Anticholinergic drugs versus non-drug active therapies for non-neurogenic overactive bladder syndrome in adults
- PMID: 23235594
- PMCID: PMC7017858
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003193.pub4
Anticholinergic drugs versus non-drug active therapies for non-neurogenic overactive bladder syndrome in adults
Abstract
Background: Overactive bladder syndrome is defined as urgency with or without urgency incontinence, usually with frequency and nocturia. Pharmacotherapy with anticholinergic drugs is often the first line medical therapy, either alone or as an adjunct to various non-pharmacological therapies after conservative options such as reducing intake of caffeine drinks have been tried. Non-pharmacologic therapies consist of bladder training, pelvic floor muscle training with or without biofeedback, behavioural modification, electrical stimulation and surgical interventions.
Objectives: To compare the effects of anticholinergic drugs with various non-pharmacologic therapies for non-neurogenic overactive bladder syndrome in adults.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register (searched 4 September 2012), which includes searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) and MEDLINE, and the reference lists of relevant articles.
Selection criteria: All randomised or quasi-randomised, controlled trials of treatment with anticholinergic drugs for overactive bladder syndrome or urgency urinary incontinence in adults in which at least one management arm involved a non-drug therapy. Trials amongst patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction were excluded.
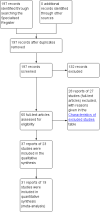
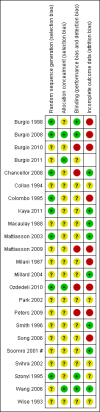
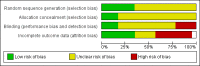
Data collection and analysis: Two authors evaluated the trials for appropriateness for inclusion and risk of bias. Two authors were involved in the data extraction. Data extraction was based on predetermined criteria. Data analysis was based on standard statistical approaches used in Cochrane reviews.
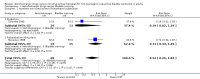
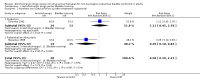
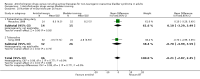
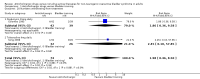
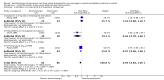
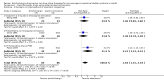
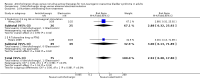
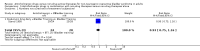
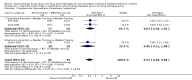
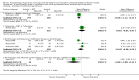
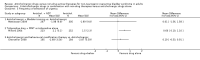
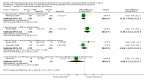
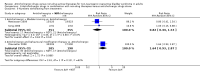
Main results: Twenty three trials were included with a total of 3685 participants, one was a cross-over trial and the other 22 were parallel group trials. The duration of follow up varied from two to 52 weeks. The trials were generally small and of poor methodological quality. During treatment, symptomatic improvement was more common amongst those participants on anticholinergic drugs compared with bladder training in seven small trials (73/174, 42% versus 98/172, 57% not improved: risk ratio 0.74, 95% confidence interval 0.61 to 0.91). Augmentation of bladder training with anticholinergics was also associated with more improvements than bladder training alone in three small trials (23/85, 27% versus 37/79, 47% not improved: risk ratio 0.57, 95% confidence interval 0.38 to 0.88). However, it was less clear whether an anticholinergic combined with bladder training was better than the anticholinergic alone, in three trials (for example 74/296, 25% versus 95/306, 31% not improved: risk ratio 0.80, 95% confidence interval 0.62 to 1.04). The other information on whether combining behavioural modification strategies with an anticholinergic was better than the anticholinergic alone was scanty and inconclusive. Similarly, it was unclear whether these complex strategies alone were better than anticholinergics alone.In this review, seven small trials comparing an anticholinergic to various types of electrical stimulation modalities such as Intravaginal Electrical Stimulation (IES), transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), the Stoller Afferent Nerve Stimulation System (SANS) neuromodulation and percutaneous posterior tibial nerve stimulation (PTNS) were identified. Subjective improvement rates tended to favour the electrical stimulation group in three small trials (54% not improved with the anticholinergic versus 28/86, 33% with electrical stimulation: risk ratio 0.64, 95% confidence interval 1.15 to 2.34). However, this was statistically significant only for one type of stimulation, percutaneous posterior tibial nerve stimulation (risk ratio 2.21, 95% confidence interval 1.13 to 4.33), and was not supported by significant differences in improvement, urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, incontinence episodes or quality of life.The most commonly reported adverse effect among anticholinergics was dry mouth, although this did not necessarily result in withdrawal from treatment. For all comparisons there were too few data to compare symptoms or side effects after treatment had ended. However, it is unlikely that the effects of anticholinergics persist after stopping treatment.
Authors' conclusions: The use of anticholinergic drugs in the management of overactive bladder syndrome is well established when compared to placebo treatment. During initial treatment of overactive bladder syndrome there was more symptomatic improvement when (a) anticholinergics were compared with bladder training alone, and (b) anticholinergics combined with bladder training were compared with bladder training alone. Limited evidence from small trials might suggest electrical stimulation is a better option in patients who are refractory to anticholinergic therapy, but more evidence comparing individual types of electrostimulation to the most effective types of anticholinergics is required to establish this. These results should be viewed with caution in view of the different classes and varying doses of individual anticholinergics used in this review. Anticholinergics had well recognised side effects, such as dry mouth.
Conflict of interest statement
Mr L Stewart has been on consultation committees for tolterodine and oxybutynin. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
























Update of
-
Anticholinergic drugs versus non-drug active therapies for overactive bladder syndrome in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD003193. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003193.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD003193. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003193.pub4. PMID: 17054163 Updated.
Comment in
-
[Physiotherapy in Women with Overactive Bladder].Aktuelle Urol. 2016 Aug;47(4):310-4. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-103986. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Aktuelle Urol. 2016. PMID: 27500849 German.
References
References to studies included in this review
Burgio 1998 {published data only}
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS. Behavioural vs drug treatment for urge urinary incontinence in older women: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1998;280(23):1995‐2000. - PubMed
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS. Combined behavioural and drug therapy for urge urinary incontinence in older women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48(4):370‐4. - PubMed
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Goode PS, Hardin JM, McDowell BJ, Candib D. Behaviour vs drug therapy for urge incontinence in older women. Proceedings of the 15th Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Urogynecology Society. 1994:48.
-
- Burgio KL, Locher JL, Roth DL, Goode PS. Psychological improvements associated with behavioural and drug treatment of urge incontinence in older women. The Journals of Gerontology. Series B, Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences 2001;56B:46‐51. - PubMed
-
- Goode PS, Burgio KL, Locher JL, Umlauf MG, LLoyd KL, Roth DL. Urodynamic changes associated with behavioural and drug treatment of urge incontinence in older women. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2002;50:808‐16. - PubMed
Burgio 2008 {published data only}
Burgio 2010 {published data only}
-
- Burgio KL, Goode PS, Richter HE, Markland AD, Johnson TM, Redden DT. Combined behavioral and individualized drug therapy versus individualized drug therapy alone for urge urinary incontinence in women. Journal of Urology 2010;184(2):598‐603. [39902] - PubMed
Burgio 2011 {published data only}
-
- Burgio KL, Goode PS, Johnson II TM, Hammontree LN, Ouslander JG, Markland AD, et al. Behavioral vs. drug treatment for overactive bladder in men: The Motive Trial (Abstract number 1516). Journal of Urology 2010;183(4 Suppl 1):e585. [42519]
-
- Burgio KL, Goode PS, Johnson TM, Hammontree L, Ouslander JG, Markland AD, et al. Behavioral versus drug treatment for overactive bladder in men: the male overactive bladder treatment in veterans (MOTIVE) trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011;59(12):2209‐16. [42742] - PubMed
Chancellor 2008 {published data only}
-
- Chancellor MB, Kianifard F, Beamer E, Mongay L, Ebinger U, Hicks G, et al. A comparison of the efficacy of darifenacin alone vs. darifenacin plus a Behavioural Modification Programme upon the symptoms of overactive bladder. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2008;62(4):606‐13. - PMC - PubMed
Collas 1994 {published data only}
-
- Collas DM, Szonyi G, Ding YY, Malone LJ. Oxybutynin with bladder retraining for detrusor instability in the elderly ‐ placebo controlled trial. Age and Ageing 1994;23S:9. - PubMed
Colombo 1995 {published data only}
-
- Colombo M, Zanetta G, Scalambrino S, Milani R. Oxybutynin and bladder training in the management of female urinary urge incontinence: A randomized study. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1995;6:63‐7.
Kaya 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kaya S, Akbayrak T, Beksac S. Comparison of different treatment protocols in the treatment of idiopathic detrusor overactivity: a randomized controlled trial.. Clinical Rehabilitation 2011;25(4):327‐38. - PubMed
Macaulay 1988 {published data only}
-
- Macaulay AJ. Psychological factors in the aetiology and treatment of urinary symptoms in women. MD Thesis Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School 1988.
-
- Macaulay AJ, Holmes D, Stanton SL, Stern RS. A prospective randomised controlled trial of bladder retraining and brief psychotherapy for urinary frequency and urgency. Proceedings of the 15th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1985:184‐5.
Mattiasson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Mattiasson A. Effect of simplified bladder training and tolterodine treatment in overactive bladder patients. Proceedings of 2nd International Consultation on Incontinence, 1‐3 July 2001 (Poster presentations). 2001:Abstract 59.
-
- Mattiasson A. Simplified bladder training augments tolterodine treatment in overactive bladder patients. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001;20(4):403‐4.
-
- Mattiasson A, Blaakaer J, Hoye K, Wein AJ. Simplified bladder training augments the effectiveness of tolterodine in patients with an overactive bladder. BJU International 2003;91(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Mattiasson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mattiasson A, Masala A, Morton R, Bolodeoku J. Efficacy of simplified bladder training in patients with overactive bladder receiving a solifenacin flexible‐dose regimen: results from a randomized study. BJU International 2009;105(8):1126‐35. - PubMed
Milani 1987 {published data only}
-
- Milani R, Scalambrino S, Carrera S Quadri G Riva D, Casolati E. A randomized trail of bladder retraining versus oxybutynin in the treatment of idiopathic urge syndrome, early results. Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1986:488‐90.
-
- Milani R, Scalambrino S, Quadri G, Carrera S, Riva D, Castolati E. Randomized drug therapy and bladder retraining in urge syndrome: late results. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS) 1987;2:133‐4.
Millard 2004 {published data only}
-
- Millard RJ. Clinical efficacy of tolterodine with or without a simplified pelvic floor exercise regimen. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2004;23:48‐53. - PubMed
Ozdedeli 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ozdedeli S, Karapolat H, Akkoc Y. Comparison of intravaginal electrical stimulation and trospium hydrochloride in women with overactive bladder syndrome: a randomized controlled study. Clinical Rehabilitation 2010;24(4):342‐51. - PubMed
Park 2002 {published data only}
-
- Park TJ, Song C, Choo M. The effects of bladder retraining, tolterodine and bladder retraining and tolterodine in female patients with overactive bladder, a prospective randomised study. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(4):434‐5.
Peters 2009 {published data only}
-
- Peters KM, Macdiarmid SA, Wooldridge LS, Leong FC, Shobeiri SA, Rovner ES, et al. Randomized trial of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus extended‐release tolterodine: results from the overactive bladder innovative therapy trial. Journal of Urology 2009;182(3):1055‐61. - PubMed
Smith 1996 {published data only}
-
- Aaronson PS, Loehner D, Bingham W, Smith JJ. Intravaginal electrical stimulation in the treatment of genuine stress urinary incontinence and detrusor instability: a controlled study. Journal of Urology 1995;153(4 Suppl):491A.
-
- Smith JJ. Intravaginal stimulation randomized trial. Journal of Urology 1996;155(1):127‐30. - PubMed
-
- Smith JJ, Loehner D, Bignham W. Intravaginal electrical stimulation in the treatment of GSUI and DI: a controlled study. Proceedings of the 15th Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Urogynecological Society. 1994:Abstract 25.
Song 2006 {published data only}
Soomro 2001 # {published data only}
-
- Soomro NA, Khadra MH, Robson W, Neal DE. A crossover randomized crossover trial of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and oxybutynin in patients with detrusor instability. Journal of Urology 2001;166(1):146‐9. - PubMed
Svihra 2002 {published data only}
-
- Svihra J, Kurca E, Luptak J, Kliment J. Neuromodulative treatment of overactive bladder ‐ non‐invasive tibial nerve stimulation. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy 2002;103(12):480‐3. - PubMed
Szonyi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Szonyi G, Collas DM, Ding YY, Malone‐Lee JG. Oxybutynin with bladder retraining for detrusor instability in elderly people: A randomized controlled trial. Age and Ageing 1995;24:287‐91. - PubMed
-
- Szonyi G, Ding YY, Malone‐Lee JG. Oxybutynin with bladder retraining for detrusor instability in elderly people. Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1994:353‐4.
Wang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang AC, Chih SY, Chen MC. Comparison of electric stimulation and oxybutynin chloride in management of overactive bladder with special reference to urinary urgency: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Urology 2006;68(5):999‐1004. - PubMed
Wise 1993 {published data only}
-
- Wise BG, Cardozo LD, Plevnik S, Kelleher C, Abbott D. A comparative study of oxybutynin and maximal electrical stimulation in the treatment of detrusor instability. Proceedings of 23rd Meeting of ICS 1993;8:236.
References to studies excluded from this review
Castleden 1986 # {published data only}
-
- Castleden CM, Duffin HM, Millar AW. A controlled clinical pilot study of dicyclomine in detrusor instability. Proceedings of the 16th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1986:373‐5.
Enzelsberger 1991 {published data only}
-
- Enzelsberger H, Schatten C, Kurz C. Vergleich von Emeproniumbromid mit intravesikal appliziertem Lidocain‐Gel bei Frauen mit Urge‐Inkontinenz. Geburtsh u Frauenheilk 1991;51:54‐7. - PubMed
Gelber 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gelber DA, Swords L. Treatment of post‐stroke urinary incontinence. Journal of Neurologic Rehabilitation 1997;11(2):131.
Goode 2011 {published data only}
-
- Goode PS, Burgio KL, Kraus SR, Kenton K, Litman HJ, Richter HE, et al. Correlates and predictors of patient satisfaction with drug therapy and combined drug therapy and behavioral training for urgency urinary incontinence in women. International Urogynecology Journal 2011;22(3):327‐34. [SR‐INCONT41557] - PMC - PubMed
Henalla 1989 {published data only}
-
- Henalla SM, Millar DR, Moon PV. The effects of terodiline and cystodistention combined with bladder drill for the treatment on the unstable bladder (preliminary results). Proceedings 19th Annual ICS meeting 1989;95:198‐9.
Henalla 1991 {published data only}
-
- Henalla SM, Millar DR, Moon PV. Medical or surgical augmentation of bladder drill for detrusor instability. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1991;11(2):128‐30.
Jarvis 1981 {published data only}
-
- Jarvis GJ. A controlled trial of bladder drill and drug therapy in the management of detrusor instability. British Journal of Urology 1981;53:565‐6. - PubMed
-
- Jarvis GJ. The unstable bladder ‐ A psychosomatic disease?. Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1981:45‐6.
Kelleher 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kelleher CJ, Filschie J, Burton G, Khullar V, Cardozo LD. Acupuncture and the treatment of irritative bladder symptoms. Acupuncture in Medicine 1994;12:9‐12.
Kim 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kim SW, Song SH, Ku JH. Bladder training versus combination of propiverine with bladder training for female urinary frequency. A prospective, randomized, comparative study. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2008;65(2):123‐7. - PubMed
Klarskov 1981 {published data only}
-
- Klarskov P, Gerstenberg T, Hald T. Bladder retraining and terodiline on urge incontinence in females with stable detrusor function. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1984:404‐5.
Klarskov 1986 {published data only}
-
- Klarskov P, Gerstenberg TC, Hald T. Bladder training and terodiline in females with idiopathic urge incontinence and stable detrusor function. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 1986;20:41‐6. - PubMed
Koonings 1987 {published data only}
-
- Koonings PP, Bergman A. Urethral relaxation: Bladder instability and stress urinary incontinence. Where is the primary pathology?. Proceedings of the 8th Annual Meeting of the American Urogynecology Society. 1987.
Koonings 1988 {published data only}
-
- Koonings P, Bergman A, Ballard CA. Combined detrusor instability and stress urinary incontinence: Where is the primary pathology?. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 1988;26:250‐6. - PubMed
Locher 2002 {published data only}
MacDiarmid 2010a {published data only}
-
- MacDiarmid SA, Peters KM, Shobeiri SA, Wooldridge LS, Rovner ES, Leong FC, et al. Long‐term durability of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation for the treatment of overactive bladder. Journal of Urology 2010; Vol. 183, issue 1:234‐40. [SR‐INCONTID35420] - PubMed
Osman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Osman T. Stress incontinence surgery for patients presenting with mixed incontinence and a normal cystogram. BJU International 2003;92(9):964‐8. - PubMed
Ouslander 1987 {published data only}
-
- Ouslander JG, Blaustein J, Connor A, Pitt A. Habit training and oxybutynin for incontinence in functionally disabled nursing home patients with detrusor hyperreflexia: A placebo controlled trial. Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1987:153‐4.
Ouslander 1988 {published data only}
-
- OuslanderJG, Blaustein J, Connor A, Pitt A. Habit training and oxybutynin for incontinence in nursing home patients. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1988;36:40‐6. - PubMed
Ouslander 1995 # {published data only}
-
- Ouslander JG, Schnelle JF, Uman G, Fingold S, Glatler Nigam J, Thico E, et al. Does oxybutynin add to the effectiveness of prompted voiding for urinary incontinence among nursing home residents? A placebo controlled trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1995;43(6):610‐7. - PubMed
Pennisi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pennisi M, Grasso‐Leanza Panella P, Pepe P. [Rehabilitation therapy in the treatment of female urinary incontinence. Our experience with 121 patients] [Italian] [La teapia riabilitativa nel trattamento dell'incontinenza urinaria femminile]. Minerav Urologica e Nefrologica 1994;46(4):245‐9. - PubMed
Peters 2010 {published data only}
-
- Peters KM, Carrico DJ, Perez‐Marrero RA, Khan AU, Wooldridge LS, Davis GL, Macdiarmid SA. Randomized trial of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation versus Sham efficacy in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome: results from the SUmiT trial. Journal of Urology 20/02/2010;183(4):1438‐43. - PubMed
Visco 2011 {published data only}
-
- Visco A, Meikle S. Efficacy and impact of botulinum toxin A versus anticholinergic therapy for the treatment of bothersome urge urinary incontinence. www.ClinicalTrials.gov [accessed 23 June 2011] 2011. [SR‐INCONT41587]
Weil 1995 {published data only}
-
- Weil EHJ, Eerdmans PHA, Janknegt RA. A new randomized study on neuromodulation versus conventional treatment for incontinence or dysfunctional voiding patterns: a preliminary study. Proceedings of the 25th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS). 1995:382‐3.
Weil 2000 {published data only}
-
- Weil EHJ, Ruiz‐Cerda JL, Eerdmans PHA, Janknegt RA, Bemelmans BLH, Kerrebroeck PhEV. Sacral root neuromodulation in the treatment of refractory urinary urge incontinence: A Prospective randomized clinical trial. European Urology 2000;37:161‐71. - PubMed
Wise 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wise BG, Cardozo LD, Cutner A, Kelleher C, Burton G. Maximal electrical stimulation: An acceptable alternative to anticholinergic therapy. Proceedings of the 13th Annual Meeting of the American Urogynecolgy Society. 1992:Abstract 32.
Wiseman 1990 {published data only}
-
- Wiseman P, Malone‐Lee JG, Rai G. A Study of terodiline with bladder retraining in the treatment of detrusor instability in the frail elderly. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1990;9(4):410‐1.
Additional references
Abrams 1988
-
- Abrams PH, Blaivas JG, Stanton SL, Andersen JT. Standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1988;7(5):403‐27.
Abrams 2002
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Subcommittee of the International Continence Society. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21:167. - PubMed
Andersson 2002
-
- Waldeck K, Larsson B, Sandberg B, Andersson KE, Larsson B, Sandberg B, et al. Actions of the new antimuscarinic compound Lu 25‐109 on isolated human and pig detrusor. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(1):92‐8. - PubMed
Cardozo 1978
-
- Cardozo L, Stanton SL, Hafner J, Alan V. Biofeedback in the treatment of detrusor instability. British Journal of Urology 1978;50(4):250‐4. - PubMed
Cody 2012
Cody 2012a
-
- Cody JD, Nabi G, Dublin N, McClinton S, Neal DE, Pickard R, Yong SM. Urinary diversion and bladder reconstruction/replacement using intestinal segments for intractable incontinence or following cystectomy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003306.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
de Groat 1997
-
- Groat WC. A neurologic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 1997;50(6A Suppl):36‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Dublin 2004
-
- Dublin N, Alhasso AA, Stewart L. Anticholinergic drugs versus other medications for overactive bladder syndrome in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003190.pub2] - DOI
Dumoulin 2010
Duthie 2011
Fall 1985
-
- Fall M. Electrical pelvic floor stimulation for control of detrusor instability. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1984;4:329‐5.
Gameiro 2012
Herbison 2009
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Holmes 1983
-
- Holmes DM, Stone AR, Bary PR, et al. Bladder training ‐ 3 years on. BJU International 1983;55:640‐4. - PubMed
Hu 2003
-
- Hu Tw, Wagner TH, Bentkover JD, Leblanc K, Piancentini A, Stewart WF. Estimated economic costs of overactive bladder in the United States. Urology 2003;61:1123‐8. - PubMed
Kobelt 1997
-
- Kobelt G. Economic considerations and outcome measurement in urge incontinence. Urology 1997;50(6A Suppl):100‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Madhuvrata 2012
Milsom 2001
-
- Milson I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Roberts RG, Thuroff J, Wein AJ. How widespread are symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population based prevalence study. BJU International 2001;87:760. - PubMed
Nabi 2006
Ouslander 1982
-
- Ouslander JG, Kane RL, Abrass IB. Urinary incontinence in elderly nursing home patients. JAMA 1982;248(10):1194‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ouslander 1986
-
- Ouslander JG, Hepps K, Raz S, Su HL. Genitourinary dysfunction in a geriatric outpatient population. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1986;34(7):507‐14. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shaker 1998
-
- Shaker HS, Hassouna M. Sacral nerve root neuromodulation: an effective treatment of refractory urge incontinence. Journal of Urology 1998;159:1516‐9. - PubMed
Stewart 2001
-
- Stewart W, Herzog AR, Wein A, Abrams P, Payne C, Corey R, et al. Prevalence and impact of overactive bladder in US: results from NOBLE program. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001;20:406.
Thuroff 1991
-
- Thuroff JW, Bunke B, Ebner A, Faber P, Geeter P, Hannappel J, et al. Randomized, double‐blind, multicenter trial on treatment of frequency, urgency and incontinence related to detrusor hyperactivity: oxybutynin versus propantheline versus placebo. Journal of Urology 1991;145(4):813‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Kerrebroeck 1998
-
- Kerrebroeck PE, Amarenco G, Thuroff JW, Madersbacher HG, Lock MT, Messelink EJ, et al. Dose‐ranging study of tolterodine in patients with detrusor hyperreflexia. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1998;17(5):499‐512. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

