CCR5 is a receptor for Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin ED
- PMID: 23235831
- PMCID: PMC3536884
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11724
CCR5 is a receptor for Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin ED
Abstract
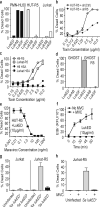
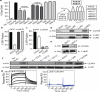
Pore-forming toxins are critical virulence factors for many bacterial pathogens and are central to Staphylococcus aureus-mediated killing of host cells. S. aureus encodes pore-forming bi-component leukotoxins that are toxic towards neutrophils, but also specifically target other immune cells. Despite decades since the first description of staphylococcal leukocidal activity, the host factors responsible for the selectivity of leukotoxins towards different immune cells remain unknown. Here we identify the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) co-receptor CCR5 as a cellular determinant required for cytotoxic targeting of subsets of myeloid cells and T lymphocytes by the S. aureus leukotoxin ED (LukED). We further demonstrate that LukED-dependent cell killing is blocked by CCR5 receptor antagonists, including the HIV drug maraviroc. Remarkably, CCR5-deficient mice are largely resistant to lethal S. aureus infection, highlighting the importance of CCR5 targeting in S. aureus pathogenesis. Thus, depletion of CCR5(+) leukocytes by LukED suggests a new immune evasion mechanism of S. aureus that can be therapeutically targeted.
Figures


Comment in
-
Antibacterial drugs: New antibiotics on the horizon?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Feb;12(2):99. doi: 10.1038/nrd3940. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23370240 No abstract available.
References
-
- Foster TJ. Immune evasion by staphylococci. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:948–958. - PubMed
-
- Bischofberger M, Iacovache I, Gisou van der Goot F. Pathogenic pore-forming proteins: function and host response. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12:266–275. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.005. - PubMed
-
- Menestrina G, et al. Ion channels and bacterial infection: the case of beta-barrel pore-forming protein toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 2003;552:54–60. doi:S0014579303008500 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Van de Velde H. Etude sur le mécanisme de la virulence du staphylocoque pyogène. La Cellule. 1894:403–460.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

