Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease
- PMID: 23235603
- PMCID: PMC11357690
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004136.pub3
Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Various blood pressure-lowering agents, and particularly inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), are widely used for people with diabetes to prevent the onset of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2003 and updated in 2005.
Objectives: This systematic review aimed to assess the benefits and harms of blood pressure lowering agents in people with diabetes mellitus and a normal amount of albumin in the urine (normoalbuminuria).
Search methods: In January 2011 we searched the Cochrane Renal Group's Specialised Register through contact with the Trials Search Co-ordinator.
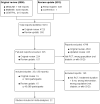
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing any antihypertensive agent with placebo or another agent in hypertensive or normotensive patients with diabetes and no kidney disease (albumin excretion rate < 30 mg/d) were included.
Data collection and analysis: Two investigators independently extracted data on kidney and other patient-relevant outcomes (all-cause mortality and serious cardiovascular events), and assessed study quality. Analysis was by a random effects model was applied to analyse results which were expressed as risk ratio (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
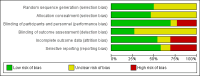
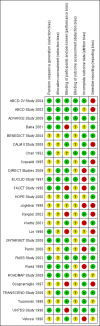
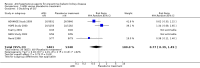
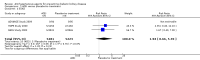
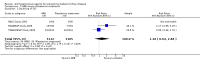
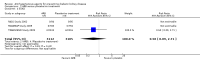
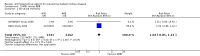
Main results: We identified 26 studies that enrolling 61,264 participants. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) reduced the risk of new onset of microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria or both when compared to placebo (8 studies, 11,906 patients: RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.56 to 0.89), with similar benefits in people with and without hypertension (P = 0.74), and when compared to calcium channel blockers (5 studies, 1253 participants: RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.42 to 0.85). ACEi reduced the risk of death when compared to placebo (6 studies, 11,350 participants: RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.97). No effect was observed for angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) when compared to placebo for new microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria or both (5 studies, 7653 participants: RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.68 to 1.19) or death (5 studies, 7653 participants: RR 1.12, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.41); however, meta-regression suggested possible benefits from ARB for preventing kidney disease in high risk patients. There was a trend towards benefit from use of combined ACEi and ARB for prevention of DKD compared with ACEi alone (2 studies, 4171 participants: RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.00).The risk of cough was significantly increased with ACEi when compared to placebo (6 studies, 11,791 patients: RR 1.84, 95% CI 1.24 to 2.72), however there was no significant difference in the risk of headache or hyperkalaemia. There was no significant difference in the risk of cough, headache or hyperkalaemia when ARB was to placebo. On average risk of bias was judged to be either low (27% to 69%) or unclear (i.e. no information available) (8% to 73%). Blinding of participants, incomplete outcome data and selective reporting were judged to be high in 23%, 31% and 31% of studies, respectively.
Authors' conclusions: ACEi were found to prevent new onset DKD and death in normoalbuminuric people with diabetes, and could therefore be used in this population. More data are needed to clarify the role of ARB and other drug classes in preventing DKD.
Conflict of interest statement
Vlado Perkovic is supported by a fellowship from the Heart Foundation of Australia and a various grants from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. He has received speakers fees from Roche, Servier and Astra Zeneca, funding for a clinical trial from Baxter, and serves on Steering Committees for trials funded by Johnson and Johnson, Boehringer Ingelheim, Vitae and Abbott. His employer conducts clinical trials funded by Servier, Johnson and Johnson, Roche and Merck.
Celine Foote has been supported by general research grants from both Amgen and the NHMRC. Both Amgen and the NHMRC have played no part in the design, conduct and reporting of this research project.
JL has received grant support from Pfizer for hypertension research, and also is a recipient of a Research Fellowship supported by Amgen.
Figures
















Update of
-
Antihypertensive agents for preventing diabetic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19;(4):CD004136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004136.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD004136. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004136.pub3. PMID: 16235351 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
ABCD‐2V Study 2004 {published data only}
-
- Estacio RO, Coll JR, Tran ZV, Schrier RW. Effect of intensive blood pressure control with valsartan on urinary albumin excretion in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Hypertension 2006;19(12):1241‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Esler A, Lundgren R, Schrier RW. Aggressive blood pressure control with valsartan in normotensive Type 2 diabetic patients results in regression of albuminuria. [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2004;15(Oct):568A.
ABCD Study 2002 {published data only}
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers B, Biggerstaff S, Schrier RW. Effects of a calcium channel antagonist versus an ace inhibitor on diabetic nephropathy [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1998;9(Program & Abstracts):114A.
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23(Suppl 2):B54‐64. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Hiatt WR, Biggerstaff SL, Gifford N, Schrier RW. The effect of nisoldipine as compared with enalapril on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes and hypertension. New England Journal of Medicine 1998;338(10):645‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Estacio RO, Mehler P, Esler A, Schrier RW. Aggressive lowering of blood pressure in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients: beneficial effects on stroke, progression of retinopathy and nephropathy [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2001;12(Program & Abstracts):146A.
-
- Estacio RO, Savage S, Nagel NJ, Schrier RW. Baseline characteristics of participants in the Appropriate Blood Pressure Control in Diabetes trial. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(3):242‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ADVANCE Study 2009 {published data only}
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group. ADVANCE‐‐Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: patient recruitment and characteristics of the study population at baseline. Diabetic Medicine 2005;22(7):882‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Collaborative Group, Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(24):2560‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- ADVANCE Management Committee. Study rationale and design of ADVANCE: action in diabetics and vascular disease ‐ preterax and diamicron MR controlled evaluation. Diabetologia 2001;44(9):1118‐20. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. Rationale and design of the ADVANCE study: a randomised trial of blood pressure lowering and intensive glucose control in high‐risk individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: PreterAx and DiamicroN Modified‐Release Controlled Evaluation. Journal of Hypertension ‐ Supplement 2001;19(4):S21‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chalmers J. ADVANCE Study: objectives, design and current status [Etude ADVANCE : objectifs, protocole et état actuel]. Drugs 2003;63 Spec No. 1:39‐44. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Baba 2001 {published data only}
-
- Baba S, The J‐MIND Study Group. Nifedipine and enalapril equally reduce the progression of nephropathy in hypertensive type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2001;54(3):191‐201. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
BENEDICT Study 2004 {published data only}
-
- BENEDICT G. The BErgamo NEphrologic DIabetes Complications Trial (BENEDICT): design and baseline characteristics. Controlled Clinical Trials 2003;24(4):442‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Remuzzi G, Macia M, Ruggenenti P. Prevention and treatment of diabetic renal disease in type 2 diabetes: the BENEDICT study. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2006;17(4 Suppl 2):S90‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Ilieva AP, Iliev IP, Chiurchiu C, Rubis N, et al. Effects of verapamil added‐on trandolapril therapy in hypertensive type 2 diabetes patients with microalbuminuria: the BENEDICT‐B randomized trial. Journal of Hypertension 2011;29(2):207‐16. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Ruggenenti P, Fassi A, Parvanova Ilieva A, Bruno Petrov Iliev I, Brusegan V, Rubis N, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;351(19):1941‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CALM II Study 2005 {published data only}
-
- Andersen NH, Knudsen ST, Poulsen PL, Poulsen SH, Helleberg K, Eiskjaer H, et al. Dual blockade with candesartan cilexetil and lisinopril in hypertensive patients with diabetes mellitus: rationale and design. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2003;4(2):96‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Andersen NH, Poulsen PL, Knudsen ST, Poulsen SH, Eiskjaer H, Hansen KW, et al. Long‐term dual blockade with candesartan and lisinopril in hypertensive patients with diabetes: the CALM II study. Diabetes Care 2005;28(2):273‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Knudsen ST, Andersen NH, Poulsen SH, Eiskjaer H, Hansen KW, Helleberg K, et al. Pulse pressure lowering effect of dual blockade with candesartan and lisinopril vs. high‐dose ACE inhibition in hypertensive type 2 diabetic subjects: a CALM II study post‐hoc analysis. American Journal of Hypertension 2008;21(2):172‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chan 1992 {published data only}
-
- Chan JC, Ko GT, Leung DH, Cheung RC, Cheung MY, So WY, et al. Long‐term effects of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibition and metabolic control in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney International 2000;57(2):590‐600. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Nicholls MG, Cheung CK, Law LK, Swaminathan R, Cockram CS. Factors determining the blood pressure response to enalapril and nifedipine in hypertension associated with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1995;18(7):1001‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chan JC, Yeung VT, Leung DH, Tomlinson B, Nicholls MG, Cockram CS. The effects of enalapril and nifedipine on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1994;17(8):859‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Crepaldi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Crepaldi G, Carraro A, Brocco E, Adezati L, Andreani D, Bompiani G, et al. Hypertension and non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes. Acta Diabetologica 1995;32(3):203‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
DIRECT Studies 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bilous R, Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Fuller J, Klein R, Orchard T, et al. Effect of candesartan on microalbuminuria and albumin excretion rate in diabetes: three randomized trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151(1):11‐20, W3‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bilous RW, Parving H, Nishi C. DIRECT‐Renal: The effect of the angiotensive type 1 receptor blocker candesartan on the development of microalbuminuria in type 1 and type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2008, (Abstracts Issue).
-
- Chaturvedi N, Porta M, Klein R, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, et al. Effect of candesartan on prevention (DIRECT‐Prevent 1) and progression (DIRECT‐Protect 1) of retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: randomised, placebo‐controlled trials. Lancet 2008;372(9647):1394‐402. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi N, Sjoelie AK, Svensson A, DIRECT Programme Study Group. The DIabetic Retinopathy Candesartan Trials (DIRECT) Programme, rationale and study design. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2002;3(4):255‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Sjolie AK, Klein R, Porta M, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, et al. Effect of candesartan on progression and regression of retinopathy in type 2 diabetes (DIRECT‐Protect 2): a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372(9647):1385‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
EUCLID Study 1997 {published data only}
-
- Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Stephenson JM, Abrahamian H, Keipes M, Castellarin A, et al. Effect of lisinopril on progression of retinopathy in normotensive people with type 1 diabetes. The EUCLID Study Group. EURODIAB Controlled Trial of Lisinopril in Insulin‐Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Lancet 1998;351(9095):28‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi N, Stevenson J, Fuller JH, Rottiers R, Ferriss B, Karamanos B, et al. Randomised placebo‐controlled trial of lisinopril in normotensive patients with insulin‐dependent diabetes and normoalbuminuria or microalbuminuria. The EUCLID Study Group. Lancet 1997;349(9068):1787‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Fuller JH, Anzalone D and EUCLID Study Group. Renal effect of lisinopril in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) without hypertension [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 1996;7(9):1357.
-
- Penno G, Chaturvedi N, Talmud PJ, Cotroneo P, Manto A, Nannipieri M, et al. Effect of angiotensin‐converting enzyme (ACE) gene polymorphism on progression of renal disease and the influence of ACE inhibition in IDDM patients: findings from the EUCLID Randomized Controlled Trial. EURODIAB Controlled Trial of Lisinopril in IDDM. Diabetes 1998;47(9):1507‐11. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Schalkwijk CG, Chaturvedi N, Twaafhoven H, Hinsbergh VW, Stehouwer CD, EUCLID Study Group. Amadori‐albumin correlates with microvascular complications and precedes nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2002;32(7):500‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
FACET Study 1998 {published data only}
-
- Tatti P, Pahor M, Byington RP, Mauro P, Guarisco R, Strollo G, et al. Outcome results of the Fosinopril Versus Amlodipine Cardiovascular Events Randomized Trial (FACET) in patients with hypertension and NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1998;21(4):597‐603. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
HOPE Study 2000 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. The HOPE (Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation) Study: the design of a large, simple randomized trial of an angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor (ramipril) and vitamin E in patients at high risk of cardiovascular events. The HOPE study investigators. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 1996;12(2):127‐37. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC. Diabetes and the HOPE study: implications for macrovascular and microvascular disease. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2001;117(Suppl):8‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Bosch J, Pogue J, Taylor DW, Zinman B, Yusuf S. Rationale and design of a large study to evaluate the renal and cardiovascular effects of an ACE inhibitor and vitamin E in high‐risk patients with diabetes. The MICRO‐HOPE Study. Microalbuminuria, cardiovascular, and renal outcomes. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation. Diabetes Care 1996;19(11):1225‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gerstein HC, Pogue J, Mann JF, Lonn E, Dagenais GR, McQueen M, et al. The relationship between dysglycaemia and cardiovascular and renal risk in diabetic and non‐diabetic participants in the HOPE study: a prospective epidemiological analysis. Diabetologia 2005;48(9):1749‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO‐HOPE substudy. Lancet 2000;335(9200):253‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Joglekar 1998 {published data only}
-
- Joglekar SJ, Nanivadekar AS. A randomized, controlled, multicenter study to compare prazosin GITS with enalapril in hypertensive patients with diabetes mellitus. Bombay Hypertension Study Group. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 1998;Suppl 1:52‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kavgaci 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kavgaci H, Sahin A, Onder EH, Erem C, Ozdemir F. The effects of losartan and fosinopril in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2002;58(1):19‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kvetny 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kvetny J, Gregersen G, Smith Pedersen R. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of perindopril in normotensive, normoalbuminuric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Qjm 2001;94(2):89‐94. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lin M, Yang YF, Chiang HT, Lee D, Wang SP, Chang MS, et al. Beneficial effects of angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors on cardiovascular and renal functions in patients with hypertension and diabetes. Acta Cardiologica Sinica 1995;11(1):30‐8. [EMBASE: 1995122137]
ONTARGET Study 2008 {published data only}
-
- Barzilay JI, Gao P, O'Donnell M, Mann JF, Anderson C, Fagard R, et al. Albuminuria and decline in cognitive function: The ONTARGET/TRANSCEND studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(2):142‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cukierman‐Yaffe T, Gerstein HC, Anderson C, Zhao F, Sleight P, Hilbrich L, et al. Glucose intolerance and diabetes as risk factors for cognitive impairment in people at high cardiovascular risk: results from the ONTARGET/TRANSCEND research programme. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2009 Mar;83(3):387‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Gallieni M, Cozzolino M, Brancaccio D, Giovannini M. Renal outcomes in the ONTARGET study. Lancet 2008;372(9655):2019‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Schumacher H, Redon J, Verdecchia P, Schmieder R, Jennings G, et al. Blood pressure targets recommended by guidelines and incidence of cardiovascular and renal events in the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination With Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial (ONTARGET). Circulation 2011;124(16):1727‐36. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mann JF, Schmieder RE, McQueen M, Dyal L, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Renal outcomes with telmisartan, ramipril, or both, in people at high vascular risk (the ONTARGET study): a multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372(9638):547‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perrin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Perrin NE, Jaremko GA, Berg UB. The effect of candesartan/placebo treatment on renal function and morphology in diabetes type 1 [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007;18(Abstracts):327A.
-
- Perrin NE, Jaremko GA, Berg UB. The effects of candesartan on diabetes glomerulopathy: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Pediatric Nephrology 2008;23(6):947‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
RASS Study 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Donnelly S, Goodyear P, Ly J, Klein R, Moss S, Sinsiko A, et al. Renal biopsy complications in the RASS study [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:559A.
-
- Donnelly S, Sinaiko A, Strand T, Zinman B, Drummond K, Gardiner R, et al. Effects of renin angiotensin system (RAS) blockade on diabetic nephropathy (DN)‐a primary prevention trial: study design and baseline results [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2002;13(Program & Abstracts):651A.
-
- Katavetin P, Katavetin P. Renal and retinal effects of enalapril and losartan in type 1 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2009;361(14):1410‐1. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mauer M, Strand T, Zinman B, Gardiner R, Suissa S, Sinaiko A, et al. The Renin Angiotensin System Study (RASS): compliance in a long‐term kidney biopsy based diabetic nephropathy (DN) primary prevention trial in Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) patients (pts) [abstract]. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2005;16:554A.
-
- Mauer M, Zinman B, Gardiner R, Drummond KN, Suissa S, Donnelly SM, et al. ACE‐I and ARBs in early diabetic nephropathy. Journal of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System 2002;3(4):262‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ravid 1998 {published data only}
-
- Ravid M, Brosh D, Levi Z, Bar‐Dayan Y, Ravid D, Rachmani R. Use of enalapril to attenuate decline in renal function in normotensive, normoalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1998;128(12 Pt 1):982‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ROADMAP Study 2009 {published data only}
-
- Haller H, Ito S, Izzo JL, Januszewicz A, Katayama S, Menne J, et al. Olmesartan for the delay or prevention of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine 2011;364(10):907‐17. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Haller H, Viberti GC, Mimran A, Remuzzi G, Rabelink AJ, Ritz E, et al. Preventing microalbuminuria in patients with diabetes: rationale and design of the Randomised Olmesartan and Diabetes Microalbuminuria Prevention (ROADMAP) study. Journal of Hypertension 2006;24(2):403‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Haller HG, Viberti GV, Ritz E, Ruilope LM, Rabelink TJ, for the ROADMAP Steering Committee Members. Prevention of albuminuria and cardiovascular morbidity with olmesartan, the ROADMAP trial. ASN Renal Week. 2009:LB‐005.
-
- Januszewicz A, Ritz E, Viberti G, Mimran A, Rabelink AJ, Rump LC, et al. Office and ambulatory pulse pressure‐‐association with clinical characteristics and cardiovascular risk factors in normoalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes (ROADMAP study). Journal of Human Hypertension 2011;25(11):679‐85. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Menne J, Izzo JL Jr, Ito S, Januszewicz A, Katayama S, Chatzykirkou C, et al. Prevention of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2012;30(4):811‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Scognamiglio 1997 {published data only}
-
- Scognamiglio R, Nosadini R, Marin M, Nisti S, Fasoli G, Palisi M, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and tolerability of nitrendipine in reducing both pressure and left ventricular mass in hypertensive type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1997;20(8):1290‐2. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
TRANSCEND Study 2009 {published data only}
-
- Barzilay JI, Gao P, O'Donnell M, Mann JF, Anderson C, Fagard R, et al. Albuminuria and decline in cognitive function: The ONTARGET/TRANSCEND studies. Archives of Internal Medicine 2011;171(2):142‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Cukierman‐Yaffe T, Gerstein HC, Anderson C, Zhao F, Sleight P, Hilbrich L, et al. Glucose intolerance and diabetes as risk factors for cognitive impairment in people at high cardiovascular risk: results from the ONTARGET/TRANSCEND research programme. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice 2009;83(3):387‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Held C, Gerstein HC, Yusuf S, Zhao F, Hilbrich L, Anderson C, et al. Glucose levels predict hospitalization for congestive heart failure in patients at high cardiovascular risk. Circulation 2007;115(11):1371‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mann JF, Schmieder RE, Dyal L, McQueen MJ, Schumacher H, Pogue J, et al. Effect of telmisartan on renal outcomes: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151(1):1‐10. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Telmisartan Randomised AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease (TRANSCEND) Investigators. Yusuf S. Teo K. Anderson C. Pogue J. Dyal L, et al. Effects of the angiotensin‐receptor blocker telmisartan on cardiovascular events in high‐risk patients intolerant to angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372(9644):1174‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tuominen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Tuominen JA, Ebeling P, Koivisto VA. Long‐term lisinopril therapy reduces exercise‐induced albuminuria in normoalbuminuric normotensive IDDM patients. Diabetes Care 1998;21(8):1345‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
UKPDS Study 1998 {published data only}
-
- Anonymous. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS). VIII. Study design, progress and performance. Diabetologia 1991;34(12):877‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- UK PDS Group. Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998;352(9131):837‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Velussi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Velussi M, Brocco E, Frigato F, Zolli M, Muollo B, Maioli M, et al. Effects of cilazapril and amlodipine on kidney function in hypertensive NIDDM patients. Diabetes 1996;45(2):216‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ALLHAT 2002 {published data only}
-
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. The Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Major outcomes in high‐risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 2002;288(23):2981‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Messerli HF. Implications of discontinuation of doxazosin arm of ALLHAT. Antihypertensive and Lipid‐Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial. Lancet 2000;355(9207):863‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CAPPP 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Niskanen L, Lanke J, Hedner T, Niklason A, et al. Effect of angiotensin‐converting‐enzyme inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP) randomised trial. Lancet 1999;353(9153):611‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hansson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Ekbom T, Dahlof B, Lanke J, Schersten B, et al. Randomised trial of old and new antihypertensive drugs in elderly patients: cardiovascular mortality and morbidity the Swedish Trial in Old Patients with Hypertension‐2 study. Lancet 1999;354(9192):1751‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
HOT 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, Dahlof B, Elmfeldt D, Julius S, et al. Effects of intensive blood‐pressure lowering and low‐dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. Lancet 1998;351(9118):1755‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
INSIGHT 2000 {published data only}
-
- Brown MJ, Palmer CR, Castaigne A, Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Rosenthal T, et al. Morbidity and mortality in patients randomised to double‐blind treatment with a long‐acting calcium‐channel blocker or diuretic in the International Nifedipine GITS study: Intervention as a Goal in Hypertension Treatment (INSIGHT). Lancet 2000;356(9227):366‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
NORDIL 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hansson L, Hedner T, Lund‐Johansen P, Kjeldsen SE, Lindholm LH, Syvertsen JO, et al. Randomised trial of effects of calcium antagonists compared with diuretics and beta‐blockers on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Nordic Diltiazem (NORDIL) study. Lancet 2000;356(9227):359‐65. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tuomilehto 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tuomilehto J, Rastenyte D, Birkenhager WH, Thijs L, Antikainen R, Bulpitt CJ, et al. Effects of calcium‐channel blockade in older patients with diabetes and systolic hypertension. Systolic Hypertension in Europe Trial Investigators. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;340(9):677‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
ADA 2010
Adler 2003
-
- Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney International 2003;63(1):225‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bucher 1997
-
- Bucher HC, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE, Walter SD. The results of direct and indirect treatment comparisons in meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1997;50(6):683‐91. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
CDA 2008
-
- Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Canadian Diabetes Association 2008 clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in Canada. Canadian Journal of Diabetes 2008; Vol. 32, issue Suppl 1:S1‐S201. - PubMed
Chadban 2010
Chaturvedi 2008
-
- Chaturvedi N, Porta M, Klein R, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, et al. Effect of candesartan on prevention (DIRECT‐Prevent 1) and progression (DIRECT‐Protect 1) of retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: randomised, placebo‐controlled trials. Lancet 2008;372(9647):1394‐402. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chobanian 2003
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003;289(19):2560‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
ESH‐ESC 2007
-
- Mancia G, Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, et al. 2007 ESH‐ESC Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: ESH‐ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Journal of Hypertension 2007;25(9):1751‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gerstein 2001
-
- Gerstein HC, Mann JF, Yi Q, Zinman B, Dinneen SF, Hoogwerf B, et al. Albuminuria and risk of cardiovascular events, death, and heart failure in diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. JAMA 2001;286(4):421‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hasslacher 1985
-
- Hasslacher C, Ritz E, Terpstra J, Gallasch G, Kunowski G, Rall C. Natural history of nephropathy in type I diabetes. Relationship to metabolic control and blood pressure. Hypertension 1985;7(6 Pt 2):74‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
IDF 2009
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/ (accessed 26 September 2012).
KDOQI 2007
-
- American Kidney Foundation. KDOQI clinical practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendations for diabetes and chronic kidney disease. http://www.kidney.org/professionals/KDOQI/guideline_diabetes/guide3.htm (accessed 26 September 2012). - PubMed
Klausen 2004
-
- Klausen K, Borch‐Johnsen K, Feldt‐Rasmussen B, Jensen G, Clausen P, Scharling H, et al. Very low levels of microalbuminuria are associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease and death independently of renal function, hypertension, and diabetes. Circulation 2004;110(1):32‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Levey 2009
-
- Levey AS, Cattran D, Friedman A, Miller WG, Sedor J, Tuttle K, et al. Proteinuria as a surrogate outcome in CKD: report of a scientific workshop sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation and the US Food and Drug Administration. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2009;54(2):205‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Messent 1992
-
- Messent JW, Elliott TG, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Keen H, Viberti GC. Prognostic significance of microalbuminuria in insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus: a twenty‐three year follow‐up study. Kidney International 1992;41(4):836‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mogensen 1976
-
- Mogensen CE. Progression of nephropathy in long‐term diabetics with proteinuria and effect of initial anti‐hypertensive treatment. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 1976;36(4):383‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ninomiya 2009
Parfrey 2009
-
- Parfrey PS. Angiotensin‐receptor blockers in the prevention or treatment of microalbuminuria. Annals of Internal Medicine 2009;151(1):63‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Perkovic 2008
Ritz 1999
-
- Ritz E, Orth SR. Nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 1999;341(15):1127‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ruggenenti 1997
-
- Ruggenenti P, Remuzzi G. The diagnosis of renal involvement in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes mellitus. Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension 1997;6(2):141‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sjølie 2008
-
- Sjølie AK, Klein R, Porta M, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, et al. Effect of candesartan on progression and regression of retinopathy in type 2 diabetes (DIRECT‐Protect 2): a randomised placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2008;372(9647):1385‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Song 2000
-
- Song F, Glenny AM, Altman DG. Indirect comparison in evaluating relative efficacy illustrated by antimicrobial prophylaxis in colorectal surgery. Controlled Clinical Trials 2000;21(5):488‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Strippoli 2004
USRDS 2009
-
- U S Renal Data System. USRDS 2009 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End‐Stage Renal Disease in the United States, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD, 2009. http://www.usrds.org/atlas09.aspx (accessed 25 September 2012).
References to other published versions of this review
Strippoli 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

