Methionine-restricted C57BL/6J mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance but have low bone density
- PMID: 23236485
- PMCID: PMC3518083
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051357
Methionine-restricted C57BL/6J mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance but have low bone density
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e104050
Abstract
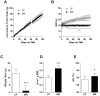
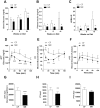
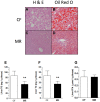
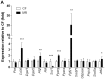
Dietary methionine restriction (MR) extends lifespan, an effect associated with reduction of body weight gain, and improvement of insulin sensitivity in mice and rats as a result of metabolic adaptations in liver, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. To test whether MR confers resistance to adiposity and insulin resistance, C57BL/6J mice were fed a high fat diet (HFD) containing either 0.86% methionine (control fed; CF) or 0.12% methionine (methionine-restricted; MR). MR mice on HFD had lower body weight gain despite increased food intake and absorption efficiency compared to their CF counterparts. MR mice on HFD were more glucose tolerant and insulin sensitive with reduced accumulation of hepatic triglycerides. In plasma, MR mice on HFD had higher levels of adiponectin and FGF21 while leptin and IGF-1 levels were reduced. Hepatic gene expression showed the downregulation of Scd1 while Pparg, Atgl, Cd36, Jak2 and Fgf21 were upregulated in MR mice on HFD. Restriction of growth rate in MR mice on HFD was also associated with lower bone mass and increased plasma levels of the collagen degradation marker C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen (CTX-1). It is concluded that MR mice on HFD are metabolically healthy compared to CF mice on HFD but have decreased bone mass. These effects could be associated with the observed increase in FGF21 levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Winzell MS, Ahren B (2004) The high-fat diet-fed mouse: a model for studying mechanisms and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53 Suppl 3: S215–S219. 53/suppl_3/S215 [pii]. - PubMed
-
- Lin S, Thomas TC, Storlien LH, Huang XF (2000) Development of high fat diet-induced obesity and leptin resistance in C57Bl/6J mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24: 639–646. - PubMed
-
- Koteish A, Diehl AM (2001) Animal models of steatosis. Semin Liver Dis 21: 89–104. - PubMed
-
- Malloy VL, Krajcik RA, Bailey SJ, Hristopoulos G, Plummer JD, et al.. (2006) Methionine restriction decreases visceral fat mass and preserves insulin action in aging male Fischer 344 rats independent of energy restriction. Aging Cell 5: 305–314. ACE220 [pii];10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00220.x [doi]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

