Intravenous immunoglobulin for myasthenia gravis
- PMID: 23235588
- PMCID: PMC7133495
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002277.pub4
Intravenous immunoglobulin for myasthenia gravis
Abstract
Background: Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease in which autoantibodies interfere with neuromuscular transmission. As with other autoimmune diseases, people with myasthenia gravis would be expected to benefit from intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). This is an update of a review first published in 2003 and last updated in 2007.
Objectives: To examine the efficacy of IVIg for treating exacerbations of myasthenia gravis or for chronic myasthenia gravis.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group Specialized Register (11 October 2011), CENTRAL (2011, Issue 3), MEDLINE (January 1966 to September 2011) and EMBASE (January 1980 to September 2011) using 'myasthenia gravis' and 'intravenous immunoglobulin' as the search terms.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs in which IVIg was compared with no treatment, placebo or plasma exchange, in people with myasthenia gravis.
Data collection and analysis: One review author extracted the data and two others checked these data. For methodological reasons, no formal meta-analysis was performed.
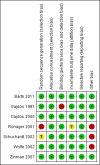
Main results: We identified seven RCTs. These trials differ in inclusion criteria, comparison with alternative treatment and outcomes. In a trial comparing IVIg with placebo, including 51 participants with myasthenia gravis worsening, the mean difference (MD) in quantitative myasthenia gravis score (QMGS) (MD 95% CI) after 14 days was: -1.60 (95% CI - 3.23 to 0.03) this result being borderline statistically significant in favour of IVIg. In an unblinded study of 87 participants with exacerbation comparing IVIg and plasma exchange there was no difference in myasthenic muscle score (MMS) after 15 days (MD -1.00; 95% CI -7.72 to 5.72). In a study of 84 participants with worsening myasthenia gravis there was no difference in change in QMGS 14 days after IVIg or plasma exchange (MD -1.50; 95% CI -3.43 to 0.43). In a study of 12 participants with moderate or severe myasthenia gravis, which was at high risk of bias from skewed allocation, the mean fall in QMGS both for IVIg and plasma exchange after four weeks was significant (P < 0.05). A study with 15 participants with mild or moderate myasthenia gravis found no difference in change in QMGS 42 days after IVIg or placebo (MD 1.60; 95% CI -1.92 to 5.12). A study included 33 participants with moderate exacerbations of myasthenia gravis and showed no difference in change in QMGS 14 days after IVIg or methylprednisolone (MD -0.42; 95% CI -1.20 to 0.36). All these three smaller studies were underpowered. The last trial, including 168 people with exacerbations, showed no evidence of superiority of IVIg 2 g/kg over IVIg 1 g/kg on the change of MMS after 15 days (MD 3.84; 95% CI -0.98 to 8.66). Adverse events due to IVIg were moderate (fever, nausea, headache), self-limiting and subjectively less severe than with plasma exchange (although, given the available data, no statistical comparison was possible). Other than where specific limitations are mentioned the trials were generally at low risk of bias.
Authors' conclusions: In exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, one RCT of IVIg versus placebo showed some evidence of the efficacy of IVIg and two did not show a significant difference between IVIg and plasma exchange. Another showed no significant difference in efficacy between 1 g/kg and 2 g/kg of IVIg. A further, but underpowered, trial showed no significant difference between IVIg and oral methylprednisolone. In chronic myasthenia gravis, there is insufficient evidence from RCTs to determine whether IVIg is efficacious.
Conflict of interest statement
One review author (PG) conducted two trials on IVIg supported by the Laboratoire Francais de Biotechnologie (LFB). This support consisted of the provision of IVIg but no other financial support. One review author (KVT) participated in the trial by Schuchardt 2002 (unpublished) as the chairman of the Advisory Board (receiving compensation of the equivalent of 500 Euros) and as a senior co‐author of the manuscript originally submitted but not published (no payments received). He participated in a conference of IgG treatments in chronic inflammatory neruopathy (receiving a payment of 3000 US$) and performed a research project on the neutralising role of IgG in animal models of inflammatory neuropathies and of Lambert‐Eaton myasthenic syndrome (public funding, no payments).
Figures














Update of
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin for myasthenia gravis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jan 23;(1):CD002277. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002277.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD002277. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002277.pub4. PMID: 18254004 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Barth 2011 {published data only}
Gajdos 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gajdos P, Chevret S, Clair B, Tranchant C, Chastang C. Clinical trial of plasma exchange and high‐dose intravenous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia Gravis Clinical Study Group. Annals of Neurology 1997;41(6):789‐96. [PUBMED: 9189040] - PubMed
Gajdos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gajdos P, Tranchant C, Clair B, Bolgert F, Eymard B, Stojkovic T, et al. Treatment of myasthenia gravis exacerbation with intravenous immunoglobulin: a randomized double‐blind clinical trial. Archives of Neurology 2005; Vol. 62, issue 11:1689‐93. [PUBMED: 16286541] - PubMed
Ronager 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ronager J, Ravnborg M, Hermansen I, Vorstrup S. Immunoglobulin treatment versus plasma exchange in patients with chronic moderate to severe myasthenia gravis. Artificial Organs 2001;25(12):967‐73. [PUBMED: 11843764] - PubMed
Schuchardt 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Schuchardt V, Kohler W, Hund E, Scheglmann K, Fleisher E, Jung K, et al. A randomized controlled trial of high dose intravenous immunoglobulin versus methylprednisolone in myasthenia gravis. An interim analysis. 2002. Data on file.
Wolfe 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wolfe GI, Barohn RJ, Foster BM, Jackson CE, Kissel JT, Day JW, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of intravenous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis. Muscle and Nerve 2002;26(4):549‐52. [PUBMED: 12362423] - PubMed
Zinman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zinman L, Ng E, Bril V. IV immunoglobulin in patients with myasthenia gravis. A randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2007;68(11):837‐41. [PUBMED: 17353471] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Liu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Liu JF, Wang WX, Xue J, Zhao CB, You HZ, Lu JH, et al. Comparing the autoantibody levels and clinical efficacy of double filtration plasmapheresis, immunoadsorption, and intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of late‐onset myasthenia gravis. Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis 2009;14:153‐60. [PUBMED: 20438536] - PubMed
Additional references
Achiron 2000
-
- Achiron A, Barak Y, Miron S, Sarova‐Pinas I. Immunoglobulin treatment in refractory myasthenia gravis. Muscle & Nerve 2000;23(4):551‐5. - PubMed
Arsura 1986
-
- Arsura EL, Bick A, Brunner NG, Namba T, Grob D. High dose intravenous immunoglobulin in the management of myasthenia gravis. Archives of Internal Medicine 1986;146(7):1365‐8. - PubMed
Arsura 1989
-
- Arsura EL. Experience with intravenous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology 1989;53(2 Pt 2):S170‐9. - PubMed
Besinger 1983
-
- Besinger UA, Toyka KV, Homberg M, Heininger K, Hohlfeld R, Fateh‐Moghadam A. Myasthenia gravis: long‐term correlation of binding and bungarotoxin blocking antibodies against acetylcholine receptors with changes in disease severity. Neurology 1983;33(10):1316‐21. - PubMed
Blanchette 1994
-
- Blanchette V, Imbach P, Andrew M, Adams M, McMillan J, Wang E, et al. Randomised trial of intravenous immunoglobulin G, intravenous anti‐D and oral prednisone in childhood acute immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Lancet 1994;344(8924):703‐7. - PubMed
Buchwald 2002
-
- Buchwald B, Ahangari R, Weishaupt A, Toyka KV. Intravenous immunoglobulins neutralize blocking antibodies in Guillain‐Barre syndrome. Annals of Neurology 2002;51(6):673‐80. - PubMed
Buchwald 2005
-
- Buchwald B, Ahangari R, Weishaupt A, Toyka KV. Presynaptic effects of immunoglobulin G from patients with Lambert‐Eaton myasthenic syndrome: their neutralization by intravenous immunoglobulins. Muscle and Nerve 2005;31(4):487‐94. - PubMed
Cosi 1991
-
- Cosi V, Lombardi M, Piccolo G, Erbetta A. Treatment of myasthenia gravis with high‐dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1991;84(2):81‐4. - PubMed
Dalakas 1993
-
- Dalakas MC, Illa I, Dambrosia JM, Souiedan SA, Stein DP, Otero C, et al. A controlled trial of high dose intravenous immune globulin infusions as treatment for dermatomyositis. New England Journal of Medicine 1993;329(27):1993‐2000. - PubMed
Dalakas 1999
-
- Dalakas MC. Intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of autoimmune neuromuscular diseases: present status and practical therapeutic guidelines. Muscle and Nerve 1999;22(11):1479‐97. - PubMed
Dau 1977
-
- Dau PC, Lindstrom JM, Cassel CK, Denys EH, Shev EE, Spitler LE. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. New England Journal of Medicine 1977;297(21):1134‐40. - PubMed
Dwyer 1992
-
- Dwyer JM. Manipulating the immune system with immune globulin. New England Journal of Medicine 1992;326(2):107‐16. - PubMed
Fateh‐Moghadam 1984
-
- Fateh‐Moghadam A, Wick M, Besinger U, Geursen RG. High dose intravenous gammaglobulin for myasthenia gravis. Lancet 1984;1(8381):848‐9. - PubMed
Gajdos 1983
-
- Gajdos P, Simon N, Rohan‐Chabot P, Raphael JC, Goulon M. Long term effects of plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Results from a randomised study [Effet à long terme des échanges plasmatiques au cours de la myasthénie. Résultats d'une étude randomisée]. Presse Médicale 1983;12(15):939‐42. - PubMed
Gajdos 1984
-
- Gajdos P, Outin HD, Elkharrat D, Brunel D, Rohan‐Chabot P, Raphaël JC, et al. High dose intravenous gammaglobulin for myasthenia gravis. Lancet 1984;1(8373):406‐7. - PubMed
Gajdos 1987
-
- Gajdos P, Outin HD, Morel E, Raphaël JC, Goulon M. High dose intravenous gamma globulin for myasthenia gravis: an alternative to plasma exchange. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1987;505:842‐44. [IDS ‐ R6891, ISSN ‐ 0077 8923, Accession ‐ 1988146240]
Gajdos 2002
Godeau 1993
-
- Godeau B, Lesage S, Divine M, Wirquin V, Farcet JP, Bierling P. Treatment of adult chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura with repeated high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Blood 1993;82(5):1415‐21. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hilkevich 2001
-
- Hilkevich O, Drory VE, Chapman J, Korczyn AD. The use of intravenous immunoglobulin as maintenance therapy in myasthenia gravis. Clinical Neurophamacology 2001;24(3):173‐6. - PubMed
Hohlfeld 1996
-
- Hohlfeld R, Melms A, Toyka KV, Drachman DB. [Therapy for myasthenia gravis]. Neurological disorders: course and treatment. San Diego, CA: Academic Press, 1996:947‐64.
Imbach 1981
-
- Imbach P, Barandun S, d'Apuzzo V, Baumgartner C, Hirt A, Morell A, et al. High dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet 1981;1(8232):1228‐31. - PubMed
Jaretzki 2000
-
- Jaretzki A 3rd, Barohn RJ, Ernstoff RM, Kaminski HJ, Keesey JC, Penn AS, et al. Myasthenia gravis: recommendations for clinical research standards. Neurology 2000;55(1):16‐23. - PubMed
Jensen 2008
-
- Jensen P, Bril V. A comparision of the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange as preoperative therapy of myasthenia gravis. Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease 2008;9(3):352‐5. - PubMed
Kornfeld 1981
-
- Kornfeld P, Ambinder EP, Mittag T, Bender AN, Papatestas AE, Goldberg J, et al. Plasmapheresis in refractory generalized myasthenia gravis. Archives of Neurology 1981;38(8):478‐81. - PubMed
McConville 2004
-
- McConville J, Farrugia ME, Beeson D, Kishore U, Metcalfe R, Newsom‐Davis J, et al. Detection and characterization of MuSK antibodies in seronegative myasthenia gravis. Annals of Neurology 2004;55(4):580‐4. - PubMed
Newsom‐Davis 1979
-
- Newsom‐Davis J, Wilson SG, Vincent A, Ward CD. Long term effects of repeated plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Lancet 1979;1(8114):464‐8. - PubMed
NIH Consensus 1986
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. The utility of therapeutic plasmapheresis for neurological disorders. The Journal of the American Medical Association 1986;256(10):1333‐7. - PubMed
NIH Consensus 1990
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Intravenous immunoglobulin: prevention and treatment of disease. The Journal of the American Medical Association 1990;264(24):3189‐93. - PubMed
Oosterhuis 1983
-
- Oosterhuis HJGH, Limburg PC, Hummel‐Tappel E, The TH. Anti‐acetylcholine receptor antibodies in myasthenia gravis. Part 2. Clinical and serological follow‐up of individual patients. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1983;58(3):371‐85. - PubMed
Osserman 1971
-
- Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a twenty‐year experience in over 1200 patients. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine 1971;38(6):497‐537. - PubMed
Perez‐Nellar 2001
-
- Perez‐Nellar J, Dominguez AM, Llorens‐Figueroa JA, Ferra‐Betancourt A, Pardo A, Quiala M, et al. A comparative study of intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis preoperatively in myasthenia [Estudio comparativo entre immunoglobulina intravenosa y plasmaferesis en el perioperatorio de la miastenia gravis]. Revista de Neurologia 2001;33(5):413‐6. [IDS ‐ 487WH, ISSN ‐ 0210‐0010] - PubMed
Pinching 1976
-
- Pinching AJ, Peters DK. Remission of myasthenia gravis following plasma exchange. Lancet 1976;2(8000):1373‐6. - PubMed
PSGBS Group 1997
-
- Plasma exchange/Sandoglobulin Guillain‐Barré Syndrome Trial Group. Randomised trial of plasma exchange, intravenous immunoglobulin, and combined treatments in Guillain‐Barré syndrome. Lancet 1997;349(9047):225‐30. - PubMed
Qureshi 1999
-
- Qureshi AI, Choudhry MA, Akbar MS, Mohammad Y, Chua HC, Yahia AM, et al. Plasma exchange versus intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in myasthenic crisis. Neurology 1999;52(3):629‐32. - PubMed
Rodnitzky 1984
-
- Rodnitzky RL, Bosch EP. Chronic long interval plasma exchange in myasthenia gravis. Archives of Neurology 1984;41(7):715‐7. - PubMed
Sharshar 2000
-
- Sharshar T, Chevret S, Mazighi M, Chillet P, Huberfeld G, Berreotta C, et al. Validity and reliability of two muscle strength scores commonly used as endpoints in assessing treatment of myasthenia gravis. Journal of Neurology 2000;247(4):286‐90. - PubMed
Tindall 1987
-
- Tindall RSA, Rollins JT, Phillips, Greenlee RG, Wells L, Belendiuk G, et al. Preliminary results of a double blind, randomized, placebo controlled trial of cyclosporine in myasthenia gravis. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;316(12):719‐724. - PubMed
Toyka 2007
-
- Toyka KV, Gold R. Treatment of myasthenia gravis. Schweizer Archiv Fur Neurologie Und Psychiatrie 2007;158:309‐21.
Van der Meché 1997
-
- Meché FG, Doorn PA. The current place of high‐dose immunoglobulins in the treatment of neuromuscular disorders. Muscle & Nerve 1997;20(2):136‐47. - PubMed
Vincent 2003
-
- Vincent A, Bowen J, Newsom‐Davis J, McConville J. Seronegative generalised myasthenia gravis: clinical features, antibodies, and their targets. Lancet Neurology 2003;2(2):99‐106. - PubMed
Wolfe 2008
-
- Wolfe GI, Oh SJ. Clinical phenotype of muscle‐specific tyrosine kinase antibody positive myasthenia gravis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2008;1132:71‐5. [PUBMED: 18567855] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

