Rationale for recommending a lower dose of primaquine as a Plasmodium falciparum gametocytocide in populations where G6PD deficiency is common
- PMID: 23237606
- PMCID: PMC3546849
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-418
Rationale for recommending a lower dose of primaquine as a Plasmodium falciparum gametocytocide in populations where G6PD deficiency is common
Abstract
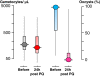
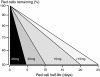
In areas of low malaria transmission, it is currently recommended that a single dose of primaquine (0.75 mg base/kg; 45 mg adult dose) be added to artemisinin combination treatment (ACT) in acute falciparum malaria to block malaria transmission. Review of studies of transmission-blocking activity based on the infectivity of patients or volunteers to anopheline mosquitoes, and of haemolytic toxicity in glucose 6-dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficient subjects, suggests that a lower primaquine dose (0.25 mg base/kg) would be safer and equally effective. This lower dose could be deployed together with ACTs without G6PD testing wherever use of a specific gametocytocide is indicated.
Figures
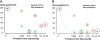



References
-
- Luzzatto L, Poggi V. In: Nathan & Oski's Hematology of Infancy and Chilhood. Orkin S, Nathan DG, Ginsburg D, Look AT, Fisher DE, Lux SE, editor. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2008. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; pp. 883–907.
-
- Howes RE, Piel FB, Patil AP, Nyangiri OA, Gething PW, Dewi M, Hogg MM, Battle KE, Padilla CD, Baird JK, Hay SI. G6PD deficiency prevalence and estimates of affected populations in malaria endemic countries: a geostatistical model-based map. PLoS Med. 2012;9:e1001339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001339. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
-
- World Health Organization Global Malaria programme. Global plan for artemisinin resistance containment (GPARC) Geneva: World Health Organization; http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/artemisinin_resistance_cont... (accessed Nov 1, 2012)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

