Structural characterization of the interaction of human lactoferrin with calmodulin
- PMID: 23236421
- PMCID: PMC3516504
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051026
Structural characterization of the interaction of human lactoferrin with calmodulin
Abstract
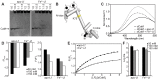
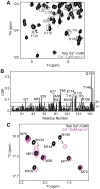
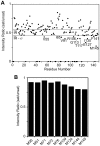
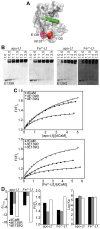
Lactoferrin (Lf) is an 80 kDa, iron (Fe(3+))-binding immunoregulatory glycoprotein secreted into most exocrine fluids, found in high concentrations in colostrum and milk, and released from neutrophil secondary granules at sites of infection and inflammation. In a number of cell types, Lf is internalized through receptor-mediated endocytosis and targeted to the nucleus where it has been demonstrated to act as a transcriptional trans-activator. Here we characterize human Lf's interaction with calmodulin (CaM), a ubiquitous, 17 kDa regulatory calcium (Ca(2+))-binding protein localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus of activated cells. Due to the size of this intermolecular complex (∼100 kDa), TROSY-based NMR techniques were employed to structurally characterize Ca(2+)-CaM when bound to intact apo-Lf. Both CaM's backbone amides and the ε-methyl group of key methionine residues were used as probes in chemical shift perturbation and cross-saturation experiments to define the binding interface of apo-Lf on Ca(2+)-CaM. Unlike the collapsed conformation through which Ca(2+)-CaM binds the CaM-binding domains of its classical targets, Ca(2+)-CaM assumes an extended structure when bound to apo-Lf. Apo-Lf appears to interact predominantly with the C-terminal lobe of Ca(2+)-CaM, enabling the N-terminal lobe to potentially bind another target. Our use of intact apo-Lf has made possible the identification of a secondary interaction interface, removed from CaM's primary binding domain. Secondary interfaces play a key role in the target's response to CaM binding, highlighting the importance of studying intact complexes. This solution-based approach can be applied to study other regulatory calcium-binding EF-hand proteins in intact intermolecular complexes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Legrand D, Mazurier J (2010) A critical review of the roles of host lactoferrin in immunity. Biometals 23: 365–376. - PubMed
-
- Vogel HJ (2012) Lactoferrin, a bird’s eye view. Biochem Cell Biol 90: 233–244. - PubMed
-
- Baker HM, Baker EN (2012) A structural perspective on lactoferrin function. Biochem Cell Biol 90: 320–328. - PubMed
-
- Jenssen H, Hancock RE (2009) Antimicrobial properties of lactoferrin. Biochimie 91: 19–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

