268] - PubMed
WHO 1992
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Nonorganic enuresis. In: WHO editor(s). The ICD‐10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: WHO, 1992.
References to other published versions of this review
Glazener 2000
Glazener 2003
Lister‐Sharp 1997
-
- Lister‐Sharp D, O'Meara S, Bradley M, Sheldon TA. A systematic review of the effectiveness of interventions for managing childhood nocturnal enuresis. NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

